
The acceleration of digital manufacturing has pushed cybersecurity for manufacturing to the top of every executive agenda. As automation expands and production systems connect across global plants, the attack surface grows. Disruptions now threaten not only data but also physical operations, making resilience a core business requirement. Manufacturers that once relied on traditional controls must now adopt enterprise cybersecurity solutions built for modern industrial environments.
Across the United States, leaders are recognizing that the rising cyber threats to manufacturing industry ecosystems require a new level of intelligence, speed, and visibility. Legacy architectures cannot protect interconnected equipment, supply chains, and industrial workflows. This shift has accelerated investment in cybersecurity for the manufacturing industry, driving demand for trusted partners capable of delivering transformation at scale. Veritis has become a strategic choice for executives seeking industry specific cybersecurity services that strengthen operations without slowing innovation.
Executive Strategic Brief | 2025
- 26 to 40% Most Targeted Sector
- $17B Total Ransomware Losses
- 11 Days Avg. Operational Disruption
- 858 Ransomware Attacks
- $260K Cost Per Hour Downtime
- 71% Attacks Involving Ransomware
Veritis supports leading manufacturers in redefining modern protection. Our approach integrates cybersecurity and manufacturing into a unified defense model that safeguards uptime, protects intellectual property, and ensures compliance across all facilities.
With deep expertise in industrial security, supply chain protection, and OT and IT convergence, Veritis enables organizations to adopt proven Cybersecurity Trends, operationalize Cybersecurity Best Practices, and implement Risk Mitigation Strategies that position them to lead with confidence.
Schedule Manufacturing Cyber Risk Assessment
What is Cybersecurity for Manufacturing?
Cybersecurity for manufacturing is the protection of digital and operational systems that support factories, production lines, and industrial supply chains. As organizations adopt automation, innovative equipment, and connected workflows, the demand for stronger cybersecurity in manufacturing industry has grown rapidly. It ensures operations remain safe from ransomware, system breaches, and other cyber threats in manufacturing environments.
Effective programs unify IT and OT security, strengthen resilience, and support continuous operations across plants. Veritis delivers industry aligned cybersecurity solutions and cybersecurity services that blend modern controls with proven cybersecurity trends, cybersecurity best practices, and risk mitigation strategies to help manufacturers protect uptime and accelerate secure digital growth.
The Manufacturing Threat Landscape
Critical Threat Statistics:
- 47% of manufacturing breaches now involve ransomware.
- 68% of industrial ransomware attacks specifically target the manufacturing sector.
- 2% year over year increase in manufacturing data breaches.
- 431% surge in supply chain attacks since 2021.
- 10% of total incidents specifically target ICS/OT equipment.
Manufacturing is the prime target for a simple economic reason: leverage. Unlike data centric industries, where a breach might result in privacy fines, a breach in manufacturing halts production. The complex interplay of interconnected systems means that a single entry point can cascade into a complete operational shutdown.
The Digital Transformation Paradox: While Industry 4.0 initiatives drive efficiency through connectivity, they also expose machinery that was never designed for the public internet. Legacy OT systems, often running on outdated protocols with no native security, are now meeting modern IT networks. This “air gap” erosion provides attackers with direct pathways from corporate emails to factory floor controllers.
Furthermore, the sector faces a dual threat: sophisticated criminal enterprises seeking to extort money through ransomware and nation state actors seeking to steal intellectual property or disrupt critical infrastructure.
How Does Cybersecurity for Manufacturing Compare with Other Industries?
1) Higher Impact on Physical Operations
In most sectors, a cyber incident disrupts data. In cybersecurity for manufacturing, it can stop machines, slow production, and delay shipments. This makes cybersecurity for the manufacturing industry more closely tied to operational continuity and plant safety.
2) IT and OT Convergence Challenges
Other industries secure traditional IT systems. The cybersecurity manufacturing industry must protect industrial controllers, sensors, robots, and production networks. This mix of old and new technologies increases risk and demands specialized cybersecurity solutions.
3) Broader Supply Chain Exposure
Manufacturers rely on global vendors and connected logistics systems. This creates more entry points for cyber threats to manufacturing industry environments. Effective cybersecurity for manufacturers must secure access to partners and data exchanges across all tiers.
4) Higher Regulatory and Safety Expectations
Compliance in manufacturing extends beyond data protection. Safety standards, product integrity, and operational reliability shape the requirements of cybersecurity in manufacturing industry programs, making controls more complex than in typical corporate settings.
5) Greater Need for Industrial Grade Resilience
While many industries focus on recovery, cybersecurity, and manufacturing must prioritize prevention to avoid downtime. Veritis supports this need through advanced cybersecurity services, proven cybersecurity trends, cybersecurity best practices, and targeted risk mitigation strategies.
Useful link: Cybersecurity Best Practices: Protecting Your Business From Data Breaches in 2026
What Are the Main Cybersecurity Risks in Manufacturing?
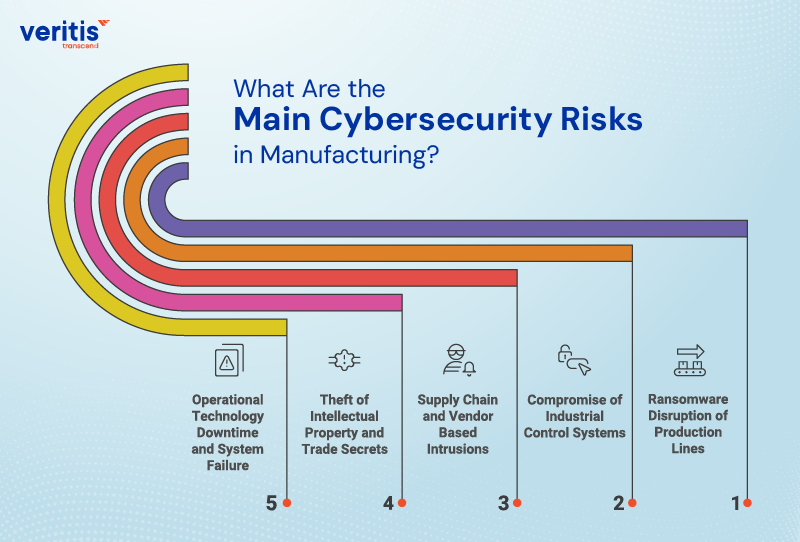
1) Ransomware Disruption of Production Lines
A) Impact on Operations
Ransomware is one of the most damaging cybersecurity risks for manufacturing, as it halts production, disables machinery, and freezes plant floor systems.
B) Why Manufacturing is Targeted?
Attackers know downtime is costly, making the cybersecurity manufacturing industry a prime target for extortion.
2) Compromise of Industrial Control Systems
A) Vulnerabilities Across OT Equipment
PLCs, SCADA, HMIs, and robotic systems were not designed with modern security controls. This creates weaknesses across cybersecurity for the manufacturing industry ecosystems.
B) Operational and Safety Consequences
When attackers manipulate equipment logic, production accuracy, worker safety, and product integrity are all at risk.
3) Supply Chain and Vendor Based Intrusions
A) Expanded Attack Surface
Manufacturers rely on hundreds of suppliers, making vendor access a significant cybersecurity vulnerability.
B) Threat Propagation Across the Network
A single compromised partner can infiltrate procurement, logistics, and ERP systems, amplifying cyber threats to manufacturing industry operations.
4) Theft of Intellectual Property and Trade Secrets
A) High Value Targets
Engineering designs, formulas, and production processes make manufacturing a top target for espionage.
B) Industry Wide Competitive Risk
IP theft undermines global competitiveness and is a growing challenge across cybersecurity and manufacturing.
5) Operational Technology Downtime and System Failure
A) Direct Production Loss
OT disruptions lead to equipment shutdowns, reduced throughput, and missed delivery commitments, increasing the urgency of robust cybersecurity in manufacturing industry.
B) Financial and Reputational Damage
Extended downtime results in multimillion dollar losses, making resilience a priority for modern cybersecurity services and advanced cybersecurity solutions delivered by Veritis.
What Are the Latest Ransomware Trends in Manufacturing?

1) Focus on Shutting Down Production
A) What is Happening?
Ransomware groups are now engineering attacks to shut down lines and shut down plants, not just encrypting office files. In cybersecurity for manufacturing, the primary focus has shifted to uptime and throughput, as each hour of downtime directly impacts the bottom line.
B) Executive Impact
This trend makes cybersecurity for the manufacturing industry a core operations issue, not only an IT topic. Boards want assurance that ransomware cannot halt critical assets, which raises expectations on resilience, segmentation, and recovery planning.
2) Attacks Moving From IT into OT
A) What is Happening?
Campaigns increasingly start in corporate IT and then pivot into operational technology, including SCADA, PLCs, and plant networks. This is now one of the most serious cyber threats to manufacturing industry operations.
B) Executive Impact
Traditional controls that protect email and business systems are no longer sufficient. Modern cybersecurity programs in the manufacturing industry must treat IT and OT as a single risk surface and invest in solutions that understand industrial protocols, assets, and processes.
3) Multistage and Multi Extortion Tactics
A) What is Happening?
Attackers are combining encryption, data theft, and operational blackmail. They threaten to leak sensitive engineering data or supplier contracts while plants are offline. This is the new normal in the cybersecurity manufacturing industry landscape.
B) Executive Impact
The damage now spans operations, reputation, compliance, and competitive position. Leading cybersecurity strategies for manufacturers must include legal, communications, and partner management response, not technical restoration.
5) Exploiting Suppliers and Remote Access
A) What is Happening?
Ransomware operators increasingly enter through third parties, remote maintenance tools, and unmanaged vendor accounts. This makes the extended supply chain a significant weak link in cybersecurity and manufacturing.
B) Executive Impact
Security cannot stop at the factory gate. Executives need cybersecurity services and governance that enforce controls on vendor connectivity, remote support, and shared platforms, backed by clear Risk Mitigation Strategies for supplier incidents.
6) Stealthier attacks and longer dwell time
A) What is happening?
Many campaigns now use legitimate tools already within the environment to avoid noisy malware signatures. They blend into regular admin activity and wait for the right production window before triggering encryption.
B) Executive impact
Detection based on signatures or perimeter rules is insufficient for cybersecurity in the manufacturing industry. They need behavior based monitoring, anomaly detection, and automated containment as part of their cybersecurity solutions and Cybersecurity Best Practices.
7) Shift from backup thinking to resilience thinking
A) What is happening?
Executives are realizing that backups alone do not guarantee rapid recovery. If networks, identities, and applications are not designed for restart under pressure, recovery can still take days.
B) Executive impact
Modern cybersecurity for manufacturing programs emphasizes segmented architecture, immutable backups, pre tested recovery runbooks, and end to end drills. Veritis supports this shift with industrial grade cybersecurity services that align with current Cybersecurity Trends and deliver resilience that boards can measure and trust.
Useful link: How Are AI Automation Tools in Cybersecurity Transforming Enterprise Defense?
The Financial Impact of Cybercrime in Manufacturing
Cybercrime has become one of the most costly risks in manufacturing cybersecurity, with incidents often costing companies millions. Unlike other sectors, attacks disrupt physical operations, halt production lines, delay shipments, and damage equipment. These losses make the cybersecurity manufacturing industry one of the most financially vulnerable sectors.
For many organizations, the cost extends beyond recovery. Cyber threats to manufacturing industry environments can trigger supply chain disruptions, regulatory exposure, and long term intellectual property loss. This is why executives in the manufacturing industry now prioritize cybersecurity as a core business protection strategy.
Veritis helps manufacturers reduce these financial risks with industry focused cybersecurity solutions and cybersecurity services, supported by Cybersecurity Trends, Cybersecurity Best Practices, and proven Risk Mitigation Strategies that protect operations and revenue continuity.
Key Cybersecurity Measures for Manufacturing
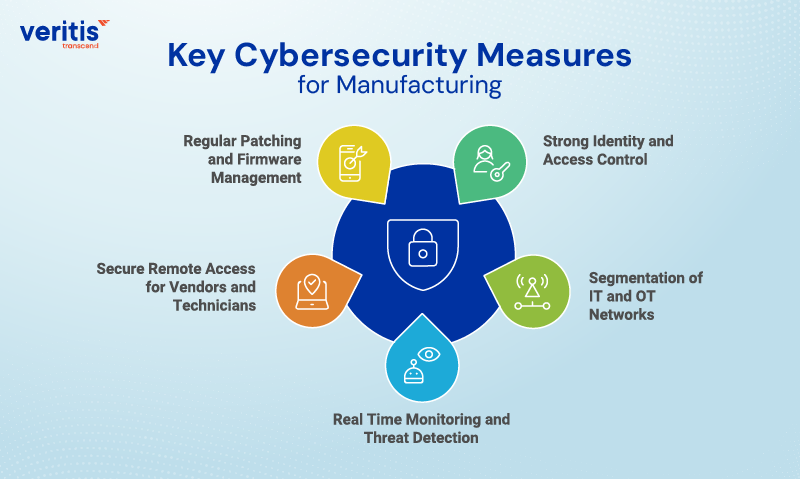
1) Strong Identity and Access Control
Limiting access to critical systems reduces the risk of unauthorized changes across production networks. This is essential for cybersecurity for manufacturing and protects both IT and OT environments.
2) Segmentation of IT and OT Networks
Separating plant systems from corporate networks prevents ransomware and other cyber threats from spreading across manufacturing facilities.
3) Real Time Monitoring and Threat Detection
Continuous visibility is a core requirement in the cybersecurity manufacturing industry. Modern analytics and behavioural tools help detect anomalies before they impact production.
4) Secure Remote Access for Vendors and Technicians
Manufacturers depend on suppliers and service partners. Controlled access and authentication help strengthen cybersecurity for the manufacturing industry and reduce supply chain risk.
5) Regular Patching and Firmware Management
Keeping industrial systems up to date prevents the exploitation of known vulnerabilities. This is a foundational cybersecurity solution and remains critical to the plant’s overall resilience.
Benefits of Cybersecurity for Manufacturing
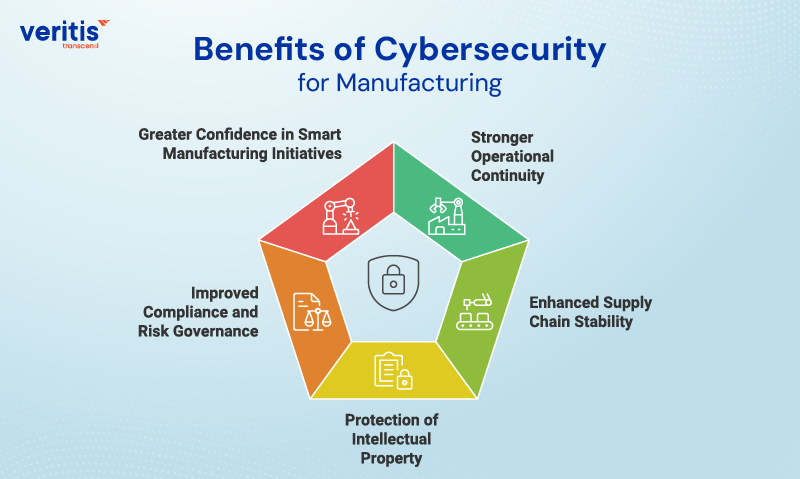
1) Stronger Operational Continuity
A) Protecting Production Uptime
Modern cybersecurity for manufacturing helps prevent attacks that halt machinery, disrupt workflows, or pause plant operations.
B) Reducing Costly Downtime
Executives gain confidence that operations can continue even when cyber threats rise, supporting predictable output and customer commitments.
2) Enhanced Supply Chain Stability
A) Securing Supplier Connectivity
With increased dependence on digital suppliers, strong cybersecurity for the manufacturing industry ensures safe data exchange and controlled vendor access.
B) Preventing Disruptions Across Networks
Protection extends across logistics, procurement, and distribution, reducing vulnerabilities exploited in cyber threats to manufacturing industry ecosystems.
3) Protection of Intellectual Property
A) Safeguarding Designs and Engineering Data
Manufacturers hold valuable formulas, blueprints, and proprietary processes. Cybersecurity for manufacturers prevents IP theft and competitive damage.
B) Blocking Espionage Attempts
Strong controls limit unauthorized access to innovation pipelines and sensitive R&D systems.
4) Improved Compliance and Risk Governance
A) Meeting Industry and Regulatory Standards
Effective programs align cybersecurity in manufacturing industry operations with strict safety, quality, and data protection standards.
B) Stronger Oversight for Executives
Leadership gains real time visibility into risks and can enforce consistent policies across facilities.
5) Greater Confidence in Smart Manufacturing Initiatives
A) Enabling Automation and Digital Investments
As plants adopt robotics, IoT, AI, and analytics, cybersecurity and manufacturing must advance in tandem to protect these new digital capabilities.
B) Supporting Scalable Innovation
Secure digital foundations allow organizations to accelerate modernization without compromising safety or uptime.
Challenges for Cybersecurity in Manufacturing
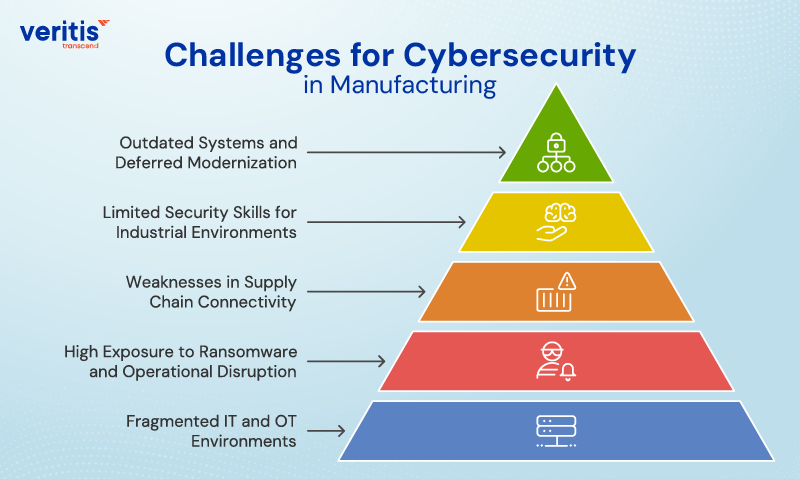
1) Fragmented IT and OT Environments
Manufacturers operate a mix of legacy controllers, modern platforms, sensors, and cloud enabled systems. This creates visibility gaps and increases the attack surface across plants.
Veritis Solution
Veritis unifies IT and OT security with an integrated architecture that centralizes monitoring, strengthens endpoint protection, and ensures seamless policy enforcement across production networks.
2) High Exposure to Ransomware and Operational Disruption
Ransomware targeting factories can halt production lines, disable equipment, and halt shipments, making it one of the most damaging cybersecurity risks for manufacturing.
Veritis Solution
Veritis deploys layered defenses, segmentation strategies, and rapid response automation to contain attacks before they reach critical OT assets, ensuring operational continuity.
3) Weaknesses in Supply Chain Connectivity
Vendors, contractors, and remote technicians often access plant systems, creating entry points for cyber threats to manufacturing industry operations.
Veritis Solution
Veritis secures all third party interactions through zero trust access controls, identity validation, and continuous monitoring to ensure secure collaboration across the supply chain.
4) Limited Security Skills for Industrial Environments
Most security teams are trained for IT systems, not for industrial protocols or plant floor technologies. This skill gap challenges effective cybersecurity for the manufacturing industry.
Veritis Solution
Veritis provides dedicated industrial cybersecurity expertise, assessments, and managed services that bring specialized skills directly into the client environment without increasing internal overhead.
5) Outdated Systems and Deferred Modernization
Many plants run legacy machines and firmware that cannot be easily patched or replaced, increasing the risk of compromise.
Veritis Solution
Veritis evaluates legacy equipment, develops compensating controls, and implements secure modernization pathways that strengthen protection without disrupting operations.
Useful link: Securing Digital Transactions: Addressing Unique Challenges for Cybersecurity in Banking IT
Investment and ROI Framework
Security investments should be framed as business enablers that protect revenue streams and ensure delivery reliability. The ROI is calculated by comparing the cost of protection against the staggering costs of a breach.
| Cost of Breach (The Risk) | Value of Prevention (The Investment) |
| Immediate Remediation: $4.88M to $10.22M | Operational Resilience: Guaranteed uptime |
| Downtime Losses: $1.3M to $2.73M | Competitive Advantage: Trusted Supplier status |
| Ransom Payments/Response: $1.3M to $2.73M | Regulatory Assurance: Avoidance of fines |
| Long term Reputation Damage: Incalculable | IP Protection: Safeguarding future revenue |
The Path Forward: Executive Action Plan
1) Immediate (0 to 90 Days)
- Risk Assessment: Conduct a comprehensive audit of OT/IT environments to identify “crown jewel” assets.
- Asset Inventory: develop an automated inventory of all connected devices.
- Incident Response: Establish and drill a cross functional incident response team.
- Quick Successes: Patch critical vulnerabilities and enforce MFA on all remote access points.
2) Short Term (90 to 180 Days)
- Control Deployment: Deploy endpoint protection and network monitoring tools tailored for OT.
- Vendor Management: Audit and secure all third party connections.
- Training: Launch role specific security awareness training for plant floor and office staff.
- Segmentation: Begin architectural planning for network segmentation (Purdue Model).
3) Strategic (6 to 12 Months)
- Transformation: Implement a complete Zero Trust architecture across the enterprise.
- Convergence: Formalize the merged governance structure for OT and IT security.
- Supply Chain: Enforce rigorous security standards for all upstream suppliers.
- Advanced Detection: Operationalize AI driven threat detection and automated response capabilities.
What Solutions Does Veritis Offer for Manufacturing Organizations?
1) Modern Industrial Cybersecurity Architecture
Veritis designs end to end security programs that unify IT and OT environments, strengthen identity controls, protect plant networks, and reduce operational exposure. This framework supports advanced cybersecurity for manufacturing and enables secure digital operations across all facilities.
2) Ransomware and Threat Resilience Programs
Manufacturing environments face increasing cyber threats to manufacturing industry operations. Veritis deploys layered defenses, segmentation, continuous monitoring, and rapid response capabilities to protect production lines and safeguard uptime.
3) Cloud Enabled Security for Smart Manufacturing
As manufacturers adopt automation, IoT, AI, and cloud connected machinery, Veritis delivers secure modernization strategies that support innovation while reinforcing cybersecurity for the manufacturing industry and long term operational resilience.
4) Supply Chain and Vendor Risk Protection
Veritis implements controls that secure supplier access, validate identities, monitor remote sessions, and protect data exchanges. This reduces third party vulnerabilities and strengthens the broader cybersecurity manufacturing industry ecosystem.
5) Managed Cybersecurity Services for Industrial Operations
Veritis provides comprehensive cybersecurity services that support ongoing monitoring, incident response, vulnerability management, and compliance. These managed programs integrate advanced cybersecurity solutions, cybersecurity trends, cybersecurity best practices, and risk mitigation strategies to ensure continuous protection for manufacturers.
Conclusion
The manufacturing sector is now operating in a wholly digital field, where production systems, supply chains, and smart equipment depend on reliable protection. As cyber threats intensify, leaders recognize that cybersecurity for manufacturing is not only a technology requirement but a foundation for operational excellence, revenue continuity, and long term competitiveness. Organizations that invest in modern, industry aligned defense programs are better equipped to navigate disruption and accelerate growth.
Veritis supports this transformation by delivering specialized cybersecurity solutions and services tailored to the cybersecurity manufacturing industry.
With Veritis as a strategic partner, manufacturing organizations gain the confidence to scale innovation, modernize securely, and protect every stage of their production environment. The future of the cybersecurity for the manufacturing industry belongs to those who build strong, intelligent, and resilient security foundations, and Veritis stands ready to lead that journey with precision and measurable impact.