Table of contents
Financial institutions have a long history spanning centuries, during which the banking domain has evolved significantly. Despite the transformative changes in banking practices, the fundamental principles have endured. Historically, banks have maintained extensive repositories of personal and financial data belonging to their clientele. In contemporary times, digitizing these records has made them more accessible, necessitating stringent cybersecurity in banking protocols to safeguard sensitive information.
The proliferation of financial technology (fintech) has spurred numerous advancements and transformations in the financial services cybersecurity sector over recent decades. Innovations such as wire transfers, credit/debit cards, online banking, and mobile payments have reshaped the industry. As a result, banks have had to upgrade their infrastructures to accommodate these innovations and revamp their operational processes to uphold security standards when integrating new technologies.
Protecting sensitive data and implementing robust security measures to thwart cyber threats like phishing and malware attacks have become paramount in the modern banking environment. Banks are tasked with the legal obligation of safeguarding customer information and fortifying defenses against cyber intrusions or unauthorized access. In this discourse, we will delve into the strategies adopted by contemporary banks and financial institutions to fulfill these regulatory and security imperatives.
The Rise of Digital Transactions
Digital transactions have revolutionized the banking industry, allowing customers to transfer funds, pay bills, and manage their finances with just a few clicks. While this has undoubtedly improved convenience and efficiency, new opportunities have emerged for cybercriminals to exploit cybersecurity weaknesses in banking IT systems.
Understanding the Cyber Threat Field
Cyberattacks in the banking sector come in various forms, including phishing attacks, malware, ransomware, and DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks. These risks can lead to monetary losses, harm to reputation, regulatory penalties for banks, and the possible exposure of sensitive customer information.
Useful Link: The Future of IT Financial Management: Trends and Innovations
Addressing Unique Challenges in Banking
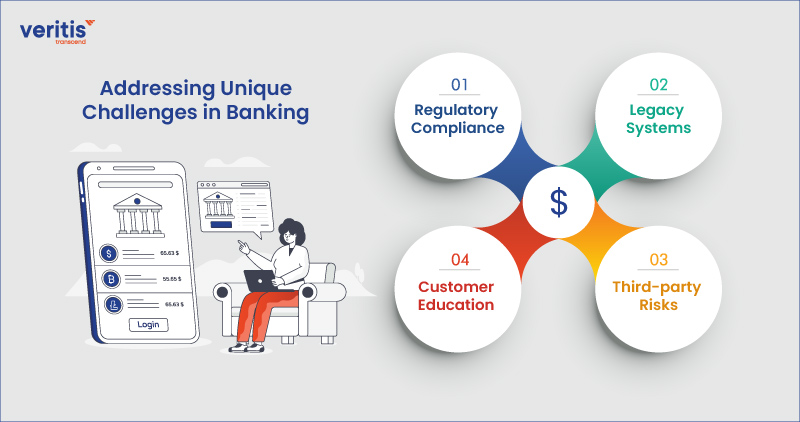
1) Regulatory Compliance
Banks must comply with stringent regulations, such as GDPR and PCI DSS, to ensure the security and privacy of customer data. Non-compliance can result in severe penalties, highlighting the importance of robust cyber security in banking measures.
2) Legacy Systems
Numerous banks rely on outdated IT systems, which may not have the essential security capabilities to withstand contemporary cyber threats. Retrofitting these systems with advanced security controls is crucial to protect against cyberattacks.
3) Third-party Risks
Banks often collaborate with third-party vendors for various services, introducing additional cybersecurity risks. To mitigate potential risks, it’s essential to vet these vendors thoroughly and ensure they adhere to stringent security standards.
4) Customer Education
Educating customers about cybersecurity best practices is paramount in safeguarding digital transactions. Banks must raise awareness about common threats like phishing scams and encourage customers to use multi-factor authentication and strong passwords.
Implementing Robust Security Measures in Banking
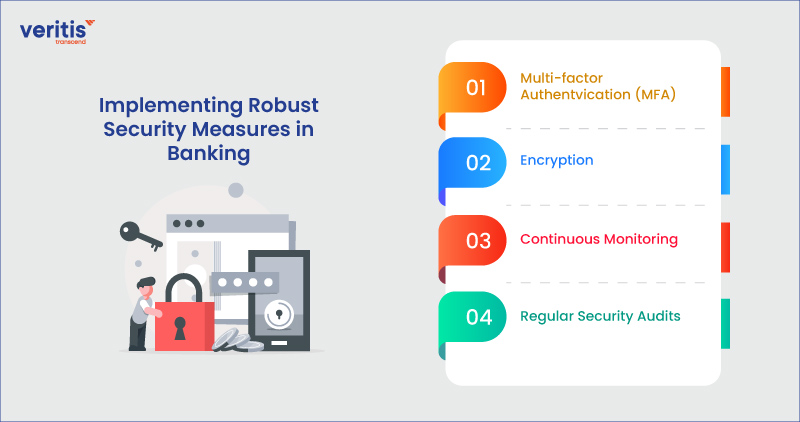
To reduce the cybersecurity risks related to digital transactions, banks can implement the following measures:
1) Multi-factor Authentication (MFA)
Introducing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) enhances security by mandating users to provide multiple verification methods before gaining access to their accounts.
2) Encryption
Encrypting sensitive data in transit and, at rest, protects it from unauthorized access. Robust encryption algorithms ensure that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable to unauthorized parties.
3) Continuous Monitoring
Financial institutions should utilize robust monitoring systems to identify and address cyber threats promptly in real-time. Automated alerts can help identify suspicious activities and mitigate potential breaches before they escalate.
4) Regular Security Audits
Regular security audits and penetration testing help proactively identify vulnerabilities in banking IT systems. Addressing these vulnerabilities strengthens the bank’s overall cybersecurity posture.
Useful Link: 8 Factors That Drive Digital Transformation in Banking Industry
5 Most Common Digital Payment Risks
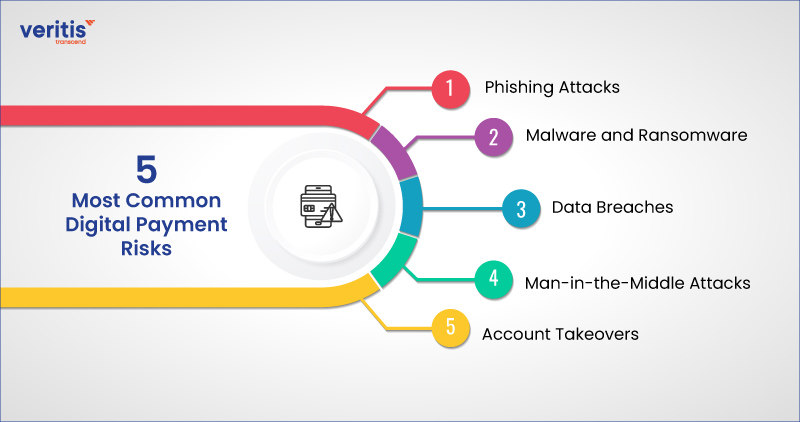
1) Phishing Attacks
Cybercriminals employ deceptive emails, messages, or websites to deceive users into disclosing sensitive data such as credit card numbers, personal identification, login credentials, and other details.
2) Malware and Ransomware
Malicious software installed on a user’s device can steal payment information, compromise security, or hold data for ransom, leading to financial cybersecurity loss or identity theft.
3) Data Breaches
Unauthorized access to a company’s database or payment processing system can result in the theft of sensitive customer information, including credit card numbers, names, and addresses, leading to potential fraud and financial losses.
4) Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
Hackers intercept communications between users and the payment gateway, allowing them to eavesdrop on sensitive information or modify transaction details, leading to unauthorized payments or identity theft.
5) Account Takeovers
Cybercriminals achieve unauthorized entry into a user’s account through stolen credentials brute-force attacks, enabling them to make fraudulent transactions or steal personal information.
Addressing these risks requires robust cybersecurity measures, including encryption, multi-factor authentication, regular security updates, employee training, and adherence to industry regulations and best practices. Moreover, users should remain vigilant, avoid sharing sensitive information with untrusted sources, and monitor their accounts for suspicious activity.
Useful Link: The Rise of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Financial Decision Making Processes
Use Cases for Cybersecurity in Action
1) Phishing Prevention
A bank implements an email filtering system that identifies and blocks phishing attempts targeting customers. The system can detect suspicious email patterns through machine learning algorithms and prevent fraudulent emails from reaching customers’ inboxes, safeguarding them against phishing scams to steal their login credentials.
2) Transaction Monitoring
A bank utilizes real-time transaction monitoring software to detect unusual customer account activity. When the system identifies potentially fraudulent transactions, such as large transfers to unfamiliar accounts or unusual spending patterns, it automatically triggers alerts for further investigation by the bank’s security team, helping to prevent financial cybersecurity losses due to unauthorized transactions.
3) Endpoint Security
A bank deploys endpoint security solutions across all employees’ devices, including desktops, laptops, and mobile devices. These solutions include antivirus software, firewalls, and endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools that protect against malware, ransomware, and other cyber threats. By securing endpoints, bank information security mitigates the risk of cyberattacks targeting employee devices, which could compromise sensitive banking information.
4) Secure Mobile Banking
A bank develops a mobile banking application with robust security features, such as biometric authentication (e.g., fingerprint or facial recognition) and secure payment systems data-transmission encryption protocols. This ensures that customers can securely access their accounts and perform transactions from their smartphones or tablets without fear of unauthorized access or data breaches.
5) Vendor Risk Management
A bank establishes a comprehensive vendor risk management program to assess the cybersecurity posture of third-party vendors and service providers. Through regular security assessments, audits, and contractual obligations, the bank’s information security guarantees that its vendors follow strict security standards and meet regulatory requirements, thereby reducing the risk of cyber threats arising from third-party relationships.
6) Incident Response Planning
A bank develops and regularly updates an incident response plan to mitigate and respond effectively to cybersecurity incidents in financial services. This plan includes predefined procedures for identifying, containing, and addressing security breaches, as well as establishing communication protocols to inform customers, regulators, and other stakeholders in case of a data breach or cyberattack.
7) Continuous Security Training
The bank organizes for employees and cybersecurity in financial services training sessions for its employees to educate them on new threats, phishing techniques, and effective methods for protecting sensitive information. By enhancing awareness and nurturing a culture of cybersecurity vigilance among staff, the bank minimizes the risk of human errors that could result in security breaches or data leaks.
8) Cloud Security
A bank migrates its infrastructure and services to cloud-based platforms while implementing robust cloud security measures, such as data encryption, access controls, and real-time monitoring. By leveraging the scalability and flexibility of cloud computing while maintaining stringent security standards, bank data security guarantees the confidentiality and integrity of customer data stored in the cloud.
These use cases demonstrate how banks can address the unique cybersecurity challenges inherent in digital transactions through technological solutions, proactive security measures, and ongoing risk management efforts. Banks’ IT security can protect their customers, preserve trust, and safeguard the integrity of the financial services cybersecurity system by prioritizing cybersecurity across all operations.
Useful Link: 5 Key Benefits of Implementing Cloud Financial Services for Your Business
Benefits of Cybersecurity in Digital Banking
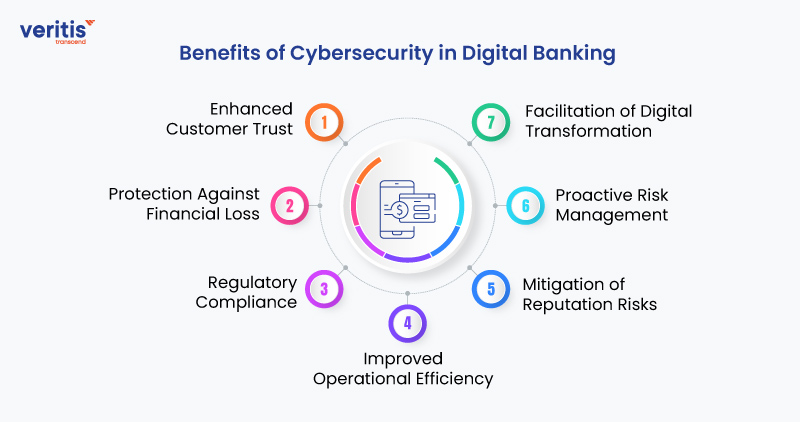
1) Enhanced Customer Trust
By implementing robust cybersecurity measures, banks can assure customers that their digital transactions are safe and secure payment systems, fostering trust and confidence in the banking institution.
2) Protection Against Financial Loss
Adequate cybersecurity safeguards mitigate the risk of financial losses resulting from fraudulent transactions, data breaches, or cyberattacks, safeguarding bank data security and its customers from potential monetary harm.
3) Regulatory Compliance
Following cybersecurity best practices helps banks meet regulatory standards and industry norms, decreasing the chances of facing regulatory fines or penalties due to non-compliance.
4) Improved Operational Efficiency
Secure online banking systems streamline operations by automating security processes, such as real-time transaction monitoring and threat detection. This allows banks to focus resources on delivering superior customer service and innovation.
5) Mitigation of Reputation Risks
By protecting customer data and preventing security incidents, banks safeguard their reputation and brand image, avoiding negative publicity or loss of trust that could arise from cybersecurity breaches.
6) Proactive Risk Management
Cybersecurity measures enable banks to proactively identify and address potential risks and vulnerabilities, minimizing the likelihood of security incidents and their associated impacts on business continuity and operations.
7) Facilitation of Digital Transformation
A robust cybersecurity framework enables banks to confidently embrace digital transformation initiatives, leveraging innovative technologies and services to meet evolving customer demands while maintaining the security and integrity of digital transactions.
Conclusion
Securing digital transactions in banking IT demands a proactive and comprehensive approach to addressing the industry’s unique cybersecurity challenges. By implementing robust security measures, adhering to regulatory requirements, and fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness, banks can effectively protect their customers’ assets and maintain trust in an increasingly digital world. As technology evolves, banks must stay one step ahead of cyber threats by continually updating and enhancing their cybersecurity strategies.
Veritis, a recipient of prestigious awards such as the Stevie and Globee Business Awards, offers cutting-edge solutions to bolster cybersecurity in banking IT. With a proven track record of excellence, Veritis provides innovative services and expertise to help banks strengthen their defenses against cyber attacks and protect their digital transactions. By partnering with industry leaders like Veritis, banks can enhance their cybersecurity posture and mitigate risks in an ever-changing digital field.
Looking for Support? Schedule A Call
Also Read:
- Impact of Information Technology on the Financial Industry
- DevOps Adoption in Financial Services Industry
- The Future of IT Financial Management: Trends and Innovations
- AI and Cybersecurity: Defending Against Evolving Threats
- AIOps Use Cases: How Artificial Intelligence is Reshaping IT Management
- Overcoming Challenges: Implementing Generative AI in Healthcare