
In a world where technology drives almost every aspect of our lives, the cloud has elevated this experience. From undertaking complex operational workloads to executing large-scale cloud disaster recovery plans, the cloud has made our day-to-day operations relatively effortless. When it comes to a complex task like managing a cloud disaster recovery, the cloud has made us ponder how difficult it was to carry out a disaster recovery plan (DR Plan) before its arrival.
Consider the time and resources invested in a data disaster recovery plan.
If your primary data center were to be affected by a disaster, you would have to look up to the backup data center and refer to the conventional disaster recovery process, which, of course, comes with double the work, including:
- Setting up a physical location and facilities to house your IT infrastructure
- Engaging contact persons and security personnel for the setup
- Enhancing server capacity to store data and match your application’s scaling requirements
- Provisioning support staff for infrastructure maintenance
- Facilitating internet connectivity with enough bandwidth to run applications
- Setup network infrastructure, including firewalls, load balancers, routers, and switches
This data disaster recovery process will sum up spiraling costs and unmanageable resources, leaving the data center as just a data backup and nothing more. With the dawn of cloud computing, cloud disaster recovery has become another effortless task that can be handled in a couple of hours or minutes.
What is Cloud Disaster Recovery?
Cloud disaster recovery, often called cloud DR, is a comprehensive approach encompassing strategies and services for safeguarding data, applications, and assets by replicating them to public cloud environments or dedicated service providers. In a disaster, this replicated data can be used to restore affected systems to a local data center or a cloud provider, enabling the enterprise to resume its standard operations.
The core objective of cloud DR mirrors that of traditional cloud disaster recovery strategy: to protect critical business resources and guarantee their accessibility and recoverability, thereby ensuring uninterrupted business continuity.
Useful Link: Cloud-Based Disaster Recovery Plan
Picking a Cloud Disaster Recovery Provider
When choosing a cloud disaster recovery (DR) provider, a company should take into account the following five key factors:
1) Scalability
Evaluate the scalability of the cloud DR solution, ensuring it can safeguard designated data, applications, and assets. It should also have the capability to expand to accommodate additional resources, delivering consistent performance even as other clients globally utilize the services.
2) Security and Compliance
Comprehend the security prerequisites for your DR content and confirm that the provider can provide essential security measures like authentication, virtual private networks, encryption, and other tools required to protect your valuable assets. Assess compliance demands to guarantee that the provider holds certifications aligning with business-related compliance standards, like Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), ISO 27001, SOC 2, and SOC 3.
3) Reliability
Assess the dependability of the cloud DR provider. While even cloud services may encounter downtime, it’s crucial to avoid service interruptions during recovery, as they can harm the business equally.
4) Distance
A business should consider the physical proximity and latency of the cloud DR provider. Placing DR too nearby increases the vulnerability to shared physical disasters while locating it too far can lead to latency and network congestion, hampering DR content accessibility. The situation becomes more complex when the DR content is required to be accessible from numerous global business sites.
5) Architecture
Examine the architectural requirements of the DR platform. DR can be approached through three fundamental methods: cold, warm, and hot disaster recovery. These terms roughly correspond to the simplicity of system recovery.
Useful Link: Disaster Recovery – No More A Budgetary Constraint with Cloud
Benefits of Cloud Disaster Recovery
Cloud-based disaster recovery (DR) and backup offer numerous advantages in contrast to conventional DR approaches:
1) Pay As You Go Model
The pay-as-you-go model of cloud services offers a significant benefit compared to traditional DR methods, where DIY facilities or managed colocation providers involve substantial upfront capital costs and long-term contracts.
Cloud services allow organizations to pay a monthly fee based on resource and service usage, converting capital costs into ongoing operational expenses. Additionally, cloud providers may offer discounts for extended resource commitments, making this model appealing to larger organizations with consistent DR requirements.
2) Scalability and Flexibility
Conventional DR methods, often employed in local or remote data centers, tend to restrict flexibility and scalability. They require businesses to purchase servers, storage, network equipment, and software tools for DR, along with the design, testing, and maintenance of the DR infrastructure. This results in substantial capital and ongoing expenses.
On the other hand, cloud DR options, including public cloud services and cloud disaster recovery strategy as a service (DRaaS), offer the advantage of on-demand access to extensive resources. This permits companies to quickly scale up or down via a self-service portal, accommodating changes in workload and data needs without the burden of hefty capital investments.
3) High Reliability and Geo-Redundancy
High reliability and geo-redundancy are vital characteristics of cloud providers. With a global presence encompassing multiple data centers in major regions, cloud providers enhance service reliability and redundancy. Businesses can easily leverage this geo-redundancy by locating DR resources in alternative regions, even across multiple regions to optimize availability. This aligns seamlessly with the cloud’s inherent off-site DR capabilities.
4) Easy Testing and Quick Recovery
Effortless testing and rapid recovery are facilitated by cloud workloads, which frequently employ VMs. This allows straightforward VM image file duplication to on-premises test servers, enabling validation of workload availability without disrupting production processes. Moreover, businesses can choose high-bandwidth and fast disk input/output options to enhance data transfer speed, ensuring they meet recovery time objectives (RTO). It’s essential to bear in mind that data transfers from cloud providers may incur costs, so testing should be conducted with awareness of these expenses, mainly related to cloud data egress.
5) No Limitations Based on Physical Location
There are no constraints related to physical location. A cloud DR service allows organizations to position their backup facility virtually anywhere globally, independent of their physical premises. This offers an extra layer of security if a disaster threatens the servers and equipment housed within the organization’s physical structure.
Useful Link: Building a Resilient IT Infrastructure With Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
A Cloud Disaster Recovery service offers organizations several benefits, including:
- Saves Time/Capital
- More Data Backup Location Options
- Easy to Implement with High Reliability
- Scalability
For organizations considering cloud disaster recovery for the first time and are wondering where to start, here’s an easy cloud disaster recovery plan that will help you plan an effective disaster recovery planning service:
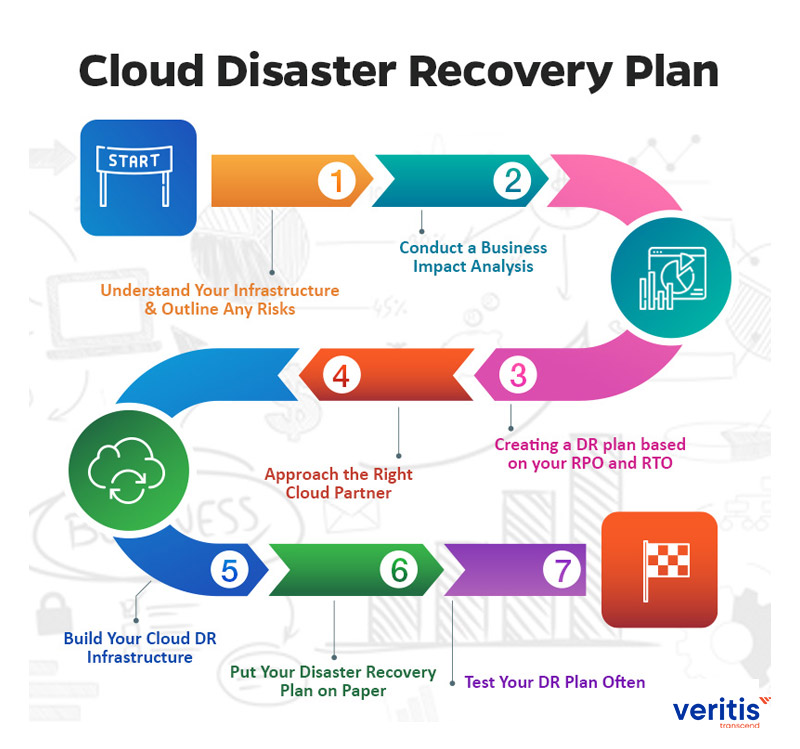
Step 1: Understand Your Infrastructure and Outline Any Risks
To create an effective disaster recovery planning process, consider your IT infrastructure, including the assets, equipment, and data you possess.
It’s also essential to assess where all this is stored and how much it is worth. Once you’ve sorted this out, you can tailor a good cloud disaster recovery plan. You now need to evaluate the risks that might affect all this. Risks can include natural disasters, data theft, and power outages.
Now that you have an account of all your assets, their quantities, and possible disaster threats, you can better design your data disaster recovery in cloud strategy to eliminate/minimize these risks.
Step 2: Conduct a Business Impact Analysis
A business impact analysis is next on the list. This will give you an understanding of the limitations of your business operations once disaster strikes, and you can consider them while forming the cloud disaster recovery plan.
The following two parameters help you assess this factor:
a) Recovery Time Objective (RTO)
b) Recovery Point Objective (RPO)
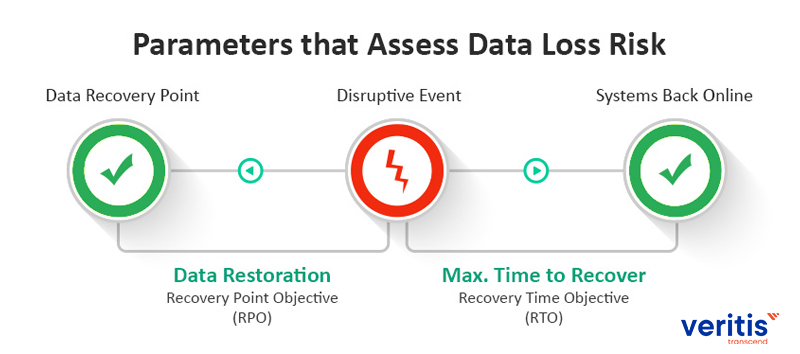
a) Recovery Time Objective (RTO)
Regarding cloud disaster recovery, RTO is the maximum time your application can stay offline before beginning to affect your business operations.
Scenario 1: If your company is dedicated to fast-paced service delivery, an application failure can cost you heavy losses.
Moreover, you’ll have to invest heavily in an IT disaster recovery planning process to resume business operations in minutes.
Scenario 2: If you have a medium-paced business and disaster affects your operations, you can still find alternative ways to carry out business operations.
Therefore, you can set your RTO for as long as one week in your DR plan. In such a case, you will not have to invest many resources into data disaster recovery in cloud planning, thus saving ample time to acquire sufficient disaster recovery cloud solution resources after the disaster strikes.
Knowing your RTO is very important, as it is equivalent to the resources you have to invest in your disaster recovery as a service plan. The time lost in the RTO can be used to gather backup resources.
b) Recovery Point Objective (RPO)
RPO is the maximum amount of time you can bear data loss from your application due to a significant crisis.
Points to consider for determining RPO:
- Possible data loss when disaster strikes
- Possible time loss before the data compromise
If you apply the scenario mentioned above, your RPO can be as little as five minutes, as your business is critical and cannot afford more than the specified time-lapse.
For Scenario 2, you may want to backup your data, but since the data isn’t time-sensitive, you will not have to invest heavily in cloud disaster recovery solutions.
Step 3: Creating a Disaster Recovery plan based on your RPO and RTO
Now that you have determined your RPO and RTO, you can focus on designing a system to meet your IT Disaster Recovery planning goals.
You can choose from the below range of Disaster Recovery strategies to implement your IT Disaster Recovery plan:
- Backup and Restore
- Pilot Light Approach
- Warm Standby
- Full replication in the Cloud
- Multi-Cloud Option
You can use a combination of these approaches to your benefit or exclusively as per your business requirement.
Step 4: Approach the Right Cloud Partner
After you have considered creating a cloud disaster recovery plan, the next step should be to find a trusted cloud service provider to help with the deployment.
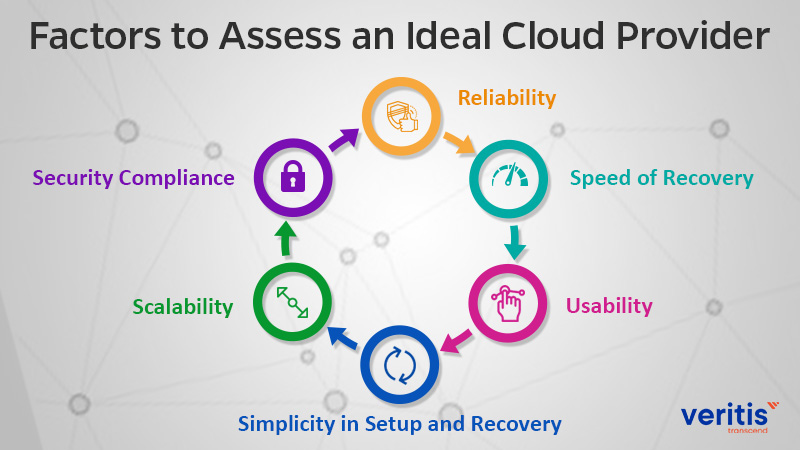
If you plan to use the full replication in the Cloud, then you would like to consider the following factors to assess an ideal cloud provider:
- Reliability
- Speed of Recovery
- Usability
- Simplicity in Setup and Recovery
- Scalability
- Security ComplianceFactors to Assess an Ideal Cloud Provider
Big cloud service providers, including AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, and IBM, have cloud disaster recovery solutions. Besides these big firms, medium and small firms offer quality Disaster Recovery-as-a-Service (DRaaS).
Useful Link: What is a Disaster Recovery Plan? How Confident Are You in Implementing it?
Step 5: Build Your Cloud DR Infrastructure
After consulting a cloud disaster recovery service partner, you can work with the provider to implement your design and set up your DR plan.
Based on the disaster recovery strategies you select, there are several logistical aspects to consider:
- What is the quantity of infrastructure components you will require?
- By what means will you copy the data to the cloud?
- What are the best ways to approach user authentication and access management?
- What security and compliance best practices will you need to set up?
- What security measures will you implement to minimize the likelihood of disasters?
Remember! Ensuring your DR plan is aligned with your RTO and RPO specifications for smooth business operations is crucial.
Step 6: Put Your Disaster Recovery Plan on Paper
It is essential to have a standard guideline or process flowchart with specific instructions for each and everyone involved in your IT disaster recovery plan. When a disaster occurs, each individual should be ready to take charge of the responsibility as per his role in the cloud disaster recovery services.
Moreover, every instruction should be clearly stated on paper, with the finest details mentioned.
These steps ensure the effectiveness of the cloud disaster recovery plan.
Step 7: Test Your Disaster Recovery Plan Often
Since your cloud disaster recovery plan is on paper, the next step would involve testing your IT discovery recovery plan more often. This helps to ensure that there are no loopholes.
On paper, the DR plan may look like the most comprehensive one, but you will know its credibility only after testing.
Your first test may not go as well as you thought; it may be worse. But then, you will learn from these experiences and upgrade your disaster recovery as a service to better brace your infrastructure against potential disasters.
The bigger your disaster recovery in cloud plan, the more critical it becomes to test it. Coming to the frequency of your tests, it is recommended that you run your DR tests every quarter.
Meanwhile, you can monitor and analyze your backup infrastructure performance daily or weekly.
Your organization will always witness change in terms of people, processes, and technologies. Testing your cloud disaster recovery solutions throughout these changes is good to ensure that the business is ever-ready for an emergency.
Conclusion
A complete knowledge of the industry’s best practices keeps your organization on the safer side. Have you identified your cloud platform? Looking for a trusted DRaaS provider? Get in touch with Veritis, Stevie Award and Globee Business Award winner, to understand the various disaster recovery strategies and identify the one that suits your business requirements!
With more than 15+ years of experience and 100+ projects to its credit, Veritis has the expertise and insight to deploy various cloud providers’ customized DRaaS offerings, including Azure, GCP, and AWS.
Got Questions? Schedule A Call Explore Cloud Solutions
[WPSM_AC id=13733]
Also Read:
- Disaster Recovery’s Strategic Approach to Organizational Growth
- AWS – Perfect Choice for Disaster Recovery
- 5 Reasons for successful On-Premises to the Cloud Migration
- 12 Best Features for Work Management Software That Matter Most
- AIOps Use Cases: How Artificial Intelligence is Reshaping IT Management
- Strategic IT Consulting: Enabling Business Growth with Veritis’ Expertise