
Enterprise leaders across automotive, healthcare, banking and finance, manufacturing, energy, government, and telecom are under constant pressure to improve performance while managing risk and cost. Many core applications that once enabled growth now slow execution, restrict integration, and limit scalability. This shift has brought the question of what is application modernization into executive planning and long term business discussions.
From a leadership standpoint, enterprise application modernization is about ensuring applications actively support current business priorities. Leaders evaluate why application modernization matters by looking at reliability, security, compliance readiness, and the ability to deliver change faster. These decisions involve choosing the right modernization technologies, defining clear goals for business application modernization, and addressing long standing challenges created by aging systems and rising maintenance effort.
Organizations that succeed treat modernization as a structured business initiative. They apply practical strategies, follow a clear framework, and stay informed on emerging trends shaping application platforms. With the right solutions and experienced consulting support, enterprises modernize critical systems without disrupting operations. Veritis works closely with leadership teams to modernize applications, strengthening stability, supporting growth, and delivering outcomes that matter at the executive level.
Talk to an Application Modernization Expert
What is Application Modernization?
Application modernization is the process of evolving existing enterprise applications to meet current business, technology, and operational demands. At an executive level, it is less about rewriting software and more about improving how applications support speed, resilience, security, and scale. When leaders ask what is application modernization, they are really asking how their applications can better serve customers, employees, and long term business goals.
In practice, enterprise application modernization involves updating architectures, platforms, and operating models to align with modern environments. This may include adopting cloud platforms, improving integration, strengthening security, and enabling faster change cycles through modern application modernization technology. The objective of business application modernization is to reduce dependency on rigid legacy systems while improving performance, reliability, and cost efficiency.
For leadership teams, application modernization becomes a strategic lever. Understanding why application modernization matters helps executives address persistent challenges, including high maintenance costs, limited agility, and growing operational risk. When guided by clear strategies and a structured framework, organizations can modernize applications in a controlled way, delivering measurable benefits without disrupting core operations. Veritis helps enterprises approach application modernization as a business transformation initiative, not a technical experiment.
Why Modernize Your Applications?
Enterprise leaders modernize applications to improve performance, reduce risk, and support growth. Legacy modernization systems often slow execution, limit integration, and increase maintenance effort, making it harder to respond to business and market changes. Understanding why application modernization matters starts with recognizing the role applications play in operational stability and business agility.
Application modernization helps organizations strengthen security, improve scalability, and simplify operations. These improvements address common application modernization challenges, including rising costs, aging architectures, and slow change cycles. When guided by clear application modernization strategies and the proper application modernization framework, enterprises can modernize with confidence. Veritis supports leadership teams with proven application modernization solutions and consulting services that deliver measurable business value.
Application Modernization Patterns
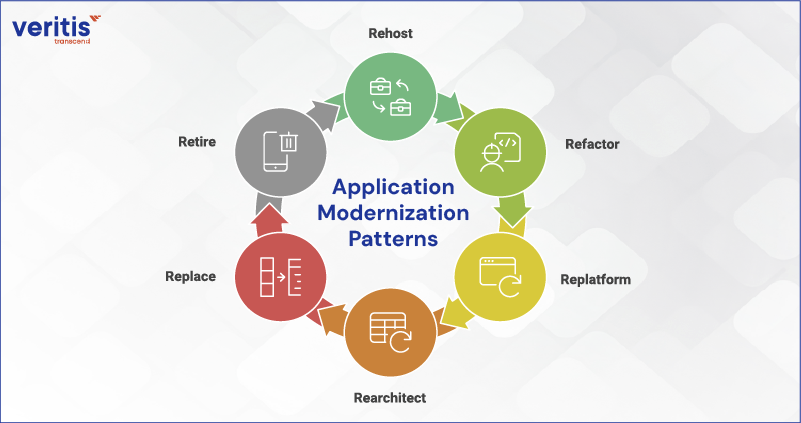
Enterprise leaders apply different application modernization patterns based on risk tolerance, business urgency, and long term goals. The following patterns are commonly used in enterprise application modernization initiatives.
1) Rehost
This pattern moves applications to modern infrastructure with minimal change. It helps organizations reduce infrastructure costs and improve stability as they prepare for deeper modernization later.
2) Refactor
App Refactoring improves application structure and performance without changing core functionality. This approach addresses scalability and reliability issues using modern application modernization technology.
3) Replatform
Replatforming introduces selective improvements, such as managed databases or cloud services. It balances speed and value, delivering early benefits from modernizing applications without major disruption.
4) Rearchitect
This pattern redesigns applications to support modern architectures and integration needs. It is often used when business application modernization requires agility, scalability, and faster innovation cycles.
5) Replace
Applications are replaced with modern platforms or packaged solutions when legacy systems no longer meet business or compliance requirements. This approach simplifies operations and reduces long term maintenance effort.
6) Retire
Retiring unused or redundant applications eliminates cost and complexity. It is a critical step in reducing application sprawl and addressing application modernization challenges.
Also Read: Improving Patient Care Through Application Support Optimization
What Technologies Require Modernization?
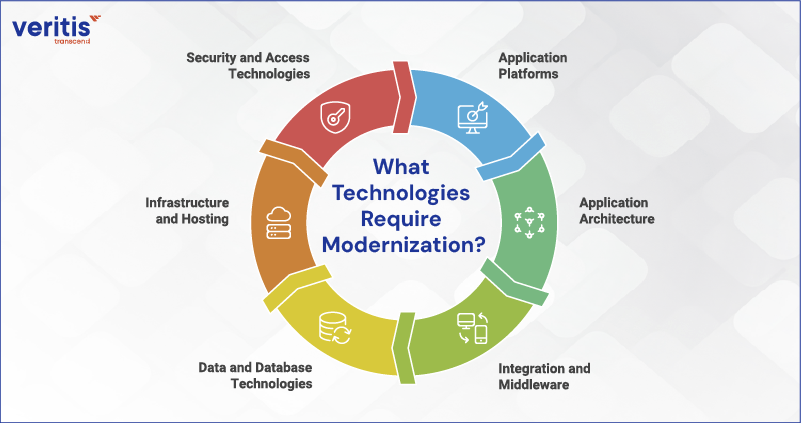
Application modernization begins by identifying technologies that constrain performance, increase risk, or drive up costs. For enterprise leaders, the objective is not wholesale replacement, but targeted modernization where business impact is highest.
1) Application Platforms
A) What Changes?
Legacy application platforms are modernized to improve scalability, reliability, and integration.
B) Business Benefits
Faster response times, improved availability, and reduced dependency on manual intervention.
C) Key Capabilities Enabled
Cloud readiness, API support, and easier integration with enterprise systems.
2) Application Architecture
A) What Changes?
Monolithic architectures are being redesigned into modular or service based structures.
B) Business Benefits
Faster release cycles reduced operational risk and improved system resilience.
C) Key Capabilities Enabled
Independent updates, fault isolation, and greater agility in business application modernization.
3) Integration and Middleware
A) What Changes?
Outdated middleware and point to point integrations are replaced with modern integration platforms.
B) Business benefits
Real time data flow, reduced reconciliation effort, and improved visibility across systems.
C) Key capabilities enabled
API management, event driven integration, and simplified data exchange.
4) Data and Database Technologies
A) What Changes?
Legacy databases are modernized to support performance, scale, and analytics.
B) Business Benefits
Faster access to data, improved reliability, and better decision support.
C) Key Capabilities Enabled
High availability, real time analytics, and support for advanced application modernization strategies.
5) Infrastructure and Hosting
A) What Changes?
Traditional hosting environments are replaced with flexible, scalable platforms.
B) Business Benefits
Lower infrastructure cost, improved uptime, and faster deployment cycles.
C) Key Capabilities Enabled
Elastic scaling, automated provisioning, and stronger resilience.
6) Security and Access Technologies
A) What Changes?
Legacy security tools are upgraded to meet modern compliance and threat landscapes.
B) Business Benefits
Reduced risk exposure, stronger governance, and improved regulatory alignment.
C) Key Capabilities Enabled
Centralized identity management, automated controls, and continuous monitoring.
Application Modernization Benefits
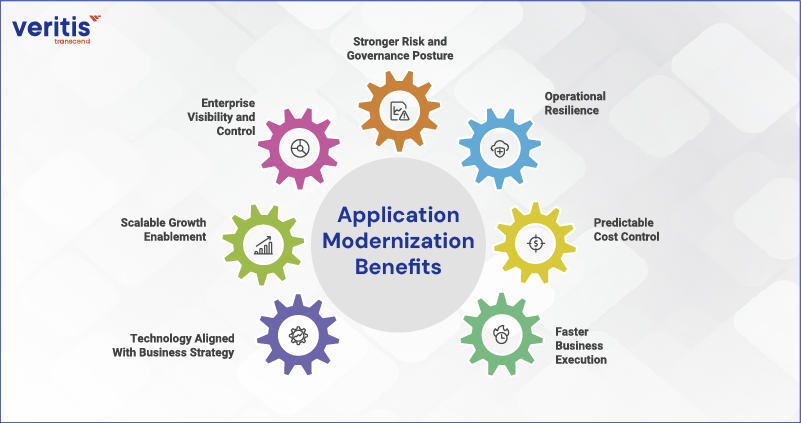
For enterprise leadership, application modernization benefits are measured by their impact on performance, risk, and long term enterprise value. Each benefit below reflects how modernization changes the operating model, not the technology stack.
1) Faster Business Execution
A) What Changes?
Release cycles are shortening, and dependencies are reducing across core systems.
B) Why It Matters?
Speed determines how quickly the organization responds to customers, markets, and regulations.
C) Executive Gain
Leadership operates at business speed rather than system speed, accelerating outcomes without disruption.
2) Predictable Cost Control
A) What Changes?
Maintenance heavy legacy environments are replaced with optimized platforms.
B) Why It Matters?
Unpredictable technology spend erodes margins and limits strategic investment.
C) Executive Gain
Enterprise application modernization stabilizes costs and redirects budgets toward growth initiatives.
3) Operational Resilience
A) What Changes?
Application reliability and availability improve across critical operations.
B) Why It Matters?
Downtime directly impacts revenue, trust, and regulatory standing.
C) Executive Gain
Leaders reduce business disruption and protect continuity across finance, healthcare, manufacturing, and government environments.
4) Stronger Risk and Governance Posture
A) What Changes?
Security, access control, and audit readiness become embedded into applications.
B) Why It Matters?
Manual controls and legacy systems increase exposure to cyber and compliance risk.
C) Executive Gain
Executives manage risk proactively while addressing core application modernization challenges.
5) Enterprise Visibility and Control
A) What Changes?
Applications integrate more cleanly, and data flows more consistently across systems.
B) Why It Matters?
Fragmented information limits accurate reporting and decision making.
C) Executive Gain
Business application modernization delivers clearer insight into performance, cost drivers, and operational risk.
6) Scalable Growth Enablement
A) What Changes?
Applications support expansion across users, regions, and workloads without added complexity.
B) Why It Matters?
Growth should not introduce instability or rising overhead.
C) Executive Gain
Leaders scale confidently using proven application modernization strategies and platforms.
7) Technology Aligned With Business Strategy
A) What Changes?
Applications evolve in line with business priorities rather than constraining them.
B) Why It Matters?
Misaligned technology slows execution and weakens competitiveness.
C) Executive Gain
With a clear application modernization framework and the right application modernization solutions, enterprises turn applications into strategic assets. Veritis supports leadership teams through disciplined application modernization consulting services that deliver measurable, long term value.
Also Read: Cybersecurity for Manufacturing: A Strategic Guide to Protecting Industrial Operations
Application Modernization Challenges
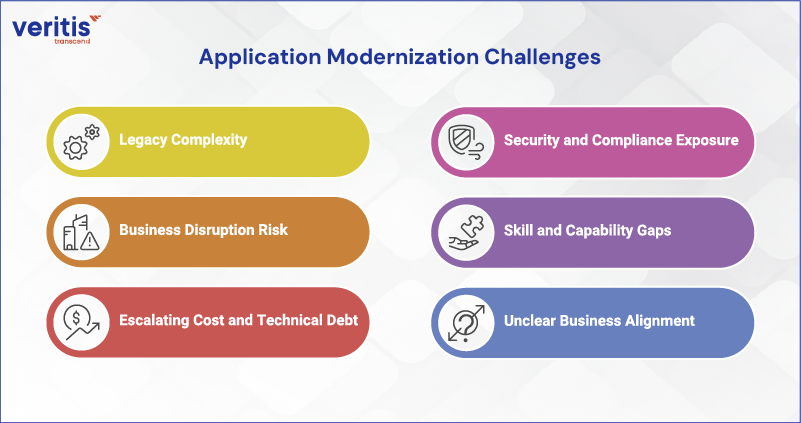
Application modernization delivers value, but enterprise leaders face clear challenges that must be addressed with precision. Each challenge below reflects a business risk, followed by how Veritis addresses it.
1) Legacy Complexity
Challenge
Many applications are deeply embedded across business processes, data, and integrations built over the years. This complexity increases risk and slows enterprise application modernization initiatives.
Veritis Solution
Veritis applies phased application modernization strategies that untangle dependencies incrementally. This approach reduces risk while maintaining continuity across business critical systems.
2) Business Disruption Risk
Challenge
Modernizing core applications raises concerns around downtime, service interruption, and customer impact, particularly in regulated environments.
Veritis Solution
Veritis follows a structured application modernization framework that prioritizes stability. Controlled rollouts, parallel environments, and staged transitions protect operations throughout modernization.
3) Escalating Cost and Technical Debt
Challenge
Legacy environments demand rising maintenance effort, consuming budgets that could otherwise fund innovation.
Veritis Solution
Through business application modernization, Veritis reduces long term support costs and redirects spend toward scalable application modernization solutions that deliver measurable value.
4) Security and Compliance Exposure
Challenge
Outdated security models and manual controls increase regulatory and cyber risk across the enterprise.
Veritis Solution
Veritis modernizes security and access layers using proven application modernization technology. Embedded governance, automated controls, and audit readiness strengthen compliance posture.
5) Skill and Capability Gaps
Challenge
Internal teams often lack experience with modern architectures, tools, and operating models, which slows progress and increases execution risk.
Veritis Solution
Veritis provides experienced application modernization consulting services that guide planning, execution, and governance, accelerating outcomes while reducing transformation risk.
6) Unclear Business Alignment
Challenge
Modernization initiatives fail when technology upgrades are not tied to clear business outcomes.
Veritis Solution
Veritis anchors application modernization benefits to business priorities such as performance, resilience, cost control, and scalability, ensuring alignment at the executive level.
Leadership Perspective
Application modernization challenges pose business risks that require structured decision making. With disciplined strategies, a proven framework, and trusted consulting, Veritis helps enterprises modernize applications in a controlled way that protects stability while delivering long term value.
Begin Your Application Modernization Journey
Application Modernization Strategies
Enterprise leaders approach application modernization through deliberate strategies that balance speed, risk, and long term value. Each strategy below reflects how executives control transformation without disrupting the business.
1) Portfolio Led Modernization
A) Modernize What Matters Most
Executives begin by assessing the full application portfolio to identify systems that directly affect revenue, customer experience, compliance, or operational stability.
B) How Leaders Govern It
Applications are prioritized based on business criticality, risk exposure, and return on modernization investment.
C) Leadership Outcome
Capital and effort are focused on high impact systems while avoiding unnecessary costs and disruption.
2) Phased Transformation Approach
A) Reduce Risk Through Incremental Change
Rather than complete scale replacement, applications are modernized in stages across the architecture, integration, and performance layers.
B) How Leaders Govern It
Milestones, success metrics, and rollback plans are defined upfront to maintain control throughout execution.
C) Leadership Outcome
Business continuity is preserved while modernization progresses in a controlled, predictable manner.
3) Cloud First Enablement
A) Build Flexibility Into the Operating Model
Applications are prepared for scalable, resilient environments that support evolving business demands.
B) How Leaders Govern It
Cloud adoption decisions are aligned with cost models, compliance requirements, and operational readiness.
C) Leadership Outcome
Enterprises gain agility, resilience, and cost transparency without forcing unnecessary migration.
4) Security and Compliance by Design
A) Embed Governance Into Applications
Security, identity, and audit requirements are incorporated directly into application design and workflows.
B) How Leaders Govern It
Policies, controls, and reporting are standardized across the modernization program.
C) Leadership Outcome
Risk exposure decreases while regulatory confidence and audit readiness improve.
5) Integration Centric Design
A) Eliminate Silos and Improve Visibility
Modernized applications are built to integrate seamlessly across enterprise systems and data sources.
B) How Leaders Govern It
Integration standards and data ownership models are defined at the enterprise level.
C) Leadership Outcome
Executives gain consistent visibility, faster insight, and reduced operational friction.
6) Business Aligned Execution
A) Tie Modernization to Measurable Outcomes
Application modernization strategies are anchored in specific business goals, such as cost reduction, improved uptime, and speed to market.
B) How Leaders Govern It
KPIs and value metrics are reviewed regularly at the leadership level.
C) Leadership Outcome
Modernization stays aligned with strategy and delivers outcomes that leadership can measure and trust.
Also Read: 8 Strategic Benefits of Digital Transformation for Enterprise Leaders
Application Modernization Trends
Application modernization trends show how enterprises are reshaping applications to improve speed, resilience, and long term value. For leadership teams, these trends signal how enterprise application modernization is evolving and where investment delivers the most substantial return.
1) Adaptive Applications
A) What is Changing?
Applications are being designed to evolve continuously rather than remain fixed for years.
B) Why It Matters to Leaders?
Adaptive systems reduce disruption and improve responsiveness, strengthening application modernization benefits tied to agility and performance.
2) Continuous Modernization
A) What is Changing?
Organizations treat modernization as an ongoing discipline rather than a one time project.
B) Why It Matters to Leaders?
This approach limits accumulated risk and cost, addressing common application modernization challenges while keeping systems aligned with business priorities.
3) Cloud Readiness
A) What Is Changing?
Applications are modernized to be cloud ready without forcing an immediate migration.
B) Why It Matters to Leaders?
Cloud readiness improves flexibility and cost control, supporting scalable business application modernization across both regulated and non regulated environments.
4) Built In Security
A) What is Changing?
Security, identity, and compliance are embedded directly into applications.
B) Why It Matters to Leaders?
Integrated governance reduces regulatory exposure and strengthens confidence in application modernization technology decisions.
5) Strong Integration
A) What is Changing?
Modern applications are designed to connect easily across enterprise systems.
B) Why It Matters to Leaders?
Improved integration enhances visibility and decision making, a key outcome of successful application modernization strategies.
6) Business Led Priorities
A) What is Changing?
Applications are modernized based on business impact, not system age.
B) Why It Matters to Leaders?
This ensures application modernization solutions deliver measurable value and align with enterprise strategy rather than technical preference.
Conclusion
Application modernization has become a leadership decision because it directly influences performance, risk, and long term growth. Enterprises that modernize with clear strategies, a structured framework, and disciplined execution turn their applications into platforms that support speed, resilience, and scale.
With the right application modernization solutions and experienced consulting support, organizations can modernize without disruption and realize measurable business value. Veritis partners with enterprise leaders to modernize applications in a controlled, outcome driven way, ensuring technology strengthens the business rather than holds it back.