
Disaster Recovery (DR) came at a time when the digital transformation was at its peak and the need to recover from a disaster was almost immediate.
Cloud Disaster Recovery is being seen as an ideal solution for business continuity in the event of a disaster, which can be power outages, network disruptions, natural calamity and more.
Living with downtime in today’s world is not an option, organizations must be quick to solve this. Lost hours in downtimes can cost reputation losses, customer dissatisfaction and endless chain of negative points for a company.
Hence, the Disaster Recovery!
But is Disaster Recovery just a solution to an ill-fated event or is there something more to it?
Disaster Recovery can not only be a remedy for downtime issues but also adds value to several aspects within a company’s structure. Creating a disaster recovery plan will put you at the forefront of competition and lead you to solve some futuristic issues well in advance.
Following is the list of benefits that an ideal Disaster Recovery-strategy can present to your organization:
What can Disaster Recovery do?
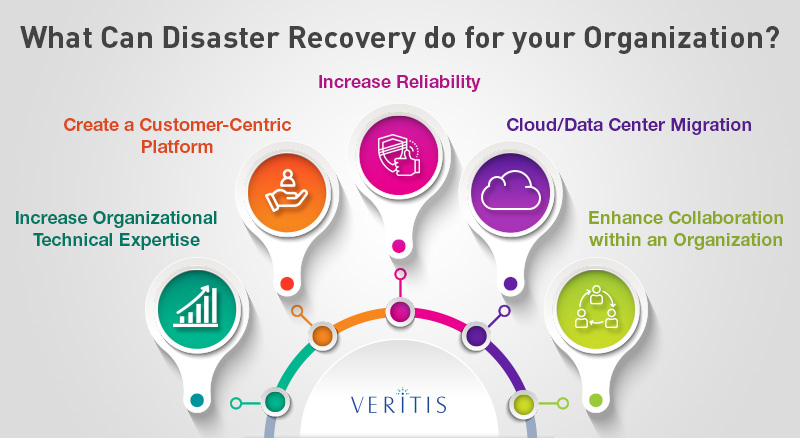
Disaster Recovery can offer a range of benefits to different organizations:
- Increase organizational technical expertise
- Create a customer-centric platform
- Increase reliability
- Cloud/Datacenter migration
- Enhance collaboration within an organization
Five ways Disaster Recovery (DR) adds value to your business operations:
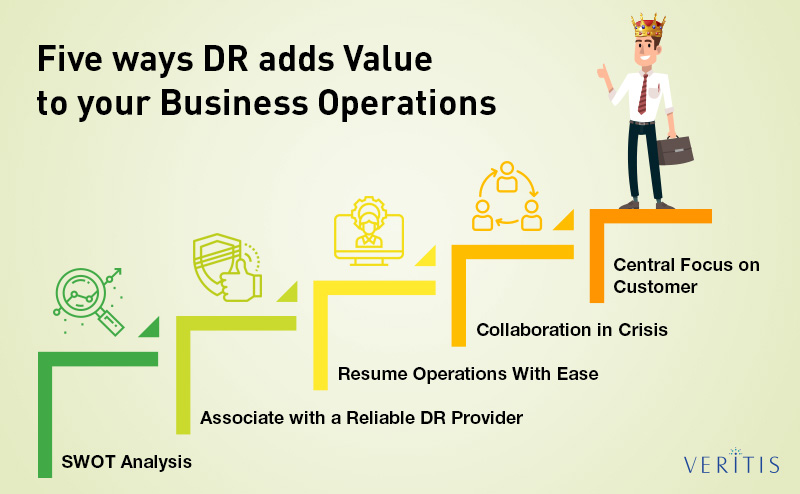
1) SWOT Analysis
It is always important to assess your Disaster Recovery (DR) strategy whether you are already employing a traditional disaster recovery plan or signing up for Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS). To begin with, you must perform an assessment of the challenges that lie ahead and what could potentially go wrong in the future.
The process also entails clear defining of the Recovery Time Objectives (RTO) and Recovery Point Objectives (RPO) in an SLA.
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO)
This is the targeted duration of time and a service level within which, a business process must be restored after a disaster to avoid unpleasant consequences as a result of break in business continuity.
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO)
This is the age of files that must be recovered from backup storage for business continuity in the event a computer, system, or network experiences failure.
But it’s important to ask oneself a few questions before creating a disaster recovery strategy. They are:
- What are the potential threats?
- To what extent can these threats pose a concern to the organization and where?
- Are our facilities secure enough? How good is your organization’s network connectivity and power?
- What kind of impact would any resulting disruption have on the business?
- Which systems and applications are most important, are they part of the organization or stored at another location?
- How are they built? Are they centralized or decentralized?
- How long can a disaster last and what implications it can have?
2) Associating with a Reliable DR Provider
Once you are sure about going ahead, the next thing is finding a reliable DR solutions provider (AWS, Azure, GCP, and More). Reliability is an underlying element of any business’s success.
Most cloud disaster recovery services providers assure organizations of the fact that they will be available to provide 24×7 customers support. But what if they fail to do so in the event of extremity?
Being able to fall back and resume failover can give you an edge in a competitive market that is filled with enterprises like you who are striving hard to increase their brand’s credibility and keep the flow of customers coming in.
Therefore, it is essential that you do proper research and study on the provider you are interacting with and have all your questions and queries clearly discussed on paper.
4) Resuming Operations With Ease
A solid DR plan can strengthen transformational-based efficiencies. For example, if you want to transfer your data to new data center or a hybrid cloud environment, then DR can prove highly beneficial. It saves time by setting up alternative versions of applications and facilitates normal functioning without any discrepancies.
5) Collaboration in Crisis
While a disaster can result in business downtime, it can have devastating effects on internal functioning, resulting in frictions between departments in the organization.
As part of the DR plan, it becomes important to communicate and take inputs from all the key stakeholders within an organization. A well-structured DR plan calls for a relaxed approach at times of disaster.
6) Central focus on Customer
With a focus on customer operations, an organization’s assessment plan should involve a Business Impact Analysis (BIA) that gives an insight into the impacts of a disaster, internally and externally.
It is important to note that the impact on the customer can differ based on the industry or an organization. For example, if an e-commerce platform experiences a downtime, then every second may cost the company, its customer base, and trust.
Therefore, it is essential to assess the amount of time and value that can be lost in a downtime, well in advance!
The Future of Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS)
According to Research and Markets DR market forecast, the DRaaS market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 17.29 percent during 2018-23 with a market share of up to USD 3,294.361 million by the end of the forecast period.
The global market for DRaaS is driven by the need for backup services for an organization’s data.
Furthermore, DRaaS presents fast recovery, cost-effectiveness and flexibility while simultaneously offering automation capability, making it a suitable and reliable option for the security of enterprise data.
It has been observed that small and large enterprises are employing DR to their benefit propelling its market growth and the demand for these solutions. However, factors such as compatibility of specific applications in the cloud environment and dependence on DRaaS providers to implement the solution in the right some of the factors that stand as challenges in its market growth.
Disaster Recovery has proved to be an ideal solution in a fast-changing market and fierce competition, but it goes a step ahead by adding value to an organization’s operations with its suite of benefits.
Related: