Azure Cloud Migration Services
Migration to the Cloud is today’s most happening trend in the IT industry, mostly due to rapid digital transformation. The trend is finding its scope all across, irrespective of the size of an organization. But the real question that continues to haunt many is, ‘Which is the best cloud option?’
In this article, we will see migration to Azure Cloud! Migrating to Microsoft’s Azure is the most sought-after option for many firms facing challenges with the on-premises infrastructure.
Cloud migration is a major trend, and Azure remains a top contender. IDC FutureScape states that cloud migration is a major driver of cloud spending, expected to reach USD 1 trillion globally in 2024.
Azure is preferred as one of the leading cloud platforms because of its services, which include Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). However, migrating to Azure migration needs precise planning followed by a four-step approach.
Step-by-Step Azure Cloud Migration Strategy
The first and foremost thing for a successful Azure migration is developing your ‘Own Azure Migration Strategy.’ Then comes the following:
Step 1: Assess
This step’s success is built on the Discovery, Mapping, and Evaluation of on-premise applications.
- Discover: Use cloud migration assessment tools and compile the inventory of your existing physical and virtual servers in the existing environment, which should also include information on the performance of your applications. The end of this step keeps you ready with information about servers and their metadata, thus helping you proceed with your cloud migration strategy.
- Map: Map your servers according to their suitability for on-premises applications and group them accordingly to represent their relevant applications. This helps you get a complete idea of those applications and their dependencies on each other.
- Evaluate: Now that you have grouped applications, it’s time to check what migration strategy suits them. This requires cloud migration assessment tools to learn Azure recommendations and migration strategies. Then, evaluate the cost factor and choose the one that suits you.
Step 2: Migrate
This step includes adopting four sub-steps: Rehost, Refactor, Rearchitect, and Rebuild.
- Rehost: Move your applications to Azure migrations as they are without needing any changes to the code. This is often termed a ‘lift-shift’ migration. But ensure the applications you move don’t require additional code changes and directly go for orchestration only in the Azure platform.
- Refactor: In this step, you make small changes to the application design but not the code. The application will later use Azure’s IaaS and PaaS benefits.
- Rearchitect: This step involves changing the application codebase to make it fit in the cloud, which can modernize, modify, or make it scalable and deployable.
- Rebuild: This step involves rebuilding an application using cloud-native applications, the service Azure PaaS offers.
Step 3: Optimize
Again, this is a three-step process involving analysis, saving, and reinvesting.
- Analyze: Use Azure Cost Management and analyze your cloud spending more efficiently with accuracy and extended transparency. This can help you plan your investment further!
- Save: Deal effectively with your migrated environment to fit in workloads using Azure’s unique offerings, such as Azure Hybrid Benefit and Azure Reserved Virtual Machine Instances.
- Re-Invest: Enjoy the flexibility that Azure migration steps offer to modify, secure, or make advancements to your migrated and existing workloads, turning that into savings.
Step 4: Secure and Manage
Safeguard your data and applications with Azure’s Secure, Data Protection, and Monitoring options.
- Secure: Get Azure Security Center for effective cloud security management and advanced threat protection for your cloud workloads. Azure Security offers additional protection, giving you complete visibility and control over cloud applications’ security and increased threat detection and recovery rates.
- Protect Data: Backing up apps in Azure protects your data from potential security threats, avoiding additional costs and business disruptions while ensuring compliance.
- Monitor: Azure Monitor helps you easily monitor and track the health of your cloud data, apps, and other infrastructure, providing the right insights and analytics.
Azure has been increasing in popularity for its effective options in the proper budgets. As the statistics show, Azure accounts for around 30 percent of the overall cloud market and 17% of the IaaS and PaaS market shares.
Useful Link: How Does Cloud Computing Help Fintech?
Four Azure Migration Alternate Strategies

For successful infrastructure migration to Microsoft Azure, the enterprises will need a migration strategy that addresses their organizational requirements.
The following are the foremost strategies for migrating an application to the Azure Cloud migration services:
1) Lift-Shift Policy: In this strategy, the applications from the on-premise platform are migrated to the cloud without impacting the underlying application settings. It is suitable for legacy migrations, and teams with limited Cloud computing and Azure skills can leverage this strategy.
- Pros: This strategy allows users to migrate to Azure easily and with fewer application breakdown issues.
- Cons: The application may not leverage the Cloud resources to the fullest.
2) Subjective to Code Changes: This strategy involves some changes only to the application code, leaving other significant aspects. Users can leverage the benefits of IaaS and PaaS derivatives such as Azure App Service, Azure Functions, and Azure SQL Database Managed containers. This is suitable for firms where application portability is a concern.
- Pros: This is a quick way to improve your infrastructure.
- Cons: It is not feasible to make significant alterations to the infrastructure.
3) Architecture Revamp: This approach involves modifying, optimizing, and deploying apps (that demand high agility, scalability, and resilience) to the Cloud platform.
- Pros: Allows you to reach scalability requirements cost-effectively. New applications can leverage Azure capabilities. Improved Agility.
- Cons: Complex, expensive, and migration involves a high risk of faults and service disruption.
4) Restructure: This approach involves redeveloping applications from scratch using cloud-based technologies, such as Azure PaaS. The firm can then avail of complete development and deployment services. This strategy suits applications with limited functionality and lifespan, slowing down business processes.
- Pros: No expense and complexity of software licenses, middleware, and existing resources.
- Cons: The level of functionalities in custom-made apps will be decreased.
Even after choosing the most beneficial strategy, you might encounter the following challenges during your cloud migration journey. Let’s have a glance!
Useful Link: 5 Reasons for successful On-Premises to the Cloud Migration
Azure Migration Challenges and Ways to Overcome Them:

1) A Paradigm Shift: The primary challenge during Azure migration services is a misunderstanding of the concepts of a cloud platform and on-premise systems. Before starting the lift and shift migration process, the management should train their teams with Azure’s unique attributes and prepare them for a paradigm shift in the Cloud platform.
2) Provisioning Local Bandwidth: When migrating to an Azure platform, the firm should calculate the required local bandwidth capacity beforehand. In the case of a hybrid cloud platform, the firm should acknowledge that traffic that previously ran over high-speed, low-latency LAN will run over the WAN. So, one should create enough local bandwidth.
3) Migration Downtime: Downtime is inevitable during the Cloud migration journey. Therefore, firms should strategically plan each step of lift and shift migration so that downtime has minimal impact.
4) Underlying Dependencies: As almost all applications are interdependent, the dependencies should be taken care of when migrating applications to the Cloud platform. These configuration connections should be determined beforehand to prevent service interruptions.
5) Security Concerns: The fear of losing confidential data and security breaches is the prime concern while moving the infrastructure and software to a Cloud platform. So, the firms must deploy security protocols and implement a virtual private network with end-to-end encryption.
6) Application Compatibility: Before initiating the Cloud migration process, the firms should ensure that applications, apart from databases, are compatible with the Cloud environment. The applications should be deployed into the Azure test environment and tested for compatibility.
7) Dealing Adversity: Hefty data loss or application errors during Azure Cloud migration are unlikely to occur. However, it is essential to have a robust resilience plan in hand. Know unique disaster scenarios adequately during cloud migration and plan accordingly.
Useful Link: The Successful Migration of a Services Firm from SailPoint to Azure AD
Azure Migration Tools

Below are the commonly utilized Microsoft Azure migration tools essential for ensuring a smooth migration process.
1) Azure Migrate
This tool is a comprehensive solution that enables organizations to monitor, manage, and execute all necessary tasks associated with migrating their workloads to Azure migrations. It provides a centralized platform for planning and executing migrations, ensuring a smooth transition to the cloud.
2) Azure Data Box
Designed for data lift and shift migration scenarios where traditional methods are impractical due to limited network availability or time constraints, Azure Data Box offers a protected and efficient way to transfer large volumes of data to Azure migrations. It provides physical devices that can be shipped to the data center for offline data transfer, ensuring data security throughout the process.
3) Azure Database Migration Service
This service simplifies the process of migrating on-premises databases to Azure. Its self-guided interface and easy-to-follow steps enable organizations to seamlessly migrate to Azure’s databases while minimizing downtime and ensuring data consistency.
4) Data Migration Assistant (DMA)
DMA is a tool specifically designed to analyze on-premises SQL servers and identify any compatibility issues or errors that may arise during migration. By conducting thorough assessments, DMA helps organizations address potential challenges proactively, ensuring a smooth and efficient migration process.
5) SQL Server Migration Assistant
This tool assists organizations in migrating their data to SQL Server or Azure Synapse Analytics. Providing guidance and tools for schema and data migration simplifies transitioning databases to Microsoft’s cloud-based platforms, enabling organizations to take advantage of cloud computing while minimizing disruptions to their operations.
Summary
Underestimating the planning scope and requisites will cause severe issues and disrupt the business process when migrating to Azure Cloud migration services. So, the key takeaway is to prepare yourself adequately before embarking on the Cloud migration strategy process.
Useful Link: Which AWS Cloud Management Tools Should You Use to Manage Your Business
Azure Cloud Migration Benefits
Migrating to the Azure cloud platform offers you key business benefits such as:

- High productivity
- Enhanced scalability
- Increased availability
- Faster disaster recovery
- Effective backup storage
- Advanced data security
- Reduced costs
AWS vs Azure vs GCP – A Breakdown of Cloud Migration Services
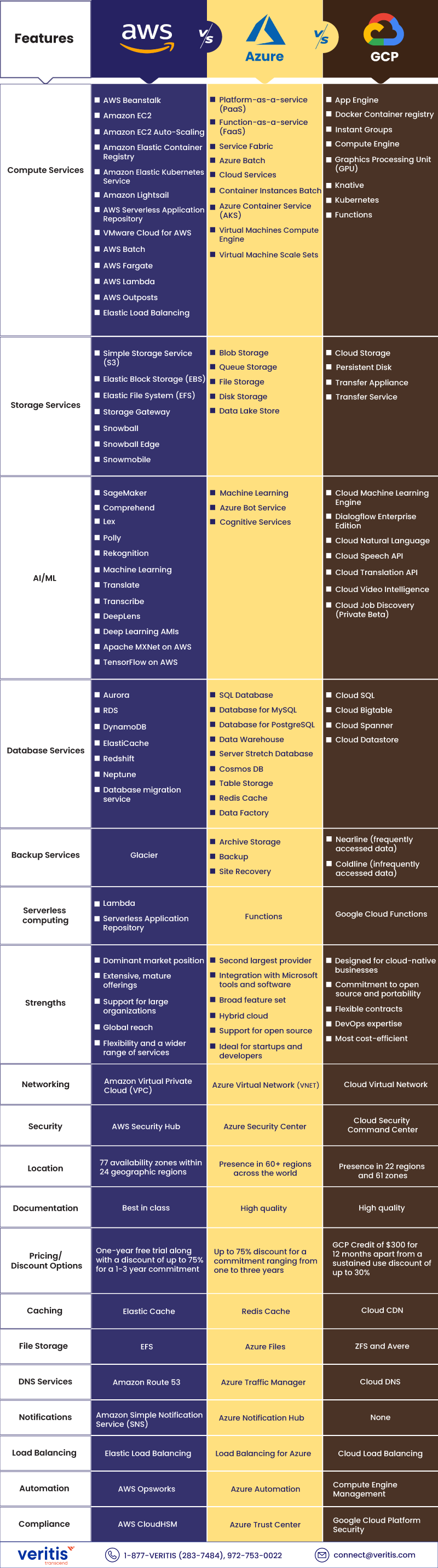
Conclusion
Migrating to Azure Cloud offers numerous benefits, such as increased productivity, scalability, availability, disaster recovery, data security, and cost reduction. However, to ensure a successful migration, it is crucial to understand and address the challenges that may arise, such as paradigm shifts, bandwidth provisioning, migration downtime, underlying dependencies, security concerns, application compatibility, and resilience planning. By following a well-defined strategy and leveraging the right tools and services provided by Microsoft Azure, firms can navigate these challenges and unlock the full potential of cloud computing.
With the assistance of experienced Azure cloud consulting experts like Veritis, the Stevie and Globee Business Awards winner, businesses can effectively plan and execute their migration process, aligning with their goals and budgetary constraints. Veritis offers comprehensive cloud migration support tailored to each client’s requirements, ensuring a smooth transition to the Azure cloud platform.
Similar Articles:

