
Many organizations’ security plans now must include (IAM) as a crucial component. As a result, businesses must ensure that their IAM tools and processes are correctly configured to gain the most significant security benefits.
Every organization has different needs and risk tolerances, making implementing an effective IAM program challenging. However, there are a few fundamental steps that IAM security teams can take at organizations of all sizes and in all sectors to master IAM.
By enforcing best practices for identity and access management framework, you can determine who has access to sensitive information and under what circumstances. To keep track of all of your components for potential threats now and in the future, you will need a comprehensive overview of your company’s IT infrastructure.
Identity and access are the two main entry points for any cyber threat incident. With the growth of digital adoption and cloud storage expansion, this risk vulnerability has grown even more. That’s when the Identity and Access Management solutions extend the helping hand!
From fulfilling the requirements of leading compliance regulations through successful audits to addressing many emerging IT security risks, IAM solutions help you in many ways.
However, the results in IAM depend on how you implement your IAM program as part of your IT security policy.
Before delving into the 12 identity and access management best practices that serve as the guide for successful Identity and Access Management (IAM) implementation, let’s consider what IAM is.
What is IAM?
Identity and access management, also known as IAM, is a framework of business procedures, laws, and technological advancements that facilitate the management of digital or electronic identities. IAM frameworks allow information technology (IT) managers to manage user access to sensitive data within their organizations.
Single sign-on systems, two-factor authentication, multifactor authentication, and privileged access management are examples of IAM technology systems. Furthermore, these technologies can safely store identity and profile data and data governance features to ensure that only required and pertinent information is shared.
IAM systems may be set up on-premises and made available by a third-party vendor under a subscription-based cloud or hybrid model.
IAM configuration fundamentally consists of the following elements:
- Understanding the distinction between identity management and authentication can help you better comprehend how people are identified in a system.
- How roles are defined in a system, and how people are given those roles.
- Updating, deleting, and adding people’s roles in a system.
- Granting different levels of access to specific people or groups of people and
- Both safeguard the system’s sensitive data and maintain system security.
The Importance of IAM
There is more organizational and governmental pressure on business executives and IT departments to protect access to corporate resources. As a result, they can no longer manually assign and track user privileges and are prone to error processes. These tasks are automated by IAM services, making it possible to audit and control granular access to all corporate assets on-site and in the cloud.
IAM, which has a long list of features that keeps growing and includes biometrics, behavior analytics, and AI, is well suited to the challenges of the new IAM security environment. For instance, IAM’s strict control over resource access in highly dispersed and dynamic environments aligns with the industry’s shift from firewalls to zero-trust models and the IoT’s security requirements. For more details on the future of IoT security, check out this video.
IAM is a technology that businesses of all sizes can use despite the misconception among IT experts that it is only appropriate for larger firms with higher budgets.
12 Identity and Access Management Best Practices
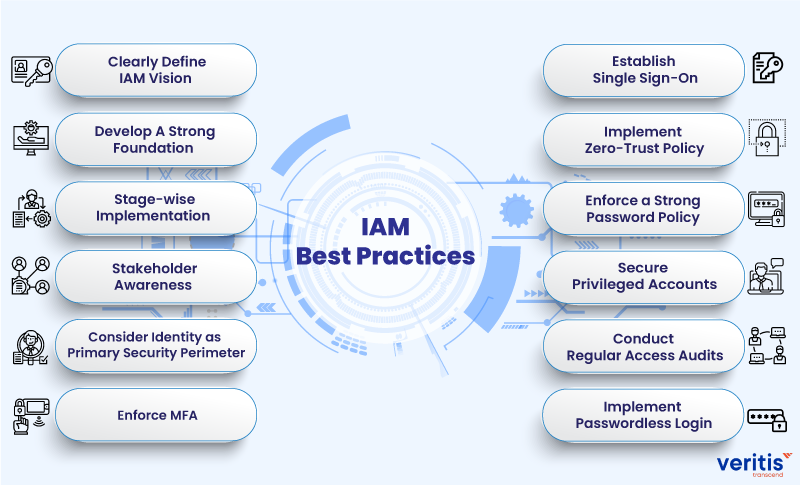
1) Clearly Define the IAM Vision
The critical fundamental for successful Identity and Access Management (IAM) implementation is understanding it as a combination of technology solutions and business processes to manage identities and access corporate data and applications.
- Start to tie business processes with your IAM program from the concept stage.
- Build your current and future IT capabilities, such as cloud-based implementations based on the current IT and network infrastructure.
- Engineer the roles between users and applications regarding privileges, rules, policies, and constraints.
- Map access privileges to business roles and identify excessive privileges, accounts, and redundant/dead groups.
- Fulfill all auditing requirements by compliance regulations, privacy, and data governance policies. This will help the teams make informed decisions.
- Implement authorization procedures, security, management, and integration across domains using an enterprise-wide approach as part of your IAM architecture.
2) Develop A Strong Foundation
This requires a comprehensive evaluation of IAM product capabilities and its sync with organizational IT. An effective risk assessment of all organizational applications and platforms should follow this.
The assessment should ideally cover:
- Comparison between standard and in-house and their versions
- Identification of OS, third-party apps currently in use, and mapping with the functionalities offered by the IAM program
- Customizations made to fulfill new requirements
- Technological capabilities and limitations
Don’t forget to involve IAM Subject Matter Experts (SMEs) in standardizing and enforcing the IAM policy.
3) Stage-wise Implementation
Based on the first two practices, the IAM program should be implemented. A stage-wise procedure is recommended to avoid complexities in the IAM implementation process.
Useful Link: Identity and Access Management Solution Implementation: A Stepwise Process
4) Stakeholder Awareness
Unlike usual training sessions, the IAM program-related stakeholder awareness program should cover detailed training on the underlying technology, product abilities, and scalability factors.
Each IAM solution implementation awareness program should have an approach tailored to the requirements of different user communities.
IT teams require more detailed knowledge of the IAM program and its core activities than anyone. Even the Operations team should know the capabilities across different stages of the IAM lifecycle.
The training process should be continuous and occur in tandem with changing processes or emerging capabilities.
5) Consider Identity as a Primary Security Perimeter
Organizations should shift from focusing on network security to considering identity as the primary security perimeter. With the cloud explosion and remote working culture, network perimeter is becoming increasingly porous, and perimeter defense can’t be effective. Centralize security controls around user and service identities.
6) Enforce Multi-Factor Authentication
Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for all your users, including administrators and C-suite executives. It checks multiple aspects of a user’s identity before allowing access to an application or database instead of regular sign-in. MFA is an integral part of identity and access management.
7) Establish Single Sign-On
Organizations must establish Single Sign-On (SSO) for their devices, apps, and services so users can use the same credentials to access the necessary resources, wherever and whenever. You can achieve SSO by using the same identity solution for all your apps and resources, whether on-premises or in the cloud.
8) Implement Zero-Trust Policy
The zero-trust model assumes every access request as a threat until verified. Access requests inside and outside the network are thoroughly authenticated, authorized, and scrutinized for anomalies before granting permission.
9) Enforce a Strong Password Policy
Implement an organization-wide password policy to ensure users set strong passwords for access. Ensure employees update their passwords regularly and avoid using sequential and repetitive characters.
10) Secure Privileged Accounts
Securing privileged accounts is imperative to protect critical business assets. Limiting the number of users having privileged access to the organization’s critical assets reduces the chance of unauthorized access to a sensitive resource. You must isolate the privileged accounts from the risk of being exposed to cybercriminals.
11) Conduct Regular Access Audits
Organizations must regularly conduct access audits to review all the granted accesses and check if they are still required. As users often request additional access or want to revoke access, these audits help you manage such requests accordingly.
12) Implement Passwordless Login
Passwordless login is the process of authenticating users without needing a password. It prevents scenarios where cybercriminals leverage weak and repetitive passwords to gain access to the network. Passwordless login can be implemented through various approaches, including email-based login, SMS-based login, and biometrics-based login.
These 12 best practices help an IAM program’s smooth and seamless implementation.
Useful Link: | Effective Identity Access Management Audit Checklist
A cost-effective IAM program can also be achieved through:
- In-depth requirement analysis as a combination of information gathering and perfect scope definition
- Effective design backed by a perfectly planned architecture and solution design
- Robust development through perfect process setup and effective integration
- Streamlined production roll-out with seamless migration from User Acceptance Testing to live release
- Adequate support and maintenance through proper training, post-production, and enhancements
Most IAM programs fail due to ineffective management in one or all implementation stages. The above-listed IAM best practices help ensure the smooth implementation of an IAM program.
Are you looking for Identity and Access Management Implementation Support in the US?

Although the identity and access management sector constantly evolves, some core IAM best practices can help your business develop its IAM strategy. These best practices can expand your IAM architecture and fortify your security posture.
With the appropriate identity and access management strategy, security experts may restrict access to endpoints and minimize the attack surface on corporate networks. As a result, they can simplify life for legitimate users while monitoring user privileges, preventing unwanted access, and reducing the danger of damaging data breaches. This is where Veritis comes in.
Choosing Veritis for IAM Solutions implementation is a good option for the following reasons:
- IAM Subject Matter Expertise support
- Strategic IAM roadmap and design
- Minimized risk scope in modifying IAM architecture designs
- Quicker product evaluation
- Expected ROI and enhanced user experience
- Tailored solutions for smooth roll-out
- Effective application on-boarding
- Easy and effective migration
- Seamless deployment of environments
Veritis, the Stevie Award Winner, can assist your business with the immediate implementation of identity and access management through our extensive infrastructure access platform.
Explore Cloud Services Got Questions? Schedule A Call
[WPSM_AC id=13768]
Additional Resources: