
Table of contents
- How Does Data Storage Work?
- Decoding Modern Data Storage
- Data Storage Devices: The Building Blocks of Enterprise Infrastructure
- Types of Storage Devices and Systems
- Forms of Data Storage: Understanding Your Strategic Options
- SAN Components: The Architecture of Enterprise Storage Excellence
- Software Defined Storage (SDS) and Related Technologies
- Choosing the Right Data Storage Architecture
- Benefits: Why Modern Data Storage Drives Business Success
- Use Cases Across Industries: Real World Applications of Strategic Storage
In the modern enterprise, data is everywhere, but value is elusive without the proper infrastructure beneath it. From real time analytics and AI deployments to regulatory compliance and customer trust, the foundation of every digital initiative is the way you store and manage your data.
Yet most storage decisions are reactive, driven by capacity limits, rising costs, or fragmented legacy systems. That approach won’t survive the demands of edge computing, multi cloud complexity, or AI models that require lightning fast access to massive datasets.
- For CEOs and COOs, data storage has evolved from a backend IT concern to a strategic business imperative.
- CIOs and CTOs must lead the shift from legacy infrastructure to scalable, hybrid, and cloud native storage models that align with enterprise growth, AI readiness, and operational efficiency.
- CISOs and Risk Officers must prioritize storage architectures that enforce encryption, zero trust access, and compliance automation; failures in these areas now carry multi million dollar consequences.
- CFOs and Finance Leaders should view modern storage not as a cost center, but as a value generating investment, cutting operational overhead, improving ROI, and enabling smarter, faster decisions.
This post is designed to reframe your perspective on data storage services. Not as a backend function, but as a lever for growth, innovation, and resilience. Because in boardrooms where digital transformation is more than a buzzword, how you store data determines how fast you can move and how far you can go.
Talk to Our Data Storage Expert
Understanding Types of Data Storage and Cloud Capabilities
To support intelligent decision making, it’s critical to understand the types of data storage available today. These include high speed SSDs for mission critical workloads, high capacity HDDs for archival storage needs, and hybrid systems that strike a balance between performance and cost.
But the fundamental shift lies in understanding how cloud data storage works. Cloud based storage goes far beyond offsite backups; it provides globally accessible, infinitely scalable infrastructure, backed by enterprise grade security and advanced analytics. Organizations that embrace cloud storage benefit from on demand elasticity, seamless collaboration, and faster innovation cycles.
Why Data Storage Defines Your Competitive Edge?
A Fortune 500 retail client approached Veritis with a critical challenge that was putting their market position at risk. Their legacy storage systems took 72 hours to process customer behavior data, while their nimble competitors were making real time pricing decisions. The result? They were hemorrhaging market share to companies half their size.
Within six months of implementing our enterprise data storage solutions, they reduced processing time from 72 hours to 3 minutes. Not 3 hours to 3 minutes. Their revenue increased by 23% in the following quarter, and they regained their position as market leader. This transformation did not happen because of better algorithms or smarter analysts. It happened because they finally understood what is data storage? In the context of strategic business advantage.
When we manage data storage effectively, we’re not organizing information; we’re architecting the nervous system of our organizations. Every decision, every insight, every competitive move depends on how quickly and reliably we can access, process, and act on data.
How Does Data Storage Work?
Understanding how does data storage works is key to strategic decision making. At its core, data storage functions through three fundamental processes: writing, reading, and maintaining data integrity across various storage media.
When data enters your system, it’s converted into binary code and distributed across storage devices based on your chosen architecture. Data storage technologies employ sophisticated algorithms to ensure optimal placement, redundancy, and accessibility while maintaining security protocols that protect your organization’s most valuable assets.
In boardrooms where digital transformation is more than a buzzword, enterprise storage decisions are shaping how fast you can innovate, how secure you remain, and how confidently you grow. This is not infrastructure, it’s your foundation for the future.
Data storage is all about the engine behind speed, insight, and adaptability.
- Manage data storage proactively, not reactively. Strategic governance ensures performance, security, and alignment with business goals.
- Choose the proper data storage types to meet specific needs, from real time responsiveness to long term archiving.
- Embrace new data storage technologies that enhance automation, intelligence, and operational efficiency.
- Continually evaluate the enterprise data storage architecture to ensure it scales with your business and supports long term resilience.
Useful link: Natural Language Processing in Healthcare: A Game-changer for Medical Data Analysis
Decoding Modern Data Storage
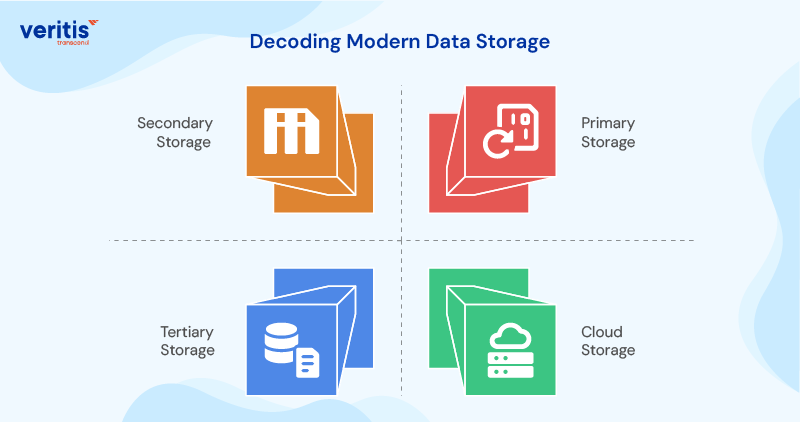
What is data storage? At its core, it’s the systematic organization, retention, and accessibility of digital information that drives business decisions. But that definition barely scratches the surface of its strategic importance.
Think of data storage as your organization’s memory bank, but one that needs to be simultaneously secure, instantly accessible, infinitely scalable, and cost effective. The challenge is not storing data; it’s creating an infrastructure that turns information into competitive intelligence faster than your competition.
Modern data storage types have evolved far beyond the simple file cabinets of yesterday’s computing. Today’s types of data storage include:
1) Primary Storage
The high speed memory that powers real time decision making. This is where your most critical, frequently accessed data lives, the information that can make or break quarterly results.
2) Secondary Storage
Your organization’s long term memory, stores historical data that informs strategic planning and regulatory compliance. This includes everything from customer transaction histories to market research data.
3) Tertiary Storage
The deep archive where you store data for compliance, legal protection, and future analysis. Think of it as your organization’s institutional knowledge vault.
4) Cloud Storage
The breakthrough innovation that’s revolutionized how we think about data storage solutions. It’s not about storing data somewhere else; it’s about accessing global infrastructure, advanced analytics, and scalability that were previously available only to tech giants.
Data Storage Devices: The Building Blocks of Enterprise Infrastructure
1) Solid State Drives (SSDs)
SSDs represent the pinnacle of performance in data storage devices. With no moving parts, they deliver lightning fast access speeds essential for scalable data storage in enterprise workloads. While more expensive per gigabyte, their reliability and speed make them indispensable for mission critical applications.
2) Hard Disk Drives (HDDs)
Traditional HDDs remain cost effective for data archiving and backup strategies. Their high capacity to cost ratio makes them ideal for storing historical data and supporting data storage for compliance and security requirements, where access speed is less critical than storage volume.
3) Hybrid Storage Systems
Combining SSDs and HDDs, hybrid systems optimize both performance and cost. They automatically tier data based on access patterns, ensuring that frequently used information resides on high speed storage while archival data utilizes cost adequate capacity storage.
4) Tape Storage
Despite being considered legacy technology, tape storage remains relevant for long term archival and data storage, particularly for compliance and security purposes. Modern tape systems offer exceptional capacity and durability for data that requires decades long retention.
Useful link: How Automated Data Collection Can Transform Your Business
What’s the Difference Between NAS and SAN?
Network Attached Storage (NAS) and Storage Area Networks (SAN) represent fundamentally different approaches to enterprise data storage solutions. Understanding these differences is crucial when you evaluate the enterprise data storage landscape.
NAS systems operate at the file level, connecting directly to your existing network infrastructure. They’re ideal for data storage solutions for businesses that prioritize simplicity and cost effectiveness. NAS excels in environments requiring shared file access across multiple users and applications.
SAN systems operate at the block level, creating dedicated storage networks that deliver superior performance and scalability. SANs represent the gold standard for scalable data storage for growing companies that demand maximum performance and reliability.
Types of Storage Devices and Systems
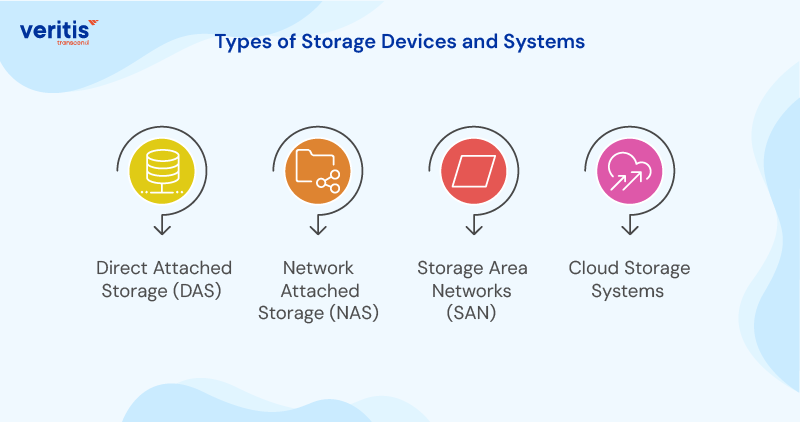
1) Direct Attached Storage (DAS)
DAS connects storage devices directly to servers, offering high performance and security. It’s ideal for applications requiring dedicated storage resources and represents one of the best data storage options for businesses with specific performance requirements.
2) Network Attached Storage (NAS)
NAS provides centralized storage accessible across your network. Its simplicity makes it attractive for business data storage requirements that emphasize ease of management and shared access capabilities.
3) Storage Area Networks (SAN)
SANs deliver enterprise grade performance and scalability. They’re essential for organizations implementing secure data storage for companies at scale, providing the foundation for mission critical applications.
4) Cloud Storage Systems
Cloud platforms offer virtually unlimited scalability and global accessibility. When considering how does data storage work in the cloud, organizations gain access to professional grade infrastructure without incurring capital investment.
Forms of Data Storage: Understanding Your Strategic Options
1) Structured Data Storage
Structured data, organized in databases and spreadsheets, forms the backbone of operational systems. Data storage solutions for structured data prioritize consistency, reliability, and transactional integrity.
2) Unstructured Data Storage
Unstructured data, including documents, images, and videos, comprises up to 80% of enterprise data. Data storage technologies for unstructured data focus on scalability and content management capabilities.
3) Semi Structured Data Storage
Semi structured data, such as JSON and XML files, requires flexible data storage solutions that can adapt to varying data formats while maintaining queryability and organization.
The Cloud Revolution
How does cloud data storage work? It’s a question we experience in every boardroom, and the answer reveals why cloud adoption has become a strategic imperative rather than a technical preference.
Cloud storage operates on a simple but powerful premise: instead of building and maintaining your data centers, you leverage the infrastructure of companies like Amazon, Microsoft, and Google. But here’s where it gets interesting for executives, how does data storage work in the cloud goes far beyond simple file hosting.
When we evaluate the enterprise data storage landscape today, cloud solutions offer three critical advantages that traditional storage simply cannot match:
1) Infinite Scalability: Remember the last time you had to tell your team to stop collecting data because you ran out of storage space? With cloud storage, that conversation becomes obsolete. Your storage scales automatically to match your growing business needs.
2) Global Accessibility: Your data becomes available anywhere, anytime, enabling remote work, international expansion, and 24/7 operations without the complexity of managing multiple data centers.
3) Advanced Security: Leading cloud providers invest billions in security infrastructure that most organizations could never afford to build independently. When you choose the right cloud data storage solutions, you’re improving your security posture.
Storage Area Networks and Data Storage for Business
SANs represent the ultimate solution for enterprise data storage solutions requiring maximum performance, reliability, and scalability. They create dedicated networks exclusively for storage traffic, eliminating the performance bottlenecks that plague traditional network storage approaches.
Storage area networks enable scalable data storage for enterprise workloads by providing high speed, low latency access to storage resources. They’re essential for applications requiring guaranteed performance levels and represent the foundation of modern secure storage infrastructure.
Useful link: 8 Benefits of Automated Data Lineage for Financial Services
SAN Components: The Architecture of Enterprise Storage Excellence
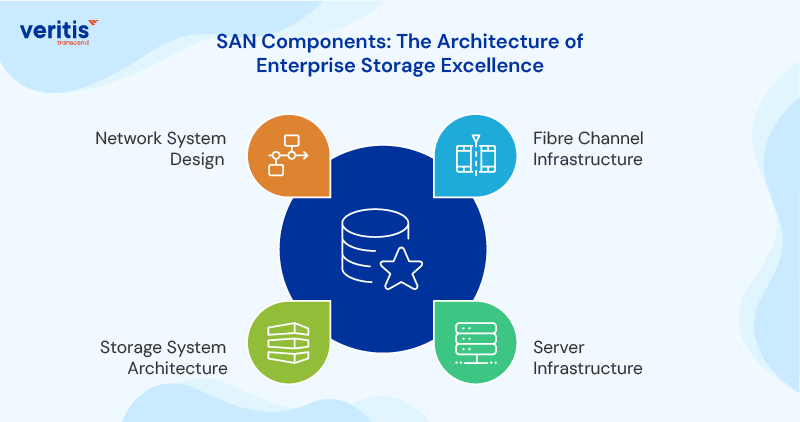
1) Fibre Channel Infrastructure
Fibre Channel provides the high speed connectivity that makes SANs possible. Operating at speeds up to 32 Gbps, Fibre Channel ensures that storage performance never becomes a bottleneck for critical business applications.
2) Server Infrastructure
SAN connected servers benefit from dedicated storage networks that eliminate competition between storage and network traffic. This separation ensures consistent performance for data storage solutions for business operations.
3) Storage System Architecture
Modern storage systems within SANs incorporate advanced features, including automated tiering, deduplication, and compression. These capabilities optimize both performance and capacity utilization across enterprise data storage solutions.
4) Network System Design
SAN network design focuses on redundancy, performance, and scalability. Multiple pathways ensure continuous availability, while high bandwidth connections support the most demanding and scalable data storage for enterprise workloads.
Software Defined Storage (SDS) and Related Technologies
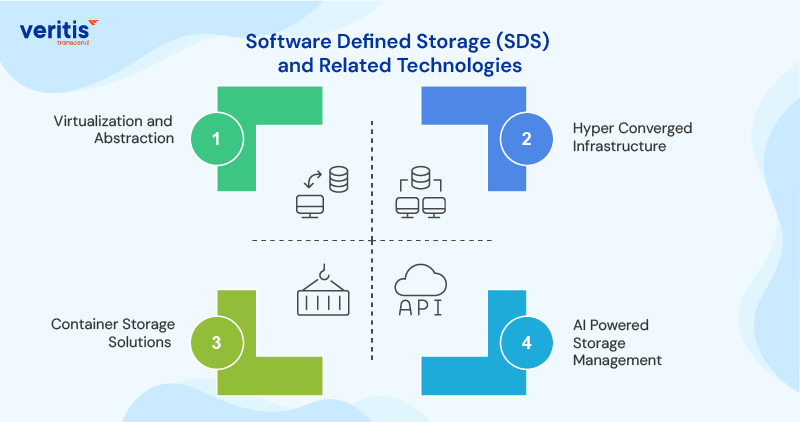
1) Virtualization and Abstraction
SDS abstracts storage hardware through software layers, enabling unprecedented flexibility in managing data storage resources. This approach allows organizations to optimize storage utilization while reducing management complexity.
2) Hyper Converged Infrastructure
Hyper converged systems combine compute, storage, and networking in software defined packages. They simplify data storage solutions deployment while providing the scalability essential for growing organizations.
3) Container Storage Solutions
Container native storage addresses the unique requirements of modern application architectures. These solutions offer the persistent storage capabilities required for containerized applications, while maintaining portability and scalability.
4) AI Powered Storage Management
Artificial intelligence transforms data storage technologies by predicting storage needs, optimizing performance, and automating routine management tasks. AI powered systems learn from usage patterns to proactively address potential issues.
Choosing the Right Data Storage Architecture
Choosing the exemplary data storage architecture requires thinking like a CEO, not a CTO. The question is not “what technology is coolest?” but “what infrastructure will drive business results?”
At Veritis, we’ve helped over 200 enterprise clients navigate this decision, and we’ve identified five critical factors that determine success:
1) Business Performance Demands
What are the different types of data storage solutions, and which ones align with your business model? A high frequency trading firm needs microsecond response times, while a manufacturing company might prioritize data durability over speed. Understanding your speed requirements shapes every storage decision.
2) Compliance and Security Imperatives
Data storage for compliance and security is not optional; it’s the foundation of business continuity. We’ve seen companies face millions in fines and irreparable damage to their reputation because they treated compliance as an afterthought rather than a fundamental design principle.
3) Growth Trajectory Planning
Scalable data storage for growing companies means building infrastructure that grows with you, not against you. I’ve watched too many promising companies hit growth walls because their storage architecture couldn’t scale with their success.
4) Total Cost of Ownership
The best data storage options for businesses prioritize long term value over upfront costs. When we factor in management overhead, security requirements, and scalability needs, the actual cost picture often comes as a surprise to executives.
5) Integration Complexity
Your storage architecture must seamlessly integrate with existing systems while positioning you for future innovations. Data storage technologies that create silos undermine agility and increase risk.
Find the Right Storage Solution
The Enterprise Imperative: Building Secure, Scalable Infrastructure
Let’s consider a manufacturing client that learned the hard way why secure storage infrastructure can’t be compromised. A cyberattack targeting their legacy storage systems shut down production for three weeks, resulting in $47 million in lost revenue and an additional $23 million in recovery costs.
The attack succeeded because they had treated storage security as a technical issue rather than a business risk. Their storage infrastructure lacked encryption, access controls, and monitoring capabilities that modern enterprise data storage solutions provide as standard features.
Secure data storage for companies requires a comprehensive approach that includes:
- Complete Encryption: Data must be encrypted both in transit and at rest, with keys managed in accordance with enterprise security policies.
- Zero Trust Access Controls: Every access request must be authenticated, authorized, and audited, regardless of the user’s location or credentials.
- Continuous Monitoring: Advanced threat detection and response capabilities that identify and neutralize security risks before they impact business operations.
- Compliance Automation: Built in capabilities that ensure data handling meets regulatory requirements across multiple jurisdictions.
Useful link: The Impact of Cloud Integration on Managed Data Services
Advanced Strategies: Data Archiving and Backup for Business Continuity
Data archiving and backup strategies separate resilient organizations from vulnerable ones. However, here’s where most companies go wrong: they treat backup and archiving as insurance policies rather than strategic assets.
Smart leaders understand that data archiving and backup strategies serve multiple business purposes:
- Regulatory Compliance: Maintaining historical data to meet legal and industry requirements while optimizing storage costs.
- Business Intelligence: Archived data provides the historical context necessary for accurate predictive modeling and strategic planning.
- Disaster Recovery: Comprehensive backup strategies ensure business continuity even in the face of catastrophic failures.
- Cost Optimization: Intelligent data tiering moves infrequently accessed data to cost effective storage solutions without sacrificing accessibility.
Comparative Analysis: Making Informed Storage Decisions
Comparing local and network data storage requires understanding the strategic trade offs, not the technical specifications.
Local storage offers complete control and predictable performance, but limits scalability and increases infrastructure overhead. Network storage offers flexibility and scalability, but it introduces a dependency on network performance and external providers.
The pros and cons of cloud data storage reveal why most forward thinking organizations are adopting hybrid approaches:
Cloud Storage Advantages
- Virtually unlimited scalability
- Professional grade security infrastructure
- Global accessibility and disaster recovery
- Predictable operational expenses
- Access to advanced analytics and AI capabilities
Cloud Storage Considerations
- Network dependency for data access
- Ongoing operational costs
- Potential vendor lock in
- Compliance complexity in regulated industries
Smart executives don’t choose between local and cloud storage; they architect hybrid solutions that optimize for both performance and strategic flexibility.
Benefits: Why Modern Data Storage Drives Business Success
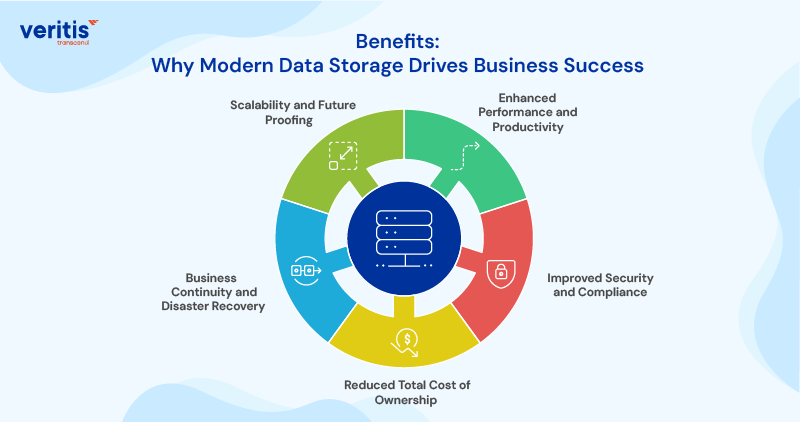
1) Enhanced Performance and Productivity
Modern data storage solutions eliminate the performance bottlenecks that constrain business operations. Faster data access translates directly to improved employee productivity and enhanced customer experiences.
2) Improved Security and Compliance
Advanced data storage features, including compliance and security measures, protect against threats while ensuring adherence to regulations. Built in encryption, access controls, and audit trails provide comprehensive protection for sensitive data.
3) Reduced Total Cost of Ownership
Efficient data storage technologies reduce both capital and operational expenses. Automated management, improved utilization, and reduced maintenance requirements contribute to compelling total cost of ownership.
4) Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
Robust data archiving and backup strategies ensure business continuity even in the face of disasters. Modern storage systems provide the redundancy and recovery capabilities essential for operational resilience.
5) Scalability and Future Proofing
Scalable data storage for growing companies ensures that their infrastructure grows in line with business needs. Modern storage architectures accommodate expansion without requiring complete system replacement.
Use Cases Across Industries: Real World Applications of Strategic Storage
1) Healthcare
Healthcare organizations rely on secure data storage for companies to protect patient information while ensuring rapid access for clinical decisions. Data storage solutions in healthcare must strike a balance between security, compliance, and accessibility requirements.
2) Financial Services
Financial services demand enterprise data storage solutions that provide both security and performance. High frequency trading and real time fraud detection require storage systems capable of microsecond response times.
3) Manufacturing
Manufacturing companies implement data storage solutions to support both operational technology (OT) and information technology (IT) requirements for their business operations. These hybrid environments require storage systems that can handle both traditional business data and industrial IoT information.
4) Media and Entertainment
Media and entertainment organizations require scalable data storage solutions for enterprise workloads that can handle massive file sizes and support collaborative workflows across global teams.
The Veritis Advantage: Transforming Storage Strategy into Business Results
At Veritis, we don’t implement data storage solutions; we architect competitive advantages. Our approach to enterprise data storage solutions combines deep technical expertise with strategic business understanding, ensuring that every storage decision drives measurable business results.
Our Data Storage Services have helped organizations across industries achieve:
- 67% reduction in data access times
- 45% decrease in storage related operational costs
- 89% improvement in compliance audit results
- 156% increase in data driven decision making speed
We understand that business data storage requirements extend far beyond technical specifications. They encompass strategic agility, competitive positioning, risk management, and growth enablement.
Implementation Framework: From Strategy to Results
When we manage data storage for enterprise clients, we follow a proven methodology that ensures both immediate results and long term success:
- Strategic Assessment: We analyze your current storage infrastructure against business objectives, identifying gaps and opportunities that impact competitive positioning.
- Architecture Design: Our team designs scalable data storage for enterprise workloads that align with your growth trajectory and strategic initiatives.
- Phased Implementation: We implement changes in carefully planned phases that minimize business disruption while maximizing value realization.
- Optimization and Evolution: Our ongoing partnership ensures that your storage infrastructure evolves in tandem with changing business needs and emerging technologies, allowing for seamless integration and adaptation.
Future Proofing Your Data Storage Strategy
Scalable data storage for growing companies is not about handling more data; it’s about building infrastructure that enables new business models, supports emerging technologies, and positions your organization for opportunities we can’t even imagine yet.
The companies that will dominate their industries in the next decade are building storage infrastructures today that support artificial intelligence, machine learning, the Internet of Things, and analytics capabilities, transforming raw data into strategic advantages.
Conclusion
At Veritis, we recognize that data storage encompasses far more than technical specifications. We architect enterprise data storage solutions that transform data into competitive advantages, ensuring your organization remains ahead of rapidly evolving market demands.
Ready to optimize your data storage strategy? Veritis delivers data storage solutions that drive measurable business results. Contact us to discover how our proven approach to enterprise data storage solutions can accelerate your organization’s success.
Transform your data storage into a competitive advantage with Veritis’ proven expertise in delivering enterprise grade storage solutions that drive business results.