
Thanks to the CI/CD environment and essential tools, creating and delivering software has become remarkably efficient in our rapidly changing digital landscape. However, amidst the seamless code integration facilitated by these CI/CD tools, we must recognize a crucial factor: CI/CD security best practices.
It highlights the vital task of fortifying your CI/CD environment against cyber threats. As technology advances, so do the tactics used by malicious actors seeking vulnerabilities in your software. Our journey takes us from continuous integration tools that merge code from various sources to continuous delivery tools that deliver that code to its destination. We’ll explore CI/CD pipeline security best practices to protect your CI/CD environment from these threats, ensuring your software remains fast and secure while adhering to proven continuous integration and deployment best practices.
The term CI/CD pipeline refers to a set of steps that include Continuous Integration (CI) and either Continuous Deployment (CD) or Continuous Delivery (CD). Typically used by DevOps teams, the CI/CD pipeline is an efficient approach for building, testing, and deploying code, primarily leveraging automation tools aligned with continuous integration and deployment best practices.
Leveraging a CI/CD pipeline has consistently streamlined the process of creating and deploying software updates, ultimately resulting in higher quality updates. This success is primarily due to ongoing collaboration and the consistent application of Agile and DevOps principles, along with CI/CD pipeline security best practices, to maintain robust tools and a secure CI/CD environment.
Let’s embark on this journey to bolster your CI/CD environment, where code integration meets CI/CD security best practices. Adhering to best practices for CI/CD pipeline security helps ensure your CI/CD environment remains resilient against evolving threats and supports reliable, secure software delivery.
Importance of CI/CD?
CI/CD is a methodology that enables DevOps teams to deliver code updates consistently and swiftly in a modern CI/CD environment. It accomplishes this by leveraging continuous integration (CI) and continuous delivery (CD) principles aligned with CI/CD best practices. At their core, CI/CD tools emphasize automating every stage of the development process, including building, testing, and deploying code within the CI/CD environment.
This automation supersedes manual processes in traditional development, enabling more frequent, faster code releases that are notably free of common issues, including bugs and security vulnerabilities. By adhering to CI/CD security best practices, teams can ensure robust workflows while proactively addressing CI/CD security concerns. Many organizations partner with DevOps consulting services to implement CI/CD pipeline security best practices, ensuring scalable automation and compliance across the CI/CD environment.
Useful Link: All You Need to Know About Kubernetes Deployment Strategies
What Are Continuous Integration (CI), Continuous Delivery (CD), and Continuous Deployment?
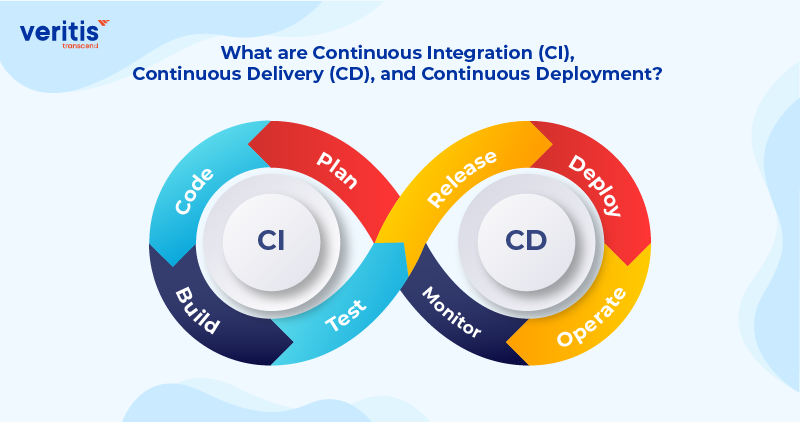
Continuous Integration (CI)
Continuous integration (CI) is a software development approach in which code changes are integrated into a shared code repository within a CI/CD environment. These changes are automatically tested as soon as they’re added. Unlike traditional methods, which test code only after development is complete, CI tests code as developers write it, aligning closely with continuous integration and deployment best practices.
The significant advantage of CI is that it reduces risks. Your team always knows where they stand in their work. They can quickly spot what’s working and what’s not, identify and fix bugs early, and understand what their team members are up to. By adhering to CI/CD security best practices and implementing best practices for CI/CD pipeline security, code conflicts are less likely because different developers’ work is regularly combined. This approach enhances collaboration and strengthens CI/CD pipeline security best practices, ensuring a safer, more efficient CI/CD environment and effectively addressing CI/CD security concerns.
Continuous Delivery (CD)
Continuous delivery, an extension of continuous integration, means your team automatically deploys new code to a repository like GitHub within the CI/CD environment. Depending on your and your users’ needs, this code can be deployed to the live website or app at any time, following proven continuous integration and deployment best practices.
The key advantage is that continuous delivery relies heavily on automation to simplify the release process. It reduces manual intervention during code implementation, accelerating delivery and making it more predictable. With continuous delivery, teams can react more quickly to market changes or emerging CI/CD security risks by applying CI/CD pipeline security best practices.
However, to ensure your CI/CD environment runs smoothly, you’ll need reliable server infrastructure and robust tooling. Your DevOps CI/CD team must also adapt from manual to automated testing workflows. By following CI/CD security best practices and best practices for CI/CD pipeline security, teams ensure automated delivery remains efficient, compliant, and secure while addressing CI/CD security concerns.
Continuous Deployment (CD)
Continuous deployment is the most advanced stage in a CI/CD environment. It differs from continuous delivery by automatically pushing every validated code change directly into production without manual approval.
For continuous deployment tools to operate reliably, extensive automated testing is critical. Because the manual review step is removed, firm adherence to CI/CD security best practices and CI/CD pipeline security best practices is essential. This ensures the deployment process remains secure, efficient, and resilient while addressing CI/CD security risks proactively.
Like continuous delivery and continuous integration, continuous deployment requires upfront investment in tooling and automation. However, the return is immediate user feedback and minimal delay between development and production. Maintaining a secure CI/CD environment through continuous integration and deployment best practices enables teams to streamline releases while preserving security and operational stability.
What is CI/CD Pipeline?
Think of the CI/CD pipeline as a series of steps that ensure your software is always up to date and working well. This pipeline forms the foundation of your DevOps team’s work in a modern CI/CD environment. Usually, your DevOps continuous integration team’s leader ensures these steps run smoothly by following continuous integration and deployment best practices while addressing critical CI/CD security concerns.
Components of a CI/CD Pipeline
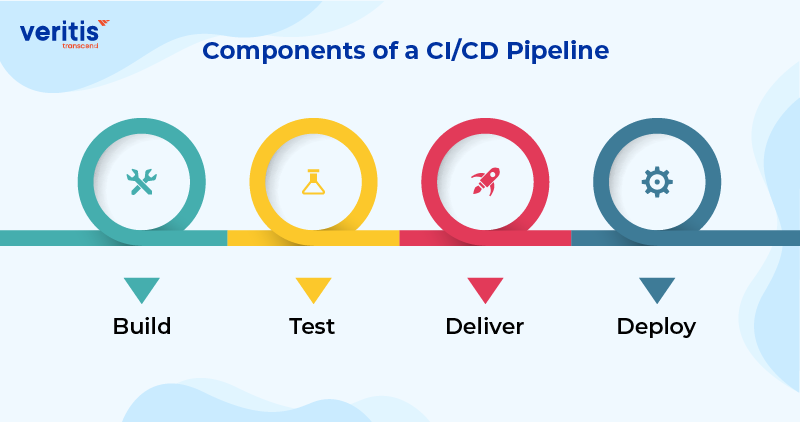
Every CI/CD pipeline is uniquely designed to suit a team’s tools, workflows, and business needs. However, most pipelines share four essential stages that support CI/CD pipeline security best practices and overall delivery efficiency.
1) Build
This is where you transform your source code into a functional software application. Imagine it like assembling a puzzle. Ensuring the build stage aligns with CI/CD security best practices and best practices for CI/CD pipeline security is vital to maintaining a secure and reliable CI/CD environment.
2) Test
Testing occurs within the continuous delivery pipeline and verifies that all components function as expected. It’s similar to checking whether every part of a machine functions correctly. Teams run unit tests to confirm new features work and regression tests to ensure existing functionality remains intact. This stage plays a crucial role in strengthening CI/CD pipeline security best practices by identifying bugs and vulnerabilities early in the CI/CD environment.
3) Deliver
After testing, the software is moved to a staging or review environment for close evaluation before broad release. This step is similar to launching a product in a limited market before full rollout. It allows Quality Assurance teams to validate quality and security, ensuring the CI/CD environment remains stable, compliant, and aligned with CI/CD security best practices.
4) Deploy
Once the software passes all validation checks, it is ready for production. With continuous delivery, a final manual review occurs before release. In continuous deployment, updates are released automatically. Regardless of the approach, implementing CI/CD security best practices and best practices for CI/CD pipeline security at this stage ensures a smooth, secure, and reliable release within the CI/CD environment.
By incorporating continuous integration and deployment (CI/CD) pipeline security best practices and overall CI/CD security best practices into each of these four stages, DevOps teams ensure their CI/CD environment remains efficient, secure, and capable of consistently delivering high quality software.
Useful Link: CI/CD Pipeline: 15 Best Practices for Successful Test Automation
Implementation Benefits of CI/CD
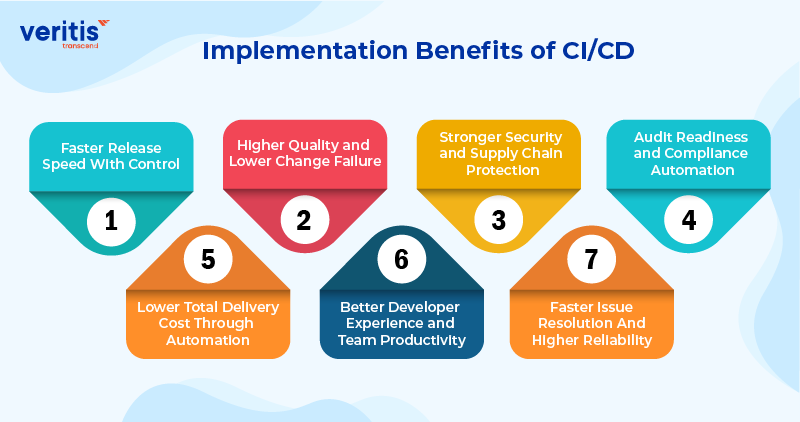
Implementing a CI/CD pipeline offers several advantages to companies and organizations:
1) Faster Release Speed With Control
A well designed CI/CD environment reduces friction from commit to production by automating build, test, and release workflows using continuous integration and deployment best practices. Faster delivery is valuable only when it remains predictable and secure, which is why CI/CD pipeline security best practices must run in line, not after deployment.
2) Higher Quality and Lower Change Failure
CI/CD improves quality by catching defects earlier and reducing the “blast radius” through more minor, more frequent changes. When teams standardize gates, testing, and approvals, they reduce rework and production issues, thereby improving stability metrics such as change failure rate and recovery time.
3) Stronger Security and Supply Chain Protection
A modern benefit is security outcomes. Embedding CI/CD security best practices directly into the pipeline (SAST, dependency checks, IaC scanning, secrets detection, signed artifacts) materially reduces exposure and strengthens the software supply chain. This is now central to best practices for CI/CD pipeline security and not optional for regulated industries.
4) Audit Readiness and Compliance Automation
CI/CD streamlines compliance by producing consistent evidence: versioned configurations, traceable approvals, repeatable deployments, and policy enforcement as code. In 2026, executives value pipelines that consistently demonstrate controls, mainly when CI/CD pipeline security best practices include identity and access hardening and robust secrets management across the CI/CD environment.
5) Lower Total Delivery Cost Through Automation
CI/CD reduces cost by minimizing manual effort, shortening release cycles, and lowering incident overhead through earlier detection and faster remediation. When you apply continuous integration and deployment best practices and standardize reusable templates, you reduce duplicated engineering effort and improve operational efficiency across teams.
6) Better Developer Experience and Team Productivity
A strong CI/CD environment removes bottlenecks. Developers spend less time waiting on environments, approvals, and manual releases, and more time shipping improvements. In practice, this means faster onboarding, consistent workflows, fewer “works on my machine” issues, and better collaboration, especially when CI/CD security best practices are automated rather than enforced through late stage reviews.
7) Faster Issue Resolution And Higher Reliability
CI/CD enables rapid rollback, progressive delivery, and smaller change sets, reducing MTTR and the impact of downtime. This aligns directly with modern performance measurement frameworks used by executives to balance delivery speed with operational resilience.
Useful Link: DevSecOps Implemention : Enhancing Security for an Energy Services Firm
Best Practices for CI/CD Pipeline Security
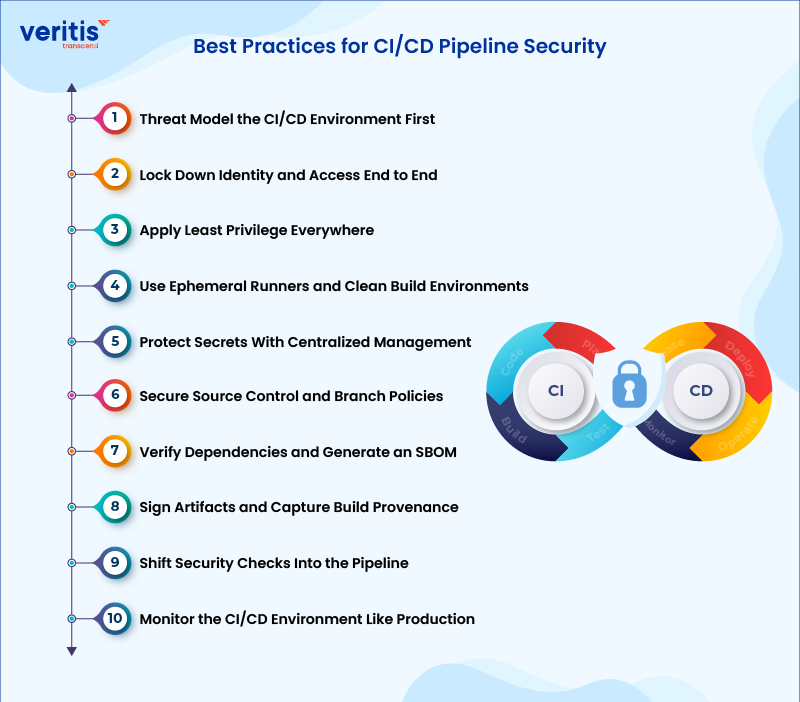
Put these CI/CD security best practices into action to protect your CI/CD environment, reduce supply chain risk, and operationalize DevSecOps.
1) Threat Model the CI/CD Environment First
Identify where the CI/CD environment touches external services, plugins, runners, registries, and secrets. Treat each integration as a trust boundary, document risks, and keep security verification steps versioned and repeatable.
2) Lock Down Identity and Access End to End
Enforce strong authentication for human and machine identities to prevent non human access. Apply role based access controls, require MFA where possible, and continuously review permissions as part of best practices for CI/CD pipeline security.
3) Apply Least Privilege Everywhere
Grant only the minimum permissions required for each pipeline job, runner, and service account. Reduce standing access, rotate credentials, and regularly verify that permissions align with current responsibilities.
4) Use Ephemeral Runners and Clean Build Environments
Prefer short lived runners and disposable build agents so credentials, tokens, and artifacts are not reused across jobs. This is a core component of modern CI/CD pipeline security best practices because it reduces opportunities for persistence and lateral movement.
5) Protect Secrets With Centralized Management
Keep secrets out of code, logs, and build output. Use a secrets manager, short lived tokens, and strict access policies. This is one of the most essential CI/CD security best practices for preventing accidental exposure in the CI/CD environment while optimizing your DevSecOps practices.
6) Secure Source Control and Branch Policies
Harden Git workflows with strong branch protections, required reviews, and controlled write access. Limit who can modify pipeline definitions, because pipeline as code is production control. This supports continuous integration and deployment best practices and reduces the risk of CI/CD tampering.
7) Verify Dependencies and Generate an SBOM
Pin dependencies, scan for known vulnerabilities, and maintain a software bill of materials. This is now central to best practices for CI/CD pipeline security because dependency compromise is a top supply chain risk.
8) Sign Artifacts and Capture Build Provenance
Implement artifact signing and provenance attestations to prove what was built, from what source, and by which pipeline. This aligns with SLSA style controls and is a leading 2026 direction for CI/CD pipeline security best practices.
9) Shift Security Checks Into the Pipeline
Run SAST, dependency scanning, container scanning, and IaC scanning inside the pipeline with clear pass fail rules. Automating these checks is a practical way to enforce CI/CD security best practices without slowing delivery.
10) Monitor the CI/CD Environment Like Production
Log pipeline activity, alert on unusual behavior, and protect audit trails. Treat the CI/CD environment as a high value target and ensure detection and response coverage match its impact.
Useful Link: Achieving Continuous Application Security with DevSecOps
Conclusion
Integrating DevSecOps into a development pipeline can be challenging, especially for teams new to this approach in a modern CI/CD environment. Without a well planned adoption strategy, internal friction may arise. Start by breaking down the adoption process into manageable steps. This enables teams to become familiar with DevSecOps tools and practices while applying continuous integration and deployment best practices, fostering a gradual, sustainable shift in team culture.
At Veritis, a recognized recipient of prestigious awards such as the Stevie and Globee Business Awards, we’ve helped organizations establish robust DevSecOps strategies aligned with CI/CD security best practices. As a trusted DevOps consulting company, we focus on efficiency and productivity by using automation and proven CI/CD pipeline security best practices to integrate security seamlessly into the development pipeline. Whether you’re in the planning phase or navigating tool selection, we help streamline DevSecOps adoption by applying best practices for CI/CD pipeline security, ensuring alignment with your CI/CD practices, and strengthening the overall CI/CD environment.
Looking for Support? Schedule A Call
Additional Resources:
- Demystifying MLOps vs DevOps: Understanding the Key Differences
- AIOPS Solutions: Enhancing DevOps with Intelligent Automation for Optimized IT Operations
- DevSecOps Implemention : Enhancing Security for an Energy Services Firm
- Building a High Performing DevOps Culture: Strategies and Best Practices for CEOs and CTOs
- Future of DevOps: Top DevOps Trends in 2025 and Beyond
- DevOps outsourcing: Things to Know About Before Getting Started
- Explained: Pros and Cons of DevOps Methodology and its Principles