Spending is the core factor that decides the business success in any industry. Better the spending optimization, better will be the resultant Return on Investment (RoI).
The spending or cost factor means a lot to the IT industry, where every penny equals to huge investment part of organizational IT expenditure.
Cloud computing is one area where the majority of IT firms brainstorm on the need for cost optimization and cost management.
While cloud services are known for their wide range of offerings, they are often spoken about when it comes to maintenance and other forms of expenditure.
2019 State of the Cloud Report on ‘Cloud Spending’
The 2019 State of the Cloud report confirms this fact by saying, “as cloud use grows, organizations focus on cloud costs and governance.”
Citing its survey of 786 technical professionals, the report concluded:
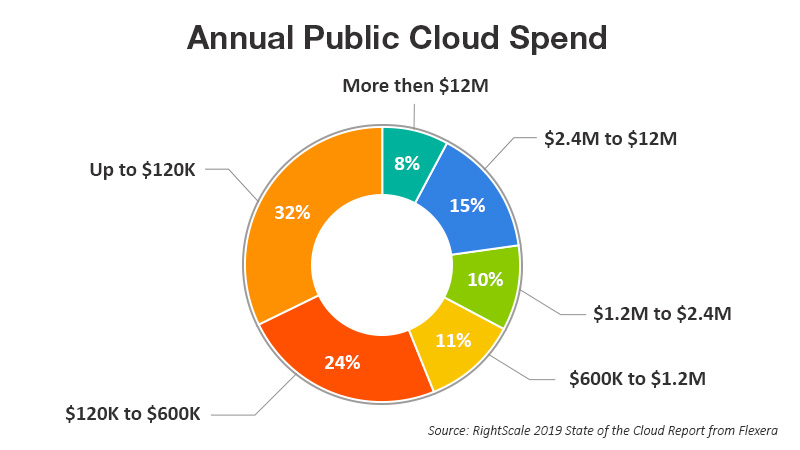
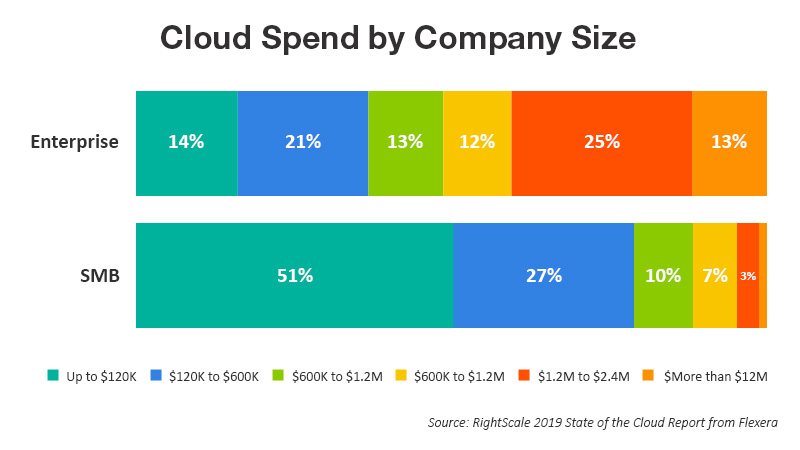
- Enterprise cloud spending is growing significantly and quickly. 23 percent of the survey respondents (including all) spend at least USD 2.4 million annually (USD 200,000 per month) on public cloud, followed by 33 percent spending at least USD 1.2 million per year (USD 100,000 per month). Among enterprises, 38 percent have annual cloud spending of more than USD 2.4 million and 50 percent spending above USD 1.2 million


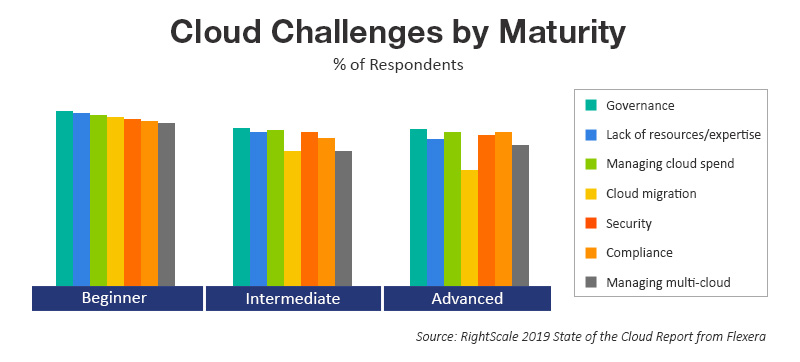
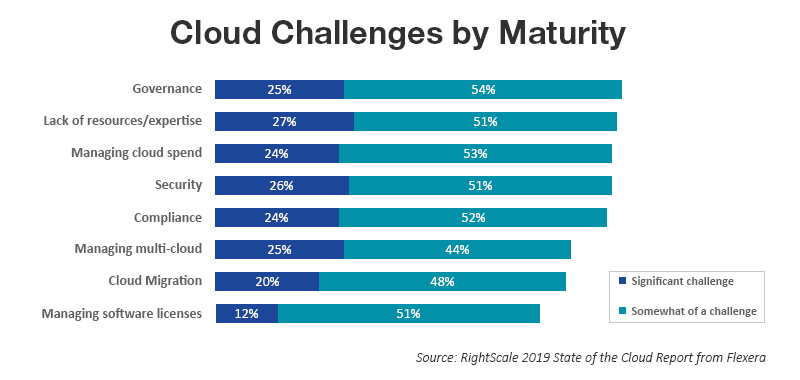
- Cloud cost management or cloud cost optimization (84 percent in 2019 over 80 percent in 2018) and cloud governance (84 percent in 2019 over 77 percent in 2018) continue to be the ‘key challenges’, regardless of cloud maturity

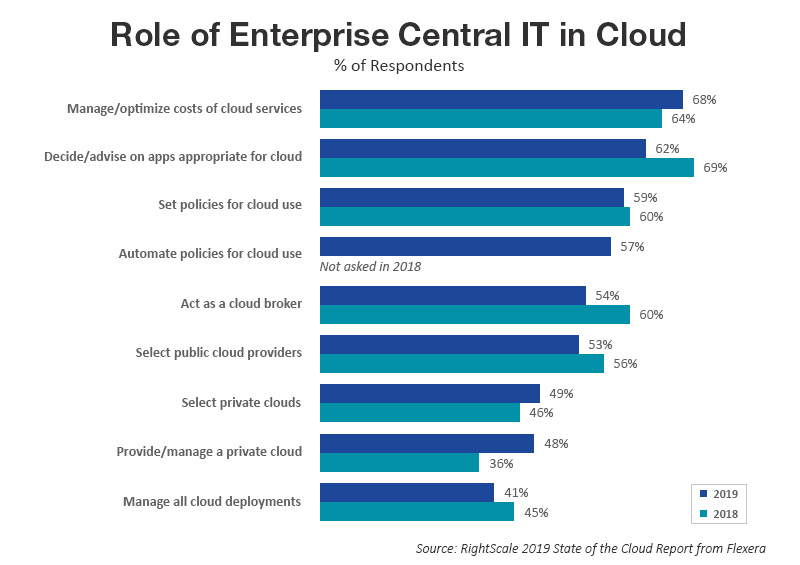
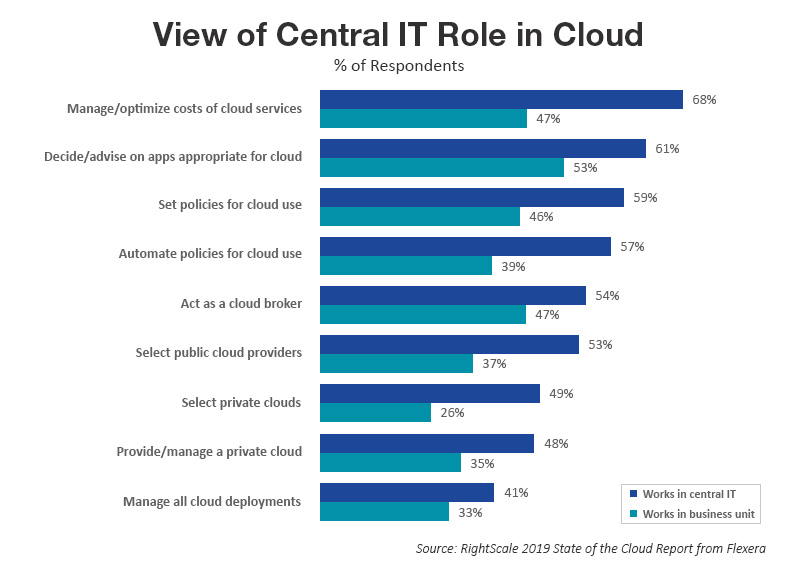
- Managing and optimization of cloud services costs (68 percent), followed by a decision on running applications matching different cloud platforms (62 percent) and setting policies for cloud usage (59 percent) continue to be the top priorities for enterprises under central IT management

- Cloud teams and infrastructure and operations groups are still shouldering the lion’s share of the work for managing cloud costs, but finance teams are taking a role in a chargeback of cloud costs and business units are often owning cloud budgets

- Analyzing and understanding cost implications of running licensed software (52 percent), followed by the complexity of license rules in public cloud (42 percent) and ensuring they are followed (41 percent) is termed as the ‘top-of-mind’ issue
- Inclination to cloud cost optimization initiatives is higher among intermediate (70 percent) and advanced cloud users (76 percent), compared to other levels (64 percent)
- Optimizing cloud usage for cost savings continues to the top initiative in 2019, for the third consecutive year
- Underestimation of wasted cloud spending. While respondents say its 27 percent for 2019, the report concludes that as 35 percent
- Despite increased emphasis on cloud cost management, only a few companies implemented automated policies such as shutting down unused workloads or rightsizing instances
- Cloud users fail to fully leverage discounting options by cloud providers. Among Amazon Web Services® (AWS) users only 47 percent use AWS Reserved Instances, while Microsoft Azure users leverage Reserved Instances only 23 percent of the time
- Advanced businesses are keen about optimizing cloud operations and cloud costs
- Increasingly ‘cloud-first strategies’ are being accompanied by the creation of a central cloud team to control cloud risk and costs
Now that we have seen the key market findings and real-time scenarios of cost-related challenges pertaining to the cloud environment, we will further move to understand the ways to cloud cost optimization and cloud cost management.
Cloud Cost Management and Optimization

Achieving cloud cost management and optimization requires a detailed understanding of the following key factors:
1) Understanding Cloud Costs
- Cloud cost evaluation – It’s important to go with a cloud adoption strategy to plan and assess your cloud requirements, which ultimately helps you cost evaluation and plan cloud spending.
- Vendor billing model – Decide the service you wish to approach a cloud solution provider for. Then analyze, compare and determine vendors by region and service-specific costs. Choosing the right vendor at the initial stages avoids vendor lock-in issues.
- Regular monitoring – Continuous monitoring of cloud infrastructure requirements is key to cloud cost management. As cloud vendors offer you pay-as-you-go services, it’s important to note that they are backed by sufficient requirements, which otherwise would incur huge expenditure.
2) Track Wastage and Optimize Costs
- Orphaned Resources
Ensure there are no unused or terminated resources lying unattended. They can cause unnecessary expenses.
| Types of Orphaned Resources | Contents |
| Orphaned Snapshots | Snapshots of expired data |
| Orphaned Volumes | Amazon EBS, Azure Virtual Disks and Block Storage in GCP, etc. |
| Unassociated IPs | Elastic IPs in AWS, Static Public IPs in Azure and Static external IP addresses in GCP |
| Load Balancers | Load balancers with no instances |
| Unused Machine Images | AMIs in AWS and images in GCP |
| Orphaned Object Storage | S3 buckets in AWS, Azure Block Bobs and Google Cloud Storage |
- Overprovisioned Resources
Make sure to choose the resources that are not overprovisioned (larger in size) than what’s required.
| Types of Overprovisioned Resources | Contents |
| Instances | Amazon EC2, Azure Virtual Machines, Google Compute Engine |
| Volumes | Amazon EBS, Azure Virtual Disks and Block Storage in GCP |
| Database Warehouses | Amazon Redshift, Google Cloud Datastore and Microsoft Azure SQL Data Warehouse |
| Relational Databases | Amazon RDS, Azure SQL and Google Cloud SQL |
- Idle Resources
Identify the resources that you wanted to run all the time and those for a limited time frame.
| Types of Idle Resources | Contents |
| Instances | Amazon EC2, Azure Virtual Machines and Google Compute Engine |
| Load Balancers | Identify load balancers with no instances or instances that run 24X7 unnecessarily |
| Relational Databases | Amazon RDS, Azure SQL and Google Cloud SQL |
| Scale Groups | Auto Scaling Groups in AWS, Azure Scale Sets and Google Scale Groups |
- Reserved Instances (RI)
| Types of RIs | Solution |
| Expired RIs | Renew and review RIs regularly |
| Unused RIs | Track RI usage and sell the unused at the vendor marketplace |
3) A 7-point Checklist Strategy
- Resource Identification – Identifying and tagging resources by usage and ownership. Doing this helps you design a layout for the overall resource usage. Identifying owners of respective resources help you understand the spending required for individual resources.
- Visibility – Make the resources (both running and reserved) visible to all the users within the organization. This avoids repetition of instances and deviation to other services.
- Fix Budget – Resource identification and their enhanced visibility makes it easy for planning budgets for individual accounts based on actual usage. This helps in planning the overall cloud budget.
- List Resources – Finalize the list of resources that are required for your cloud environment. Allow only those that are of specific sizes or support specific instances. Thus, you can make spending on only required resources and ignore the unapproved ones.
- Scheduling – Save more than 70 percent of costs by shutting down repeating instances that are not in use. Allow those requiring 24/7 functioning and schedule the rest as per needs.
- Region-wise Pricing – It is important to note that cloud costs vary with region by around 60 percent. So, keep track of regions and your workloads running there. Compare and analyzing region-wise costs can help you optimize future expenditure.
- Storage Management – Take snapshots of your storage regularly as a backup and delete large volumes that are left unused. Remember, Remember! Storage volumes cause hidden costs.
Despite these options, many enterprises wish not to take the risk of cloud cost management and optimization due to the lack of skillset and time.
And, for them, Cloud Management Platforms (CMP) are the option!
Cloud Management Platforms Are Key
In its first-ever Magic Quadrant evaluation of Cloud Management Platforms (CMPs) in 2019, renowned research firm Gartner says,
“IT and infrastructure and operations leaders, who need to provide automation, governance, and self-service brokering across multi-cloud resources as well as business unit leaders responsible for managing cloud costs, often find CMPs to be an indispensable solution.”
CMPs help organizations manage multi-cloud services and resources including cloud governance, life cycle management, brokering and automation for managed cloud resources, across the following seven key functional areas:
- Provisioning and orchestration
- Service request management
- Inventory and classification
- Monitoring and analytics
- Cost management and resource optimization
- Cloud migration and backup and Disaster Recovery
- Identity, security and compliance
Wait no more! It’s time to gear up for the cloud cost management and optimization measures to get the best of your cloud computing environment.
Related Stories