
The hybrid cloud model is gaining traction because of its ability to orchestrate between the private cloud and public cloud variants. While the private cloud promises good security, the public cloud comes with better flexibility. But, hybrid cloud comes up with both!
Due to its significant strategic advantages, the hybrid cloud infrastructure has received the attention it deserves in the context of digital transformation. As a result, many businesses are developing plans to update their application strategies, with the hybrid cloud strategy frequently cited as the top choice!
The orchestration that the hybrid cloud does is different than other models that facilitate self-management of resources. Dealing away with the concerns over either-or-choice with public and on-premise clouds, the hybrid cloud offers greater flexibility to switch between tasks with ease.
However, the aspect that many firms report as key to the hybrid cloud’s success has a ‘hybrid database strategy’ along.
While some have already realized the difference between the two, some have begun discovering that both are equally important to achieve expected success with the hybrid cloud strategy with all risks addressed.
Schedule A Call With Our Expert
What is a Hybrid Cloud Strategy?
The best configuration for your organization’s data requirements is considered when planning and constructing a mixed storage environment using both local and off-site resources. Hybrid cloud environments are complicated and intricate, even though it might go without saying.
To provide a genuine hybrid experience, you and your team or CSPs must coordinate storage, access, computing, and resources across cloud environments. The benefits of these environments stem from how well they can function together.
Due to the growing popularity of hybrid clouds for HPC applications, numerous businesses and their CSP partners are developing hybrid cloud strategies to help them make the most of their modern data architecture.
Describe the hybrid cloud strategy. It is a strategic approach to your cloud environment that aids in deciding what data goes where, what resources may be accessed through which channels, and how information and resources will be automated and prioritized.
However, a hybrid cloud strategy can span a variety of components of your hybrid architecture, including:
1) Storage: High-performance access, seamless filesystems, and databases across multiple cloud instances are priorities here, and deciding which should save data on private vs. public cloud infrastructure.
2) Performance: Here, the focus is on best practices for maximizing cloud computing infrastructure across essential cloud resources for particular applications and workload optimization.
3) Security: This area includes maintaining compliance as data moves from private to public environments and managing data-at-rest and data-in-transit security at all points of use.
4) Operations: Managing applications and infrastructure locations are necessary here (on-prem, public, etc.)
5) Usage: Who will utilize these resources, and why? What workloads (AI, analytics, etc.) will be used by what applications?
Without a clear strategy, there is no logical way to maximize a cloud investment. You might already have some of these strategic priorities if you already have a hybrid cloud deployment configuration. After that, you should monitor how well your cloud infrastructure is working for you. It entails utilizing analytics on performance, usage, and workflows to assist you in understanding the adjustments you must make to stay in alignment with your strategy or modify your strategy to align with practical applications.
What is a Hybrid Cloud Database?
Let’s look at some relevant concepts to understand better what we are talking about.
Public Cloud
A web browser is used to access resources such as servers, storage, and networks that are owned and managed cloud service provider by a third party. Your data is isolated and secure in this scenario, but you still share the infrastructure with other businesses; only you can access it.
Private Cloud
The organization owns and manages servers, storage, and networks. On-site or even in the cloud are both viable options. Many cloud service providers provide this kind of service using exclusive hardware for the client, ensuring that it is not shared with anybody else.
On-premises
On-site company resources include servers, storage, and a network. Private clouds, in which compute resources are virtualized similarly to those of public cloud providers, can be operated using the on-premises infrastructure.
Hybrid Cloud
It is a topology that combines on-premises, private, and public cloud service providers. The main distinction between this concept and a multi cloud solution is that it specifically refers to combinations of public and private cloud providers, which may also include on-premises.
As per the reports from MarketsAndMarkets, the global cloud database market is expected to touch a USD 24.8 billion market revenue by 2025 at a CAGR of 15.7 percent. One of the key drivers predicted to fuel this market’s expansion is the growing need for self-driving cloud databases.
What Led To A Hybrid Database Strategy?
The push for cloud deployment has increased the competitive spirit in the IT industry. However, deciding on the right cloud option among the three cloud variants was a tough task for many, owing to cost concerns.
Surveys show that many opt for ‘hybrid’ over other forms of cloud, particularly because of the costs involved in adopting a pure cloud model.
“Executing on new technology can be complex and costly, and completely switching from today’s current infrastructure reality to one based 100% on public cloud is so prohibitively expensive that no one’s doing it,” says one of the leading IT market research firms.
On the other side, many firms feel that the cloud is mandatory to at least stand in today’s competition, winning aside! So, the option many firms found was hybrid as an economical cloud option. 71 percent of firms are hybrid, while 81 percent are multi cloud, says one of the market’s renowned IT service providers.
But, in the journey with hybrid, many firms are reportedly missing out on something important i.e. the hybrid database strategy, which is key to enjoying the full benefits of the hybrid cloud deployment.
What difference does a Hybrid Database Strategy Make?
Statistics show that most companies currently using the hybrid cloud will need distributed data sources for their data and analytics use cases. While data is key to any application, it matters a lot in a hybrid environment!
An effective database strategy clubbed with a hybrid environment, called a hybrid database strategy, helps:
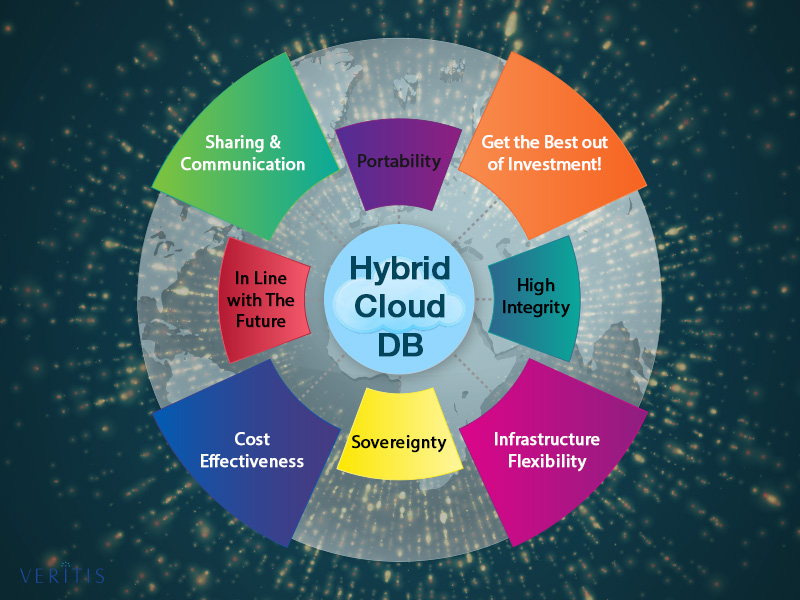
1) Portability
Easy movement of data in and out of the cloud provider, without impacting application and user experience is important for a successful cloud strategy. Whereas, hybrid cloud architecture stands vulnerable to vendor lock-in issues, making data portability challenges. A hybrid database strategy addresses this concern!
2) Get the Best out of Investment!
With a hybrid database strategy in place, you may not require learning an additional database, thus saving developers time and enjoying cost savings with what you already spent.
3) Sharing & Communication
Dealing with the cloud means the involvement of a large number of applications that require data sharing. Data sharing with the cloud often ends up in the creation of more silos. The creation of data silos prevents data-data communication among multiple applications, resulting in a slowdown of processes and application disruptions. Whereas, a hybrid database system allows a data-sharing mechanism and ensures continuous data-data communication.
4) High Integrity
A perfect hybrid database strategy enables full-fledged database availability, security, and integrity ensuring effective risk assessments and audits, all in line with regulations and GDPR across the hybrid cloud architecture.
5) Sovereignty
A hybrid cloud database gives you high data sovereignty, allowing you to configure the database in line with your preferences to store data safely in any location. It also facilitates multi-data center locations and data residency, enabling data storage in compliance with requirements.
6) Infrastructure Flexibility
Distributed hybrid cloud database gives organizations the needed flexibility to fit in the changing business requirements. This clears away concerns of getting struck into a long-term contract with a vendor that doesn’t meet your changing requirements. By allowing more control on the on-premises hardware stack, a distributed hybrid cloud database gives you enough scope to play with AI/ML features in the public cloud. Having hybrid cloud database solutions helps organizations build infrastructure as per their needs with reduced risk, less complexity, and achieve high productivity.
7) Cost-effectiveness
Public cloud resources are most preferred over the private cloud, majorly because of the cost factor. To address the cost factor and also get the benefits of private cloud, many firms chose hybrid cloud to enjoy both the cloud variants on a single platform. So, adopting a hybrid cloud database is cost-effective as capital expenditure turns into operational expenditures pushing productivity.
In Line With The Future
A hybrid cloud database works well for organizations preparing to undergo a full-fledged digital transformation and migrate to modern systems, because of its versatility in extending the life of legacy applications and facilitating new deployments.
Get on to reap the benefits of the hybrid cloud strategy!
Got Questions? Schedule A Call
More Articles:
- Hybrid Cloud Vs Multi Cloud: What’s the Difference!
- Google’s Anthos: The Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Platform That You Need
- Cloud, Hybrid IT Among Top Priorities for Information Technology Business
- Cloud Managed Services Global Forecast – A ‘USD 116 Billion’ Market By 2025!
- What is Cloud Security Posture Management?