
For enterprise leaders, data is a strategic control point, yet many organizations still confuse business intelligence vs data visualization, assuming dashboards alone deliver insight. In reality, visualization shows what happened, while business intelligence explains why it happened and what to do next.
Business intelligence and data visualization must work together to support executive decision making. Data visualization in business intelligence becomes valuable only when it is built on governed, trusted, and timely data. Without that foundation, even advanced business intelligence tools and data visualization tools produce attractive reports that lack strategic reliability.
Data visualization in business lies in speed and clarity. Executives need immediate visibility into performance, risk, and opportunity. Effective BI data visualization, powered by automated data collection and a disciplined enterprise data management strategy, enables leaders to act with confidence rather than debate the numbers.
At Veritis Group Inc., we help enterprises move beyond reporting. Our enterprise data management services align data, intelligence, and visualization into a unified system that turns information into a measurable business advantage.
Request a Business Data Assessment
What is Business Intelligence? A Strategic Overview
Business intelligence is the enterprise capability that turns data into decision ready insight that leadership can trust. It is not a reporting layer or a collection of dashboards. At the executive level, business intelligence defines how data is captured, governed, analyzed, and aligned to business objectives across finance, operations, customers, and risk. When leaders evaluate business intelligence vs data visualization, BI represents the system of record and logic, while visualization is simply how outcomes are communicated.
1) What Does It Enable for CXOs?
It creates a single operating view of performance across finance, operations, customers, and risk, enabling faster, aligned, and measurable decisions.
2) How Does It Work at an Enterprise Scale?
Business intelligence and data visualization succeed when data is captured consistently, governed by standard definitions, and powered by automated data collection to maintain accuracy in real time.
3) BI vs Data Visualization
In business intelligence vs data visualization, BI builds the logic and metrics behind decisions, while data visualization in business intelligence communicates those outcomes clearly through business intelligence tools.
Core Components of Business Intelligence Platforms
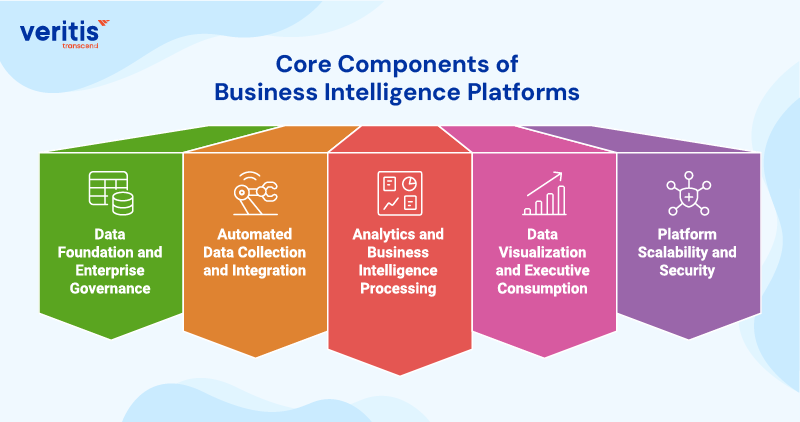
1) Data Foundation and Enterprise Governance
For US executives, BI is only valuable if the numbers are trusted. This layer establishes enterprise wide consistency, accountability, and audit readiness, so leadership teams stop debating the data and start acting on it. A strong enterprise data management strategy defines ownership, standards, lineage, and controls, while enterprise data management services enforce governance at scale across business units.
2) Automated Data Collection and Integration
Executives cannot run a modern enterprise on delayed or manually prepared reports. Automated data collection ensures timely, reliable ingestion from cloud platforms, core systems, and SaaS applications, reducing latency and operational risk. This capability keeps business intelligence and data visualization aligned with real time conditions, enabling faster visibility into performance, costs, and exposure.
3) Analytics and Business Intelligence Processing
This is the decision engine, where raw data becomes executive insight. Business intelligence tools standardize KPIs, detect trends, surface exceptions, and connect business drivers to outcomes. In business intelligence vs data visualization, this layer is what creates intelligence, not presentation, determining whether leaders gain predictive signals or historical reporting.
4) Data Visualization and Executive Consumption
Data visualization in business intelligence is the leadership interface, designed for speed, clarity, and accountability. Effective BI data visualization highlights what changed, why it changed, and what needs attention now. Supported by enterprise grade data Visualization tools, this layer enables executives to align teams around priorities and decisions without ambiguity.
5) Platform Scalability and Security
Enterprise BI must scale while protecting sensitive data and meeting regulatory requirements. Role based access, data controls, and a resilient architecture ensure the platform remains reliable during growth, audits, and operational disruptions. At Veritis Group Inc., we build BI platforms that scale securely, support executive decision making, and deliver measurable business outcomes.
At Veritis Group Inc., we design BI platforms that scale securely, align with executive priorities, and deliver sustained business value.
Useful link: How SaaS Business Intelligence is Revolutionizing Data Driven Decision Making
What is Data Visualization? A Strategic Overview
Data visualization is the executive decision interface. It converts analytical outputs into clear, decision ready views that leaders can interpret quickly and act on with confidence.
1) Role Clarity at the Enterprise Level
In business intelligence vs data visualization, business intelligence generates insights through metrics, models, and logic. Data visualization in business intelligence communicates that insight so leaders can align priorities and execution.
2) What Makes Visualization Credible?
Visualization only performs at the executive level when it is built on governed data, powered by automated data collection, and aligned to a strong enterprise data management strategy. Without that foundation, even the best data visualization tools can produce polished looking outputs that cannot be trusted.
Veritis delivers visualization as a strategic capability through scalable enterprise data management services, ensuring that business intelligence and data visualization operate as a single system that supports faster decisions, stronger accountability, and measurable business outcomes.
Core Capabilities of Data Visualization Tools

1) Interactive Exploration and Drill Down
Enterprise grade tools let executives move from KPIs to the underlying drivers in seconds using filters, drill down, and row level detail. This is critical because leadership decisions rarely come from a static chart. They come from fast exploration of what changed, where, and why.
2) Broad Data Connectivity and Cached Performance
Modern platforms connect to cloud data warehouses, hybrid systems, and SaaS applications, supporting both live queries and optimized extracts/caching to improve performance. This capability ensures executive dashboards remain responsive at scale and reduces the operational friction caused by “too slow to use” analytics.
3) Governance, Permissions, and Row Level Security
Executives need confidence that the right people see only the correct data. Leading tools provide role based permissions and controls, such as row level security, so sensitive financial, HR, and customer data is protected while still enabling self service visibility.
4) Sharing, Collaboration, and Managed Distribution
Data visualization only creates value when it is consumed. Enterprise platforms support secure sharing, controlled access, and consistent distribution of approved enterprise dashboards, enabling leadership teams to align on the same metrics and decisions and move faster.
5) Governed Metrics and Repeatable Analysis
The most critical capability for CXOs is consistency. Platforms that support governed data and repeatable analysis help prevent “multiple versions of the truth” across teams, ensuring every view uses approved definitions and trusted logic.
Useful link: Role of Artificial Intelligence in Business for CEOs and CTOs
Advantages and Disadvantages of Business Intelligence
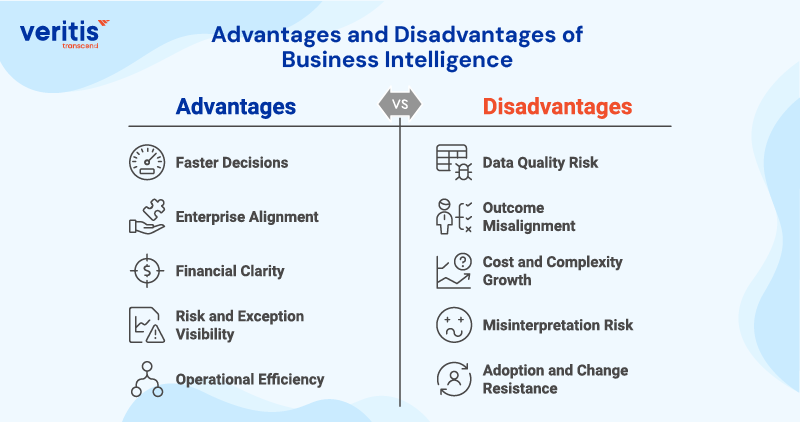
Business intelligence helps leadership run the enterprise with measurable control rather than assumptions. When governed and automated, it improves speed, accountability, and forecast confidence. When poorly executed, it creates competing truths, cost growth, and decision friction.
Advantages of Business Intelligence
1) Faster Decisions
A) What Executives Gain?
Business intelligence reduces decision latency by converting enterprise data into timely, decision ready insight. It gives leadership near real time visibility into what is changing across the business. This accelerates prioritization and execution cadence.
B) Why Does it Matter?
Faster decisions compound into faster revenue capture, faster cost correction, and faster risk response. It strengthens leadership alignment by reducing debate and delay. Business intelligence and data visualization work best when insight is delivered at the speed of business.
2) Enterprise Alignment
A) What Executives Gain?
BI creates consistent metrics across functions, enabling leadership teams to operate from a single version of the truth. It aligns finance, operations, and customer outcomes through standardized definitions. This is where an enterprise data management strategy becomes essential.
B) Why Does it Matter?
Without alignment, organizations lose time reconciling numbers instead of driving outcomes. BI reduces internal friction and improves accountability across business units. It also improves board level reporting credibility.
3) Financial Clarity
A) What Executives Gain?
Business intelligence improves forecasting confidence by highlighting drivers of variance and early margin movement. It enables CFOs to move from historical reporting to forward looking visibility. Business intelligence tools deliver faster insight into spend patterns and profitability.
B) Why Does it Matter?
This strengthens cost discipline and supports more accurate capital allocation. Leaders can detect budget leakage sooner and enforce accountability at the source. BI becomes a financial advantage, not an IT capability.
4) Risk and Exception Visibility
A) What Executives Gain?
BI surfaces exceptions before they become a material business impact. It enables early detection across operational breakdowns, compliance exposure, and customer churn signals. Data visualization in business intelligence helps leaders see what requires attention now.
B) Why Does it Matter?
Executives get fewer surprises and more control over enterprise outcomes. Risk is managed proactively instead of reactively. This improves resilience and strengthens stakeholder confidence.
5) Operational Efficiency
A) What Executives Gain?
With automated data collection, BI reduces manual reporting and repeated spreadsheet work. It improves reliability across recurring leadership dashboards and performance reviews. Teams spend less time preparing data and more time acting on it.
B) Why Does it Matter?
Efficiency at scale protects productivity and reduces operating overhead. It also increases consistency across reporting cycles and departments. BI supports sustainable execution, not visibility.
Disadvantages of Business Intelligence
1) Data Quality Risk
A) What Executives Should Watch?
BI is only as reliable as the data feeding it. If definitions are inconsistent, outputs conflict, and confidence collapses quickly. This is why enterprise data management services and governance cannot be optional.
B) Business Impact
Leaders lose trust and teams revert to manual reporting. Decision speed drops, and internal alignment weakens. BI becomes noise instead of insight.
2) Outcome Misalignment
A) What Executives Should Watch?
Many BI programs fail because they start with tools rather than with business decisions. Enterprise dashboards get built without linking to measurable outcomes or accountability. In business intelligence vs data visualization, visualization often receives the focus, while the logic of intelligence is neglected.
B) Business Impact
The platform becomes a reporting asset, not a decision system. Adoption remains low, and ROI becomes difficult to prove. Leadership effort shifts to interpretation instead of execution.
3) Cost and Complexity Growth
A) What Executives Should Watch?
BI platforms can become expensive to scale across users, data sources, and business units. Licensing, integration, and performance management require an operating model. Without discipline, complexity expands faster than value.
B) Business impact
Cost increases without proportional outcome improvement. Technical debt accumulates, and delivery slows. BI becomes harder to manage and harder to trust.
4) Misinterpretation Risk
A) What Executives Should Watch?
Visualization can oversimplify performance drivers if context and modeling are weak. Even strong data visualization tools can produce convincing views that miss underlying realities. This risk increases when stakeholders consume charts without governance.
B) Business impact
Decisions get made on incomplete signals and false confidence. Teams chase the wrong priorities and lose time correcting course. BI data visualization must be tied to controlled metrics.
5) Adoption and Change Resistance
A) What Executives Should Watch?
If BI is not embedded in the leadership cadence, teams revert to spreadsheets and shadow reporting. This creates fragmentation and competing versions of truth across the enterprise. Executive sponsorship matters as much as technology selection.
B) Business impact
The platform underperforms despite investment. Reporting becomes inconsistent, and governance weakens over time. Strategic decisions slow down due to internal misalignment.
Veritis reduces BI risk by designing systems around governance, automation, and measurable executive outcomes. Our enterprise data management strategy and services ensure that business intelligence and data visualization operate as a single decision system. The result is trusted intelligence that scales securely and drives business performance.
Useful link: Data Mining in Healthcare: IT Strategies for Transformative Results
Advantages And Disadvantages of Data Visualization

Data visualization helps leaders see performance clearly, align teams faster, and act with confidence. When connected to governed data and reliable pipelines, it improves decision speed and accountability. When built on inconsistent sources, it can create false confidence and misdirect priorities.
Advantages of Data Visualization
1) Executive Clarity
A) What Leaders Gain?
Data visualization converts complex performance signals into decision ready views that executives can interpret quickly. It makes trends, outliers, and changes visible without requiring extensive analysis. This improves focus on what matters most.
B) Why Does It Matter?
Leadership teams align faster and reduce meeting time spent debating interpretation. Decisions move from opinion to evidence. Strong Data Visualization Tools support clarity at scale.
2) Faster Alignment Across Teams
A) What Leaders Gain?
Well designed dashboards create a shared operational view across finance, operations, and technology. This supports consistent accountability and reduces fragmented reporting. It strengthens cross functional execution cadence.
B) Why Does It Matter?
Teams move in one direction with fewer delays. Business Intelligence and Data Visualization work best when leaders use the same views to drive priorities. Alignment improves execution speed across the enterprise.
3) Early Exception Detection
A) What Leaders Gain?
Data visualization quickly highlights unusual patterns, such as revenue declines, cost spikes, service degradation, or customer churn signals. Executives can detect issues early and ask the right questions immediately. This is most effective when paired with automated data collection.
B) Why Does It Matter?
Fewer surprises and faster intervention improve business continuity. Risk is addressed before it has a material impact. This increases resilience and operational control.
4) Better Decision Communication
A) What Leaders Gain?
Data visualization makes strategic decisions easier to communicate across leadership layers and teams. It reduces ambiguity by clearly showing performance context. This improves execution quality after decisions are made.
B) Why Does It Matter?
Execution becomes more consistent across regions and business units. Stakeholders understand priorities faster. Visualization improves governance and accountability across initiatives.
5) Scalable Performance Visibility
A) What Leaders Gain?
Enterprise platforms distribute standardized dashboards across roles with controlled access. This supports consistent performance monitoring without manual report creation. It improves transparency across business units.
B) Why Does It Matter?
Leadership reporting becomes repeatable and reliable. Business intelligence Vs data visualization becomes clear because visualization scales visibility, while BI scales insight. The organization gains consistent operational control.
Disadvantages of Data Visualization
1) False Confidence Risk
A) What Leaders Should Watch?
Charts can look credible even when the underlying data is incomplete or inconsistent. If definitions are not governed, enterprise dashboards can produce misleading narratives. A strong Enterprise Data Management Strategy reduces this risk.
B) Business Impact
Executives may act on signals that do not reflect reality. Decisions become harder to correct once execution begins. Trust erodes quickly across leadership teams.
2) Metric Conflicts Across Teams
A) What Leaders Should Watch?
Different teams often visualize the same KPI in different ways. Without standard definitions, dashboards create conflict rather than clarity. This problem grows with scale and complexity.
B) Business Impact
Meetings devolve into reconciliation sessions rather than decision making. Execution slows, and accountability weakens. Enterprise data management services help remove this friction.
3) Oversimplification Of Drivers
A) What Leaders Should Watch?
Visualization can compress complex drivers into a single view, obscuring the root cause. Without deeper analysis, the why behind performance may remain unclear. This happens when visualization is used without Business Intelligence Tools.
B) Business Impact
Leadership may treat symptoms instead of causes. Resources get misallocated. Decisions lose precision when the driver context is missing.
4) Adoption Without Action
A) What Leaders Should Watch?
Dashboards do not create outcomes unless tied to leadership routines and accountability. Many organizations deploy visualization but fail to embed it into decision cadence. Adoption becomes passive viewing instead of active execution.
B) Business Impact
ROI stays low despite investment. Teams revert to spreadsheets and shadow reporting. The platform becomes a reporting artifact, not a decision system.
5) Security And Exposure Risk
A) What Leaders Should Watch?
Visualization platforms can expose sensitive data if access controls are weak. Shared dashboards without role based permissions create compliance risks. Executive visibility must be secured by design.
B) Business Impact
Security gaps expose compliance and reputational risks. Enterprise grade data visualization tools must enforce role based access and governance controls.
Useful link: 8 Benefits of Automated Data Lineage for Financial Services
Data Visualization Tools
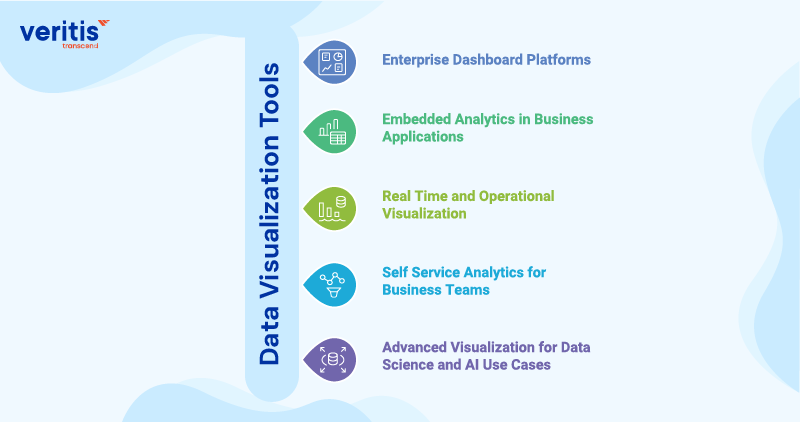
1) Enterprise Dashboard Platforms
A) What Leaders Use Them For?
Track enterprise KPIs across revenue, margin, operations, and customer performance with drill downs by region, unit, or product. Standardize leadership reporting for operating reviews and performance governance.
B) Why Does It Matter?
Creates a single, trusted view of performance and reduces time spent reconciling metrics. Improves decision speed, accountability, and execution control at scale.
C) Examples
- Microsoft Power BI
- Tableau
- Qlik Sense
- Looker
- SAP Analytics Cloud
- IBM Cognos Analytics
2) Embedded Analytics In Business Applications
A) What Leaders Use Them For?
Deliver insights inside CRM, ERP, and service platforms where teams execute daily decisions. Improve adoption by integrating analytics into the workflow rather than as a separate portal.
B) Why Does It Matter?
Reduces shadow reporting and keeps teams aligned on approved metrics. Shortens the path from insight to action across departments.
C) Examples
- Salesforce Tableau CRM (CRM Analytics)
- ServiceNow Performance Analytics
- SAP Analytics Cloud
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 Analytics
- Oracle Analytics
3) Real Time and Operational Visualization
A) What Leaders Use Them For?
Monitor infrastructure, security, application health, and digital experience in near real time. Support operational response and leadership visibility during incidents and outages.
B) Why Does It Matter?
Enables faster issue detection and reduces the impact of downtime on revenue and customers. Strengthens resilience and business continuity through proactive control.
C) Examples
- Grafana
- Kibana
- Datadog Dashboards
- Splunk Dashboards
- Dynatrace Dashboards
- New Relic Dashboards
4) Self Service Analytics for Business Teams
A) What Leaders Use Them For?
Enable business teams to explore data within governed access and standardized KPIs. Reduce dependency on IT for every report and accelerate operational decisions.
B) Why Does It Matter?
Removes reporting bottlenecks and improves productivity across functions. Increases accountability by making performance visible closer to execution.
C) Examples
- Microsoft Power BI
- Tableau
- Qlik Sense
- Looker
- ThoughtSpot
- MicroStrategy
5) Advanced Visualization for Data Science and AI Use Cases
A) What Leaders Use Them For?
Support scenario analysis, predictive outputs, anomaly detection, and advanced exploration. Enable strategic planning and model driven insights beyond historical reporting.
B) Why Does It Matter?
Improves forecasting confidence and helps leadership evaluate tradeoffs before investing. Moves the enterprise from reporting to prediction and operational readiness.
C) Examples
- Plotly
- Apache Superset
- Jupyter Notebooks
- Hex
- Streamlit
- Python Visualization Libraries
Business Intelligence Tools
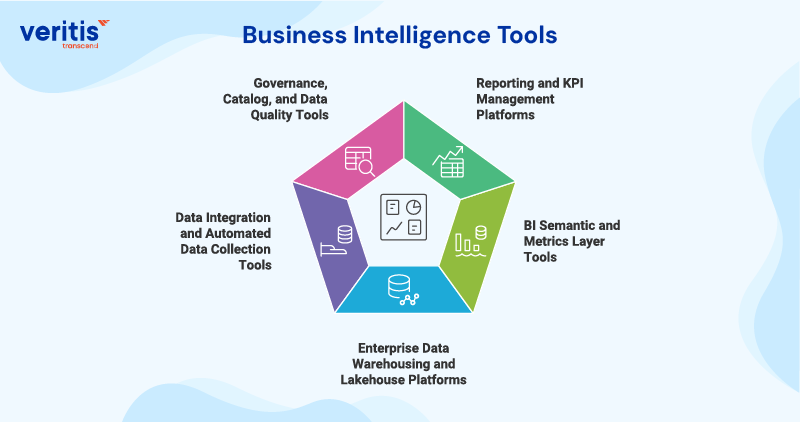
1) Reporting and KPI Management Platforms
A) What Leaders Use Them For?
Deliver enterprise reporting, scorecards, and executive KPI monitoring across functions. Standardize performance reviews and leadership reporting cadence.
B) Why Does It Matter?
Creates measurement discipline and prevents KPI conflicts across teams. Improves trust and speed of executive decisions.
C) Examples
- Microsoft Power BI
- Tableau
- Qlik Sense
- Looker
- SAP Analytics Cloud
- IBM Cognos Analytics
2) BI Semantic and Metrics Layer Tools
A) What Leaders Use Them For?
Standardize KPI definitions so every dashboard uses the same business logic. Enforce consistent measurement across finance, operations, and customer metrics.
B) Why Does It Matter?
Eliminates competing versions of truth that slow leadership execution. Strengthens audit readiness and governance confidence.
C) Examples
- Looker Semantic Layer
- Microsoft Power BI Semantic Model
- dbt Semantic Layer
- AtScale
- Cube
- SAP BW And SAP Datasphere Semantic Modeling
3) Enterprise Data Warehousing and Lakehouse Platforms
A) What Leaders Use Them For?
Provide the scalable analytics foundation for governed storage, modeling, and performance. Enable BI at enterprise volume across regions, products, and business units.
B) Why Does It Matter?
Prevents slow reporting and reduces operational complexity as data grows. Improves reliability, scale, and cost control for enterprise analytics.
C) Examples
- Snowflake
- Google BigQuery
- Amazon Redshift
- Azure Synapse Analytics
- Databricks Lakehouse
- Oracle Autonomous Data Warehouse
4) Data Integration and Automated Data Collection Tools
A) What Leaders Use Them For?
Automate ingestion from SaaS, cloud, internal systems, and partner platforms. Maintain reliable data pipelines without manual reporting dependency.
B) Why Does It Matter?
Keeps executive reporting current and reduces decision risk from stale data. Improves efficiency by eliminating redundant data preparation.
C) Examples
- Fivetran
- Informatica Intelligent Data Management Cloud
- Talend
- Azure Data Factory
- AWS Glue
- Matillion
5) Governance, Catalog, and Data Quality Tools
A) What Leaders Use Them For?
Manage lineage, ownership, policies, and quality scoring across enterprise data. Ensure access controls and compliance readiness across reporting environments.
B) Why Does It Matter?
Protects trust, reduces regulatory exposure, and strengthens decision credibility. Enables faster resolution of data issues through traceability and ownership.
C) Examples
- Collibra
- Alation
- Microsoft Purview
- Informatica Axon And Informatica Data Quality
- IBM Infosphere Information Governance Catalog
- Talend Data Quality
Useful link: What Are the Top Business Intelligence Tools to Use in 2026?
Difference Between Data Visualization and Business Intelligence
| Area | Business Intelligence | Data Visualization |
| Primary Role | Builds decision ready insights from enterprise data | Communicates insight clearly through visual views |
| Core Purpose | Creates the logic, metrics, and truth behind performance | Presents outcomes so leaders can interpret faster |
| Focus | Data accuracy, governance, modeling, and analysis | Clarity, speed of understanding, executive visibility |
| Output | KPIs, trends, drivers, exceptions, forecasts | Dashboards, charts, scorecards, executive views |
| Value To Executives | Improves control of performance, cost, risk, and execution | Improves alignment, faster decisions, and accountability |
| Dependency | Requires governance, consistent definitions, and automation | Requires trusted BI outputs to remain credible |
| Tools And Technologies | Microsoft Power BI, Tableau, Looker, Qlik Sense, SAP Analytics Cloud, IBM Cognos Analytics | Grafana, Kibana, Datadog Dashboards, Splunk Dashboards, Dynatrace, New Relic |
| Data Flow | Relies on automated data collection and governed pipelines | Consumes modeled data and approved metrics |
| Enterprise Scale Requirement | Needs an enterprise data management strategy and enterprise data management services | Needs role based access and standardized dashboards |
| Best Outcome | Trusted intelligence that drives measurable business decisions | Clear visibility that accelerates execution and alignment |
| Veritis Perspective | Veritis delivers enterprise BI foundations through enterprise data management services aligned to an enterprise data management strategy | Veritis enables executive ready BI data visualization using data visualization tools built on governed, automated data |
Conclusion
For enterprise leaders, the real question is not business intelligence vs data visualization. The real question is whether your organization is operating with trusted intelligence or managing decisions with fragmented reporting. Business intelligence creates the metrics, controls, and decision logic. Data visualization delivers clarity and speed. When business intelligence and data visualization operate together, leadership gains a single operating view that strengthens performance, cost discipline, risk visibility, and execution accountability.
At Veritis, we help enterprises make that shift with a scalable enterprise data management strategy, reliable automated data collection, and governed delivery through enterprise data management services. The result is decision ready intelligence and executive grade visibility, powered by modern business intelligence tools and data visualization tools. With Veritis, organizations move beyond dashboards and into measurable, sustained business advantage.