In modern computing, hybrid cloud and multi-cloud strategies have emerged as pivotal paradigms, reshaping how organizations structure their IT infrastructure. A hybrid cloud integrates the best of both on-premises resources and cloud capabilities, offering a flexible and balanced approach to data management.
On the other hand, the multi-cloud approach leverages the strengths of multiple cloud service providers, empowering businesses with diverse resources and reducing dependence on a single vendor. As enterprises navigate the complexities of data management, scalability, and cost optimization, these twin concepts have risen to the forefront, ushering in a new era of agile and resilient computing architectures.
Let’s Look at the Differences Between Hybrid Cloud and Multi-Cloud
Hybrid cloud and multi-cloud are prominent cloud computing models delivering flexibility, scalability, and cost efficiency to organizations. Hybrid cloud merges private and public clouds, with the former on-premises for data control and the latter hosted externally, providing diverse computing resources. Multi-cloud utilizes multiple providers to optimize workload distribution, risk mitigation, and resource accessibility.
Multi-cloud is the use of multiple public clouds. This allows organizations to exploit different cloud providers’ strengths and avoid vendor lock-in.
Email-us: connect@veritis.com; Call: 972-753-0022
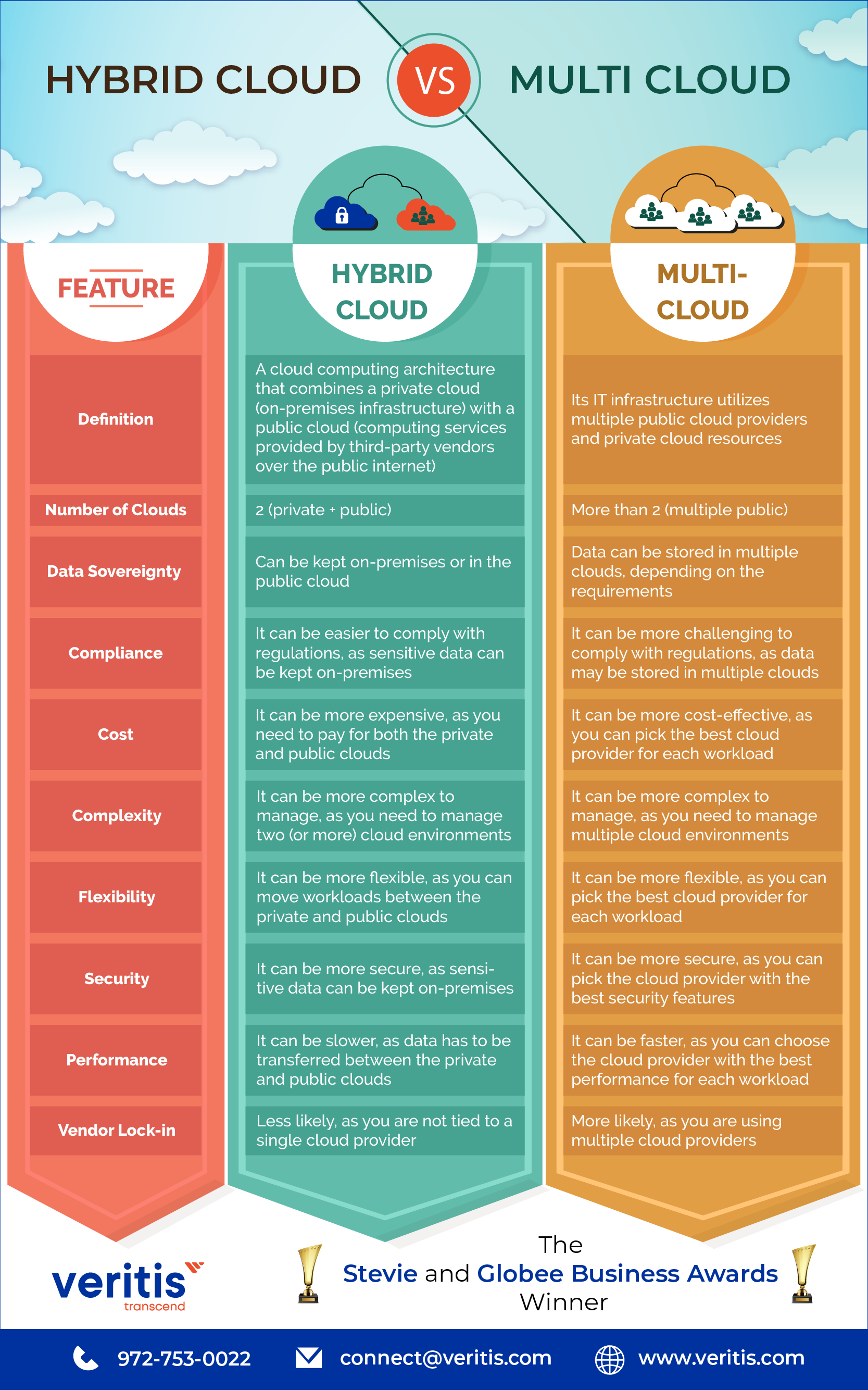
| Feature | Hybrid Cloud | Multi-Cloud |
| Definition | A cloud computing architecture that combines a private cloud (on-premises infrastructure) with a public cloud (computing services provided by third-party vendors over the public internet) | Its IT infrastructure utilizes multiple public cloud providers and private cloud resources |
| Number of Clouds | 2 (private + public) | >2 (multiple public) |
| Data Sovereignty | Can be kept on-premises or in the public cloud | Data can be stored in multiple clouds, depending on the requirements |
| Compliance | It can be easier to comply with regulations, as sensitive data can be kept on-premises | It can be more challenging to comply with regulations, as data may be stored in multiple clouds |
| Cost | It can be more expensive, as you need to pay for both the private and public clouds | It can be more cost-effective, as you can pick the best cloud provider for each workload |
| Complexity | It can be more complex to manage, as you need to manage two (or more) cloud environments | It can be more complex to manage, as you need to manage multiple cloud environments |
| Complexity | It can be more complex to manage, as you need to manage two (or more) cloud environments | It can be more complex to manage, as you need to manage multiple cloud environments |
| Flexibility | It can be more flexible, as you can move workloads between the private and public clouds | It can be more flexible, as you can pick the best cloud provider for each workload |
| Security | It can be more secure, as sensitive data can be kept on-premises | It can be more secure, as you can pick the cloud provider with the best security features |
| Performance | It can be slower, as data has to be transferred between the private and public clouds | It can be faster, as you can choose the cloud provider with the best performance for each workload |
| Vendor Lock-in | Less likely, as you are not tied to a single cloud provider | More likely, as you are using multiple cloud providers |
In a rapidly evolving digital era, hybrid and multi-cloud computing are instrumental in crafting adaptable and resourceful IT frameworks. A hybrid cloud combines versatility with data control, while multi-cloud disperses risk and amplifies service options. As technology advances, the synergy between these strategies exemplifies the evolving landscape of IT architecture.
Conclusion
Navigating the evolving IT landscape, Veritis, a Stevie award-winner, is an exemplar in providing sophisticated hybrid and multi-cloud solutions. With a deep understanding of on-premises infrastructure integration and diverse cloud provider utilization, Veritis empowers clients with adaptable resource management. In an era where seamless data control, scalability, and risk mitigation are paramount, Veritis’ technical prowess underscores the intricate potential of modern computing architectures.
Got Questions? Schedule A Call
Additional Resources:
- 5 Reasons for successful On-Premises to the Cloud Migration
- The Biggest Clouds Myths that Every Organization Must Do Away With
- AWS Vs Azure Vs GCP – The Cloud Platform of Your Choice?
- Global Cloud Market to Reach Nearly USD 800 Billion by 2028: Survey
- Cloud Computing: Trends, Challenges and Benefits
- 9 Keys to Selecting a Right Cloud Managed Services Provider (MSP)
- Cloud Computing Trends Which Shall Dominate 2023
- 5 Considerations for Drafting a Multi Cloud Strategy

