Organizations face heightened IT security challenges as cloud adoption accelerates and data flows across networks. Identity and Access Management (IAM) has become essential in improving security.
The shift towards a distributed mobile workforce necessitates a robust IAM system to safeguard data and assets effectively. Cybersecurity teams now require more robust controls to manage user identities and access across diverse environments.
Moreover, the proliferation of cloud-based applications and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) solutions presents unique challenges. Organizations must integrate robust IAM strategies to streamline access management across hybrid environments. This includes maintaining secure identities across platforms like Office365 and Salesforce, ensuring seamless operation and data protection.
Furthermore, as organizations embrace digital transformation and expand their digital footprints, the complexity of managing IAM solutions grows. The evolution towards cloud IAM solutions has become imperative, offering scalable and secure access management frameworks. This evolution addresses the challenges posed by distributed workforces and diverse IAM application landscapes and enhances IAM compliance with regulatory requirements such as GDPR and HIPAA. Implementing robust IAM frameworks ensures organizations can navigate these complexities while maintaining stringent security protocols across all operations.
Emerging IT Security Challenges and IAM Solutions
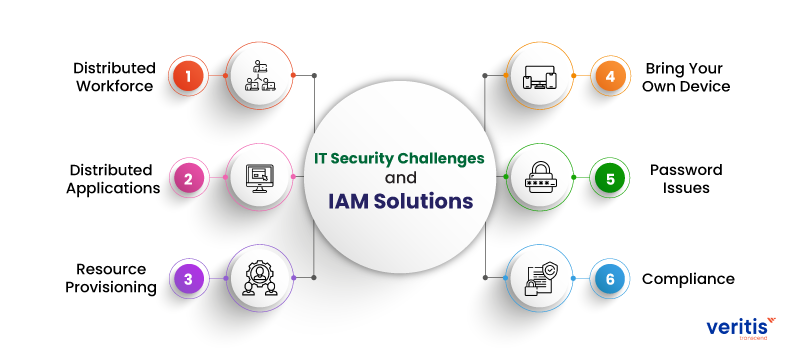
Challenge-1: Distributed Workforce
The rapid rise in remote working, accelerated by the COVID-19 crisis, has underscored the need for IAM solutions that provide enhanced visibility and access control over distributed workforces. IAM technologies ensure secure access, irrespective of employee location, without compromising security protocols.
Challenge-2: Distributed Applications
The proliferation of cloud-based and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) applications demands streamlined IAM strategies. IAM solutions simplify access management across hybrid environments, including cloud and traditional data centers. This capability is crucial for managing identities securely across diverse IAM application landscapes like Office365 and Salesforce.
Challenge-3: Resource Provisioning
Manual resource provisioning poses significant security risks and operational inefficiencies. IAM solutions automate provisioning and de-provisioning processes, ensuring timely access management and adherence to security policies. This automation enhances IT productivity while strengthening data security measures.
Challenge-4: Bring Your Own Device (BYOD)
BYOD policies enhance workforce flexibility but introduce security complexities. IAM strategies mitigate risks associated with unauthorized device access by enforcing strict access controls and policies across corporate applications. This approach balances user convenience with stringent security measures.
Challenge-5: Password Management
Managing multiple passwords across various applications can lead to security vulnerabilities and user frustration in a multi-cloud environment. IAM solutions offer Single Sign-On (SSO) capabilities, simplifying authentication processes and enhancing user experience across domains.
Challenge-6: Compliance
Meeting regulatory compliance requirements, such as GDPR and HIPAA, is critical for organizations. IAM solutions streamline compliance efforts by automating audit reporting and ensuring comprehensive access management controls. This proactive approach minimizes compliance risks and facilitates seamless regulatory audits.
ALSO READ | Best Practices for Implementing an IAM Solution
IAM Solution Implementation: A Stepwise Process

Implementing an effective IAM solution involves several strategic stages:
- Self-service Module: Enable password reset functionalities for immediate operational benefits.
- User Repository: Deploy a virtual or meta directory to centralize user identity management across the organization.
- Role Management: Implement robust role-based access controls (RBAC) to streamline access permissions.
- Identity Lifecycle Management: Automate processes for user onboarding, changes, and offboarding.
- Access Management Framework: Design and implement access controls for internal and external users to ensure secure data access.
- Single Sign-on (SSO): Integrate SSO solutions to simplify authentication and access management across multiple IAM applications.
Benefits of IAM

1) Enhanced Security
IAM enhances security by centralized control over user access to critical resources and data. It guarantees that only approved users can access particular systems and information, minimizing the chances of unauthorized access and data breaches. By enforcing strong authentication and access policies, IAM integration mitigates security threats such as phishing, insider threats, and unauthorized access attempts.
2) Improved Compliance Management
IAM solutions help organizations meet regulatory compliance requirements like GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, etc. By automating access controls, IAM integration guarantees that users are granted suitable permissions according to their roles and responsibilities. It also simplifies audit reporting and monitoring, enabling organizations to demonstrate compliance during regulatory audits.
3) Increased Operational Efficiency
IAM integration streamlines user provisioning and de-provisioning processes, reducing administrative overhead and operational costs. Automated workflows for onboarding and offboarding employees ensure prompt resource access while reducing the risk of unused accounts or access privileges. This efficiency allows IT teams to focus on strategic initiatives rather than routine administrative tasks.
4) Enhanced User Experience
IAM solutions improve user experience by providing Single Sign-On (SSO) capabilities. SSO permits users to access multiple applications and systems with a solitary set of credentials, eliminating the necessity for multiple logins. This seamless access experience enhances productivity and reduces user frustration associated with password management and login complexities.
5) Scalability and Flexibility
IAM systems are designed to scale with organizational growth and adapt to evolving IT environments. Whether deploying new applications, expanding into new markets, or accommodating a growing workforce, IAM solutions offer scalability without compromising security or performance. Flexible deployment options, including cloud-based IAM solutions, support agile business operations and enable rapid scalability as needed.
6) Risk Mitigation
IAM helps organizations mitigate risks associated with unauthorized access, data breaches, and compliance violations. IAM identifies and mitigates security risks in real time by enforcing least privilege access principles and continuous monitoring of user activities. Proactive risk management reduces the likelihood of security incidents and reduces their impact on business operations and reputation.
7) Centralized Identity Management
Centralized identity management is a core benefit of IAM, providing a single source of truth for user identities and access rights. This centralization simplifies identity lifecycle management, ensuring consistency across all IT systems and applications. Organizations gain visibility into user access patterns and behavior, enabling proactive security measures and informed decision-making.
Implementing IAM strengthens security measures, enhances operational efficiency, improves compliance management, and enhances user experience. These benefits make IAM a critical component of modern IT security strategies, supporting organizations in achieving their business objectives while safeguarding sensitive data and resources.
IAM Best Practices

1) IAM Strategy
Align IAM strategies with organizational goals and IT vision to ensure security measures effectively support business objectives. By integrating IAM solutions with broader business strategies, organizations can enhance operational efficiency, innovation, and regulatory compliance.
2) Build Scalable IAM Infrastructure
Establish a resilient IAM infrastructure supporting future growth and evolving security needs. A scalable framework for identity management, access control, and authentication mechanisms ensures robust protection against emerging IAM technology challenges.
3) Phased IAM Implementation
Deploy IAM solutions in stages to minimize disruptions and maximize effectiveness. The phased implementation allows for thorough testing, evaluation, and adjustment of IAM frameworks, ensuring alignment with organizational priorities and IAM application requirements.
4) Stakeholder Awareness and Education
Educate stakeholders about the importance of IAM and their roles in maintaining IAM IT security protocols. Promoting awareness among employees, IT teams, executives, and external partners fosters a culture of security awareness and accountability, enhancing overall IAM compliance.
5) Continuous Improvement and Integration
Foster a culture of continuous improvement in IAM practices by integrating feedback and evolving IAM strategies. Implementing best practices involves regular updates, monitoring emerging threats, and adapting IAM frameworks to address new cloud IAM solutions and regulatory requirements effectively.
Implementing these IAM best practices strengthens organizational security, improves agility, and ensures compliance with regulatory standards. Organizations can effectively manage identity and access risks in today’s dynamic IT landscape by prioritizing strategic alignment, scalability, phased deployment, stakeholder education, and continuous improvement.
Conclusion
IAM solutions are crucial in addressing organizations’ evolving IT security challenges in today’s digital landscape. As cloud adoption accelerates and businesses expand their digital footprints, robust identity and access management becomes imperative. IAM enhances security measures, improves operational efficiency, ensures regulatory compliance, and enhances user experience across diverse environments.
By centralizing control over user access, IAM helps minimize risks linked to unauthorized access, data breaches, and compliance violations. It streamlines user provisioning processes, reduces administrative overhead, and supports scalable growth without compromising security. IAM’s integration with cloud IAM solutions further enhances flexibility and agility, enabling organizations to adapt quickly to changing business needs and technological advancements.
Veritis, recognized for its expertise and achievements in IT solutions, including winning the Globee and Stevie Awards, offers comprehensive IAM solutions tailored to modern enterprises’ unique security challenges. With Veritis as your trusted partner, you can implement robust IAM frameworks that align with your business goals, enhance operational efficiency, and ensure the integrity and security of your digital assets.
More Articles:
- Best Practices for Effective ‘Identity and Access Management (IAM)’ Implementation
- IAM Best Practices for Optimal Cloud Security
- 5 Reasons Why Financial Sector Needs Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Healthcare Identity and Access Management (IAM): Five Steps to Transformation
- Robust Identity Management With ‘8-Point IAM Audit Checklist’ and ‘IAM Strategy’
- Identity and Access Management (IAM) Market Forecast: USD 25 Billion by 2026
