
A robust and dependable IT system is essential in today’s fast changing business world. As the Chief Information Officer (CIO), it’s your job to create and manage this system. It should handle problems, adjust to changes, and help your organization achieve its goals.
Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery (BCDR) planning involves creating strategies, policies, and procedures to help an organization respond, adapt, keep working, and recover when something terrible happens.
Business continuity means keeping things going as usual when things aren’t going well. Disaster recovery involves fixing technology and systems quickly after a problem. Both are important for ensuring an organization can keep working.
BCDR is even more critical because organizations face many problems that can’t always be avoided. However, with a good plan for disaster recovery and business continuity, an organization can continue operating despite all kinds of issues. These include power cuts, system issues, natural disasters, and supply chain issues.
What is a Business Continuity Plan and Disaster Recovery?
An organization’s ability to keep working when things go wrong depends on two processes: Business Continuity (BC) and Disaster Recovery (DR). BCDR aims to ensure that the organization can return to normal if something unexpected happens. These processes also help keep significant data disaster recovery safe and reduce the chances of big problems, which can protect and even enhance the organization’s reputation.
Using the BCDR framework highlights the growing awareness that business and technology leaders should collaborate closely. When planning how to respond to incidents, this collaborative approach is more effective than creating separate plans in isolation. Cloud DR solutions have become an integral part of BCDR strategies, offering flexible, scalable, and efficient ways to ensure business continuity and minimize downtime during crises.
Useful link: 8 Best Business Continuity Management Software Solutions
Why is Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery (BCDR) Important?
The primary role of BCDR is to minimize the impact of outages and disruptions on business operations. These practices are instrumental in helping an organization recover swiftly after issues arise, reducing the chances of data loss, reputation damage, and operational disruptions, while minimizing the occurrence of emergencies.
Some businesses may already have a foundation in DR within their IT departments for individual systems. However, BCDR encompasses a broader spectrum, including crisis management, employee safety, and alternative work arrangements.
Implementing a comprehensive BCDR approach demands meticulous planning and preparation. Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS) can play a pivotal role in this process, offering scalable, cost effective recovery solutions for businesses looking to streamline their disaster recovery efforts. BCDR professionals help an organization formulate a strategy to achieve resilience. This intricate process involves conducting a business impact analysis (BIA) and risk assessment, crafting BCDR plans, conducting tests and exercises, and providing training.
Planning documents are central to an effective BCDR strategy. These documents not only aid in resource management but also offer crucial information such as employee contacts, emergency procedures, vendor lists, instructions for conducting tests, equipment inventories, and technical diagrams of systems and networks.
The Interplay of Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
Business continuity planning and disaster recovery policy are like partners that help a business stay safe and running smoothly. Business continuity services ensure that a business can keep doing its essential tasks, like talking to customers and getting work done. It’s important even if something terrible, like a disaster, happens.
If something goes wrong, disaster recovery and business continuity focus on fixing the technical stuff, like computers and data, to get things back to normal quickly. These two plans work together. Business continuity services need a disaster recovery policy to ensure everything stays on track, and disaster recovery helps business continuity strategies by fixing technical problems quickly. Ultimately, these plans help businesses stay safe, keep working well, and get back up and running if something unexpected happens.
Useful link: What is a Disaster Recovery Plan? How Confident Are You in Implementing it?
Why Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery Planning Must Evolve in 2025
In 2025, Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery (BCDR) has moved beyond traditional backup strategies. Enterprises now face an increasingly hybrid, cloud centric, and threat intense IT environment. To stay resilient, your BCDR approach must evolve in three critical areas:
1) Cyber Resilience at the Core
With ransomware attacks rising 49% in the first half of 2025, totalling 4,198 incidents globally, and a staggering 63% year over year increase in Q2, organizations are doubling down on resilient backup strategies. They’re adopting air gapped backups, which are physically isolated from networks, and immutable storage, where data cannot be altered or removed. These measures, together with secure, segmented disaster recovery environments, ensure that systems can be cleanly restored even after an attack, significantly enhancing overall cyber resilience
2) Hybrid IT Demands Unified Continuity
IT environments today are complex, spanning on premises infrastructure, multiple clouds, and remote endpoints. BCDR plans must provide comprehensive coverage across all layers, ensuring synchronized recovery across cloud workloads, SaaS applications, and internal systems. This comprehensive approach will provide you with a sense of security and protection.
3) Regulatory and Insurance Driven Readiness
Cyber insurance providers and regulators now require provable, testable recovery capabilities. Organizations that fail to demonstrate a recovery testing cadence and compliance face not only rising premiums but also audit risks. This emphasis on potential risks will prompt the audience to feel the need for compliance.
Business Continuity vs Disaster Recovery Plan
The table below illustrates the differences between business continuity and IT disaster recovery plans. It addresses similar aspects but from a comprehensive business perspective.
| Business Continuity Plan | IT Disaster Recovery Plan |
| Designed to maintain business operations through and after a crisis, protecting financial stability and reputation | Focused on minimizing harm to IT assets during a disaster and achieving rapid and full recovery |
| Catalog of essential business assets, including employees, suppliers, vehicles, and buildings, among others | List of IT assets, such as network equipment, servers, endpoints, and more |
| Assessment of the impact of threats on business operations | Evaluation of threats impacting IT infrastructure |
| Incorporates a continuous proactive element for disaster prevention and preparedness | Primarily centered on reactive actions in the event of a disaster |
| This can involve moving operations to a different location, using alternative technology, or changing business processes. | This involves recovering data, restoring IT systems, and rebuilding physical infrastructure |
| To ensure business continuity during a disruption | To bring the business back to regular operations following a disaster |
| Covers all aspects of the business, including people, processes, and technology | Focuses on critical systems and data |
| It starts before a disaster occurs and continues during and after the disaster | It starts after a disaster occurs and ends when the business is restored to normal operations |
| Regularly tested to ensure it is up to date and effective | Tested less frequently than a business continuity plan |
| Cost can be expensive to develop and maintain | Cost can be less expensive than a business continuity plan |
What Elements Should be Part of a Disaster Recovery Plan?
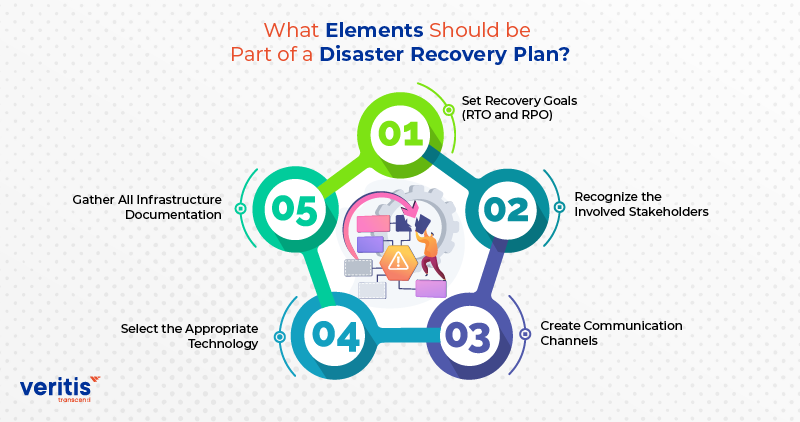
A disaster recovery planning checklist is like a to do list that helps ensure everything is ready when things go wrong. Let’s break down its importance:
1) Set Recovery Goals (RTO and RPO)
Set each important system or app’s recovery time (RTO) and recovery point objective (RPO). These define the longest acceptable downtime and data loss limits, guiding recovery. Prioritize systems and apps as RTO and RPO differ for each.
2) Recognize the Involved Stakeholders
Recognize everyone involved in cloud disaster recovery services. This includes IT teams, business units, senior management, and outside vendors. Ensure clear communication of their roles for effective collaboration during crises.
3) Create Communication Channels
Create robust communication methods for smooth disaster communication. This involves choosing primary and backup communication modes, making emergency contact lists, and setting rules for reporting and escalating incidents.
4) Gather All Infrastructure Documentation
Collect detailed records of your organization’s infrastructure, including network diagrams, system configurations, software licenses, and vendor contacts. This information is crucial for adequate recovery.
5) Select the Appropriate Technology
Choose the technologies and tools that match your recovery goals and your organization’s unique requirements. This might involve selecting backup and replication solutions, virtualization technologies, Disaster Recovery in Cloud, and data disaster recovery software.
BCDR Maturity Model and Measurable Frameworks
An effective Cloud Disaster Recovery Strategy and Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery (BCDR) plan isn’t built overnight; it evolves through defined stages of maturity. The BCDR Maturity Model serves as a powerful framework to guide this evolution. Whether you’re just beginning to formalize your Cloud Disaster Recovery Strategy or looking to advance toward automation and real time failover, understanding your current maturity level is essential to optimizing your resilience roadmap.
| Maturity Stage | Characteristics |
| Stage 1: Reactive | Backups are infrequent or ad hoc, with minimal documentation. Recovery depends on manual processes and individual effort. There is no unified business continuity strategy. |
| Stage 2: Proactive | The organization has a defined Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery plan, including recovery roles, documented RTOs and RPOs, and scheduled backups. However, recovery is still largely manual. |
| Stage 3: Resilient | Business continuity practices are automated where possible. Systems use immutable backup storage. Failover testing is conducted regularly. Compliance and risk audits guide decision making. |
| Stage 4: Intelligent | The BCDR strategy is integrated into business operations. AI and orchestration tools enable real time recovery, predictive failover, and SLA backed recovery. Plans are continuously optimized based on performance data and simulations. |
Measurable KPIs for BCDR Success
To move from planning to performance, you must define and measure your business continuity metrics. Here are the most critical KPIs to monitor:
- RTO (Recovery Time Objective): The maximum acceptable time to restore business operations after a disruption. For mission critical systems, this is often measured in minutes.
- RPO (Recovery Point Objective): The maximum tolerable amount of data loss measured in time. This defines how frequently backups or replications must occur.
- TRO (Testing Recovery Objective): The target cadence for running recovery drills and validating your Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery plan’s effectiveness.
Additionally, advanced organizations track:
- Recovery Confidence Score: Based on successful test recoveries and data integrity checks.
- Automated Recovery Coverage: The percentage of systems that support automatic failover/failback.
These metrics help convert a theoretical BCDR strategy into a performance driven, operational framework.
Best Practices to Accelerate Maturity
Regardless of where your organization currently stands on the maturity model, adopting industry best practices can accelerate your journey toward enterprise resilience:
- Apply the 3 2 1 Backup Rule: Maintain three copies of data (primary and two backups) on two different types of storage, with one backup stored offsite or offline in an immutable format.
- Leverage DRaaS (Disaster Recovery as a Service): Modern DRaaS platforms offer automated recovery workflows, geo redundancy, and SLA backed uptime guarantees—ideal for hybrid or cloud native environments.
- Run Regular, Non Disruptive Recovery Simulations: Conduct quarterly or monthly recovery drills that do not impact production but validate that systems can be restored within RTO/RPO targets.
- Integrate BCDR Testing Into Change Management: Each system change or infrastructure upgrade should trigger a continuity validation step to ensure no regressions occur.
Useful link: Business Continuity Planning: Steps To ‘Restart’ Your Stalled Operations!
Effective Approaches to Constructing a Robust IT Infrastructure
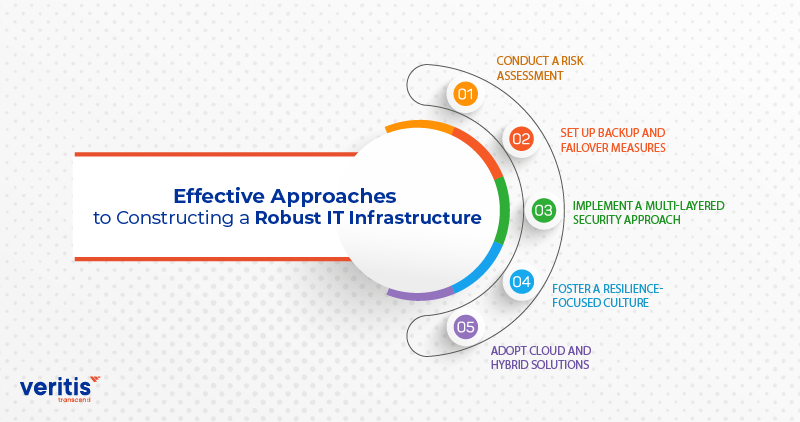
1) Conduct a Risk Assessment
Find IT infrastructure threats and vulnerabilities, focus on pressing issues, and keep your risk assessment up to date to adapt to evolving risks.
2) Set Up Backup and Failover Measures
Set up backup systems, data copies, and failover procedures to guarantee critical operations persist during disruptions. Consistently test these safeguards for optimal performance.
3) Implement a Multi Layered Security Approach
Establish a thorough security approach with multiple layers—encompassing firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, encryption, and routine security audits.
4) Foster a Resilience Focused Culture
Invest in training, resources, and support for your employees to promote a culture of resilience within your organization. This means providing them with the knowledge and tools they need to identify and manage risks proactively.
5) Adopt Cloud and Hybrid Solutions
Utilize cloud and hybrid IT solutions to enhance the flexibility and resilience of your IT infrastructure. These options offer added redundancy, scalability, and cost efficiency.
Useful link: Disaster Recovery’s Strategic Approach to Organizational Growth
The Future of Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
Enterprises are integrating cutting edge technologies to future proof their BCDR strategies:
1) AI Driven Recovery Orchestration
AI and machine learning are now empowering professionals to detect failure patterns, recommend recovery actions, and simulate impact scenarios. Predictive replication and generative AI are reducing decision making time during crises, giving professionals more control and confidence in their actions.
2) Edge and Distributed Resilience
With the rise of edge computing, BCDR strategies are becoming more adaptable, now accounting for remote branches, IoT devices, and microdata centers. This adaptability ensures that BCDR covers site level failover, network rerouting, and offline continuity, preparing you for any situation.
3) Simulation Based Planning
Human centered modeling tools are now providing a comprehensive approach to simulation based planning. They simulate disaster scenarios across supply chains, facilities, and infrastructure, allowing you to test decision trees, team coordination, and emergency escalation paths, ensuring you are well prepared for any eventuality.
Case Study Highlight: Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity for a Leading Airline
To ensure uninterrupted operations, a major airline proactively engaged Veritis to build a resilient IT infrastructure with a robust disaster recovery (DR) and business continuity framework.
Challenge:
The airline’s legacy systems lacked adequate disaster recovery capabilities, which risked prolonged downtime in the event of disruptions.
Veritis’ Solution:
Veritis designed and deployed a comprehensive disaster recovery (DR) and secondary data center solution with cloud integration, automated failover, and compliance focused configurations ensuring both resilience and readiness in every aspect.
Impact:
- Strengthened business continuity across operations
- Reduced risk of downtime and data loss
- Faster recovery with automated DR workflows
- Cost effective, scalable infrastructure
Explore the full case study: Disaster Recovery & Data Center Setup for Airlines Client.
Conclusion
By following these essential steps, CIOs can create a robust IT setup that ensures business operations continue smoothly, reduces risks, and boosts efficiency. Investing in a reliable IT system helps your organization stay flexible, competitive, and ready for unexpected disruptions.
A resilient IT infrastructure and a competitive advantage are necessary in the ever evolving business and technology landscape. It’s the key to maintaining operational efficiency, mitigating risks, and ensuring business continuity, even when facing unforeseen challenges. Building and managing such an infrastructure requires careful planning, comprehensive strategies, and the right partner.
Veritis, a distinguished Stevie and Globee Business Awards recipient, brings expertise and excellence to your IT services. With a focus on innovation and a commitment to delivering top tier solutions, Veritis is your trusted ally in navigating the complexities of the digital age.
Got Questions? Schedule A Call