
Almost every company has used cloud computing to varying degrees in its operations. To protect against the biggest threats to cloud security, the organization’s cloud security strategy must address the cloud adoption issues and everything else that follows the integration.
Many firms are moving workloads to the cloud to improve efficiency and streamline workloads. In contrast, cloud computing can give businesses a competitive edge. However, it’s crucial to be cautious when implementing it without fully comprehending the hazards. When relocating operations to these dynamic environments, a company may fail due to a lack of awareness of cloud risks and cloud security best practices.
There are various security concerns in cloud computing and difficulties with cloud computing. For instance, a third-party supplier keeps data in the cloud and accesses it online. This implies that there is limited visibility and control over the data. The issue of how it can effectively be secure is also raised. Everyone must be aware of their responsibilities, the cloud security risks posed, and cloud security best practices.
Cloud computing is still changing how companies function internally and offer their customers. Organizations may now implement remote working environments more efficiently than ever, thanks to adopting cloud computing architecture. It also gives teams the information and resources they need to work together. Businesses also gain from transitioning from an on-premises data solution to a cloud computing environment because doing so results in cost savings, increased efficiency, and scalability. Cloud computing security issues and challenges are various. Unsecure access control points, inadequate threat notifications, alerts, and security system misconfigurations are some of the security concerns cloud technology brings.
Consult our Cloud Consulting Expert
In 2023, security issues in cloud computing continue to be a significant concern for organizations, with a notable prevalence of cloud security breaches. According to AAG IT Support, approximately 45% of data breaches are now occurring in the cloud, highlighting the growing vulnerability of cloud-based systems.
Alarmingly, recent data from Pingsafe indicates that 83% of companies have experienced a cloud security breach in the past 18 months, with a staggering 80% reporting security breaches within the last year. These statistics underscore the requirement for strong cloud security framework measures to secure sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access.
The leading causes of cloud security breaches further emphasize the need for improved security practices. IBM’s findings reveal that misconfiguration is responsible for a significant 69% of cloud security breaches, while Pingsafe’s research suggests that human error is a culprit in 82% of cases. Additionally, unauthorized access accounts for 33% of cloud security breaches, reinforcing the importance of access control and user authentication measures in cloud environments.
Organizations must address these critical issues to mitigate the risk of breaches and protect their data. Data loss and leakage are paramount among the top cloud security issues, with 69% of organizations expressing apprehension, as reported by Statista. Data privacy and confidentiality, at 66%, also remain a significant worry for organizations, while 44% are concerned about accidental cloud credentials exposure. These concerns highlight the ongoing challenges and complexities of securing data in cloud environments, urging organizations to prioritize robust security strategies and continuous monitoring to safeguard their digital assets effectively.
Businesses must consider the different security threats associated with cloud computing in addition to the many advantages. According to experts, companies who move their data and operations to the cloud without a clear plan, considering the potential drawbacks, are exposed to issues later. In addition, high-profile cloud security breaches negatively affect a company’s bottom line and reputation.
Cloud service providers treat risks and challenges related to cloud security concerns as a shared responsibility. The security of the customer’s cloud storage of data is their responsibility. At the same time, the cloud service provider is entirely responsible for the security of the cloud itself. Every cloud computing security issue user is always in charge of protecting their data from security risks and managing access to it. Whether the service is infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) like Amazon Web Services (AWS) or software-as-a-service (SaaS) such as Microsoft Office 365.
Most security threats in cloud computing are connected to cloud data security. Most concerns are related to the data that consumers upload to the cloud. Whether it be because of a lack of visibility into data, an inability to regulate data, or data theft. As we implement cloud technology, several security issues in cloud computing need to be considered, as well as mitigation strategies.
Useful link: What is Cloud Computing?
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing represents a technological model where services for managing, accessing, and storing data are delivered over the internet, rather than relying on traditional on-premises servers or local storage devices. In this cloud-based approach, the term “serverless technology” often arises because it abstracts the complexities of server management, permitting users to focus on their applications and data without dealing with the underlying infrastructure.
This technology caters to various data types, encompassing digital assets such as images, audio files, videos, documents, and many other file formats. By harnessing the capabilities of data security in cloud computing, organizations and individuals can benefit from scalable, cost-effective, and flexible solutions for their data needs, all while leveraging the convenience and accessibility offered by the internet. Cloud computing has become integral to modern computing, enabling numerous applications and services to function reliably and efficiently in our interconnected world.
What is the Need for Cloud Computing?
Before adopting cloud computing, large and small IT companies traditionally employed on-premises methods for data storage, necessitating the establishment of dedicated server rooms. These server rooms typically accommodated various essential infrastructure components, including database servers, mail servers, firewalls, routers, modems, and high-speed networking equipment. This conventional approach incurred substantial costs for IT companies, as they had to invest significantly in procuring, maintaining, and operating these on-site resources.
The advent of data security in cloud computing brought about a transformative shift in the industry by offering an alternative to these costly and complex on-premises setups. Cloud technology allows companies to offload their data and computing needs to remote, highly secure data centers, eliminating the need for maintaining an in-house server room. By leveraging cloud services, businesses can access scalable, cost-effective solutions, ultimately streamlining their operations, reducing infrastructure expenses, and enjoying the flexibility and convenience that the cloud provides. This shift to cloud computing has become a strategic choice for many companies looking to enhance efficiency, lower operational costs, and stay competitive in the ever-evolving IT landscape.
Cloud Security Challenges
The challenges lie in bridging the divide between theoretical knowledge and practical implementation. Understanding the importance of having a robust cloud security framework is one thing, but initiating the process and instigating a cultural shift can be daunting. The question arises: how does one begin? What are the concrete, day-to-day measures required to effect this change?
Embracing the cloud presents companies with four distinct cloud security challenges that are encountered universally:
1) Insufficient Cloud Security Expertise and Skillsets
2) Identity and Access Management
3) Shadow IT
4) Cloud Compliance
1) Insufficient Cloud Security Expertise and Skillsets
The conventional security approaches used in data centers are ill-suited for the cloud environment. Cloud administrators must acquire fresh strategies and skill sets tailored to the unique demands of data security in cloud computing.
While the cloud offers organizational agility, it can also expose vulnerabilities, especially for those lacking the internal expertise to grasp cloud security challenges. Inadequate planning often results from misinterpreting the shared responsibility model, which delineates the security responsibilities of both the cloud provider and the user. Misunderstanding this model can potentially lead to the accidental exploitation of security weaknesses.
2) Identity and Access Management
Identity and Access Management (IAM) is undeniably crucial, but the complexity lies in the execution. Creating the necessary roles and permissions for a large enterprise with thousands of employees can be a daunting undertaking. A comprehensive IAM strategy involves three key steps: role design, privileged access management, and implementation.
The initial step involves establishing a robust role design based on the specific requirements of cloud users. This design should be conceived independently of any particular IAM system, focusing on defining the tasks performed by employees that remain consistent across various cloud providers.
Subsequently, a privileged access management (PAM) strategy should be developed, identifying roles requiring heightened protection due to their privileges. It is essential to tightly control access to privileged credentials and regularly update them.
Finally, the designed roles can be effectively implemented within the cloud provider’s IAM service. This last step becomes more manageable when roles are well-defined in advance.
3) Shadow IT
Shadow IT poses security challenges by evading the established IT approval and management protocols. This phenomenon arises as employees independently embrace cloud services to fulfill their job responsibilities. The effortless scalability of cloud resources complicates efforts to regulate its proliferation. For instance, developers can swiftly generate workloads using their individual accounts, but these assets may lack proper security measures and may be vulnerable due to default passwords and configuration errors.
The introduction of DevOps further adds complexity to the situation. Cloud and DevOps teams prioritize speed and frictionless operations, making it challenging to achieve the visibility and management levels that security teams require without impeding DevOps activities.
There is a pressing need for a seamless approach that enables DevOps to deploy secure applications and seamlessly integrate with their continuous integration/continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipeline. A unified solution must be devised to provide security teams with the necessary insights without disrupting the velocity of DevOps. This requires IT and security teams to collaborate and develop solutions that align with the pace and demands of cloud-based DevOps practices.
4) Cloud Compliance
Organizations must comply with regulations designed to safeguard sensitive information, such as PCI DSS and HIPAA, which pertain to data like credit card details and healthcare patient records. To ensure adherence to these compliance standards, many organizations implement access and user privileges restrictions. Monitoring network access can become a significant challenge without proper access control measures.
Top 10 Security Issues in Cloud Computing
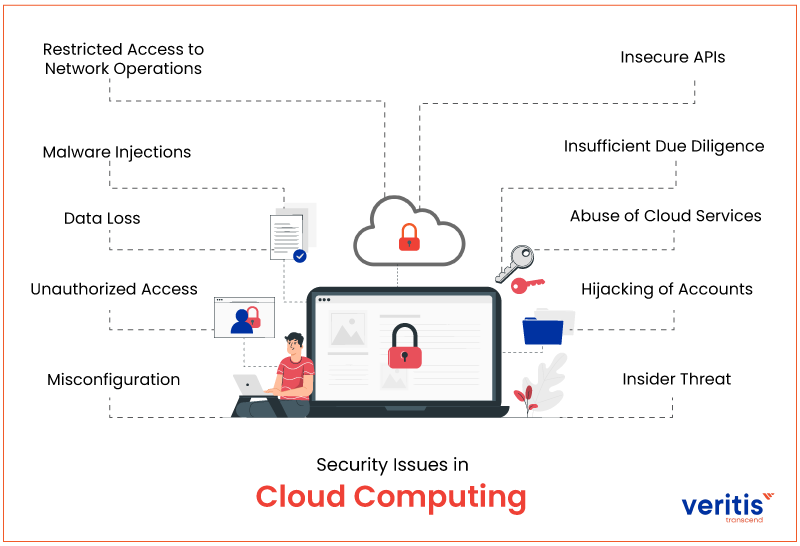
1. Misconfiguration
Incorrectly configured cloud security solutions settings frequently cause cloud data breaches. In addition, many enterprises’ cloud security posture management methodologies do not adequately protect cloud-based infrastructure.
Various things influence this. Because cloud infrastructure is intended to be user-friendly and to facilitate simple data exchange for businesses, ensuring that data is only available to authorized parties can be a concern. Therefore, enterprises adopting cloud based infrastructure must rely on the security measures provided by their cloud service provider (CSP) to establish and secure their cloud installations. Organizations using cloud-based infrastructure also need complete visibility and control over their infrastructure.
It is simple for a security lapse or misconfiguration to leave an organization’s cloud-based resources vulnerable to attackers because many organizations lack experience protecting cloud infrastructure and frequently deploy multiple clouds, each with a unique set of vendor-provided security controls.
2. Unauthorized Access
Cloud-based installations are outside the network perimeter and immediately reachable from the public Internet, in contrast to an organization’s on-premises infrastructure. However, this makes the infrastructure more accessible to users and customers. It also makes it simpler for attackers to access a company’s cloud-based services without authorization. An attacker may be able to get direct access without the organization’s knowledge if security is improperly configured or credentials are compromised.
3. Data Loss
In cloud computing, one of the problems is data loss. This is often referred to as a data leak. Insiders such as employees and business partners have access to sensitive data. Therefore, it’s feasible that hackers will gain access to our private information or sensitive data if the security of a cloud service is breached.
Enterprises using cloud computing security issues must cede part of their control to the CSP. Due to this, someone outside your IT department may oversee protecting some of the most critical data in your company. Your company will lose its data and intellectual property and be held liable for any ensuing damages if the cloud service provider is breached or attacked.
According to a recent report by Thales, a French multinational company specializing in information security and defense, 40% of organizations experienced a data breach in their cloud environment in 2023. This represents an increase from 35% in 2022. The report also found that human error was the leading cause of cloud data breaches, accounting for 55% of incidents.
4. Malware Injections
Malware injections are scripts or pieces of code that are added to cloud services. And pose as “legitimate instances” while running as SaaS from cloud servers. This implies that malicious code can be introduced into cloud services and be perceived as a component of the program or service operating on the cloud servers themselves.
Attackers can eavesdrop, jeopardize the integrity of private data, and steal data once the malware injection has been completed. And the cloud has started working in conjunction with it. The East Carolina University Report on security threats on cloud computing security risks vulnerabilities examines the risks of malware installations on cloud security security issues. And concludes that “malware injection assault has become a key security concern in cloud computing systems.”
5. Restricted Access to Network Operations
Lack of visibility into network operations is a disadvantage of switching from an on-premises data storage architecture to a cloud based infrastructure. Businesses provide CSPs with varying degrees of control over their IT infrastructure in return for advantages like cost savings and easy scalability with on-demand storage provisioning. Another essential security concern associated with cloud computing security issues is the lack of visibility.
The kind of service model determines how much control CSPs have and what data security obligations enterprises have. However, the lack of insight into cloud environments poses an ongoing threat to the companies that depend on them for mission-critical data management, regardless of the shared responsibility model.
Useful link: What You Should Know About Containers Threats in Cloud Computing
6. Insecure APIs
Application programming interfaces (API) allow customers to personalize their cloud security tools experience.
However, the very nature of APIs may pose threaten cloud security issues. They authenticate, grant access, and implement encryption, enabling businesses to tailor the features of their cloud based infrastructure services to suit their business requirements.
Security threats increase when API infrastructure expands to offer better services. APIs give developers the tools to create their programs and integrate them with other mission-critical software. For example, developers can use YouTube as a well-known and straightforward example of an API to include YouTube in their websites or applications.
An API’s vulnerability is in the communication that occurs between apps. Even though this can benefit organizations and programmers, it leaves them vulnerable to cloud security threats.
7. Insufficient Due Diligence
Most of the problems we’ve discussed thus far are technical. However, this security flaw arises when a company has a clear strategy for its objectives, resources, and cloud security framework solutions. It’s the people factor, to put it another way.
Additionally, rushing a multi cloud deployment migration without adequately planning for the possibility that the services will live up to consumer expectations might put a business at risk for security issues in cloud computing.
This is crucial for businesses that manage client financial data or whose data is subject to regulations like FERPA, PCI, PCI-DSS, and PII.
8. Abuse of Cloud Services
Both small and enterprise-level firms may now readily hold enormous volumes of data thanks to the growth of cloud-based services. However, because of the cloud’s unheard-of storage capacity, malicious software, unauthorized software, and other digital goods. It can now be hosted and distributed by authorized users and hackers.
Sometimes, the cloud service provider and its client are impacted by this practice. For instance, privileged users may violate the service provider’s terms by increasing cloud computing security risks directly or indirectly.
9. Hijacking of Accounts
Account hijacking has become a whole new set of problems because of many enterprises’ expansion and adoption of cloud security tools. Attackers can now remotely access sensitive data stored in the cloud using your (or your workers’) login details. They can even change and falsify data using credentials that have been hijacked.
In 2023, a misconfigured Amazon S3 bucket exposed the personal data of 119 million people. The same year, an attacker used a zero-day vulnerability to steal credentials from a cloud-based identity provider, affecting millions of users.
Phishing, keylogging, and buffer overflow attacks are all still common cloud security threats. However, one of the most significant new threats is the Man in the Cloud Attack, in which attackers steal tokens cloud service providers leverage to validate individual devices without requiring logins with each update and sync. These tokens can then allow unauthorized access to cloud accounts and data.
10. Insider Threat
Although an attack from within your company may seem implausible, the insider threat does occur. Employees with authorized access to a company’s cloud-based services may misuse or gain access to sensitive data such as client accounts, financial forms, and other information.
Additionally, it’s not even necessary for these insiders to be nasty.
Conclusion
A completely new realm for storage, access, flexibility, and productivity has been made possible by the cloud. But unfortunately, it has also given rise to further security concerns in cloud computing. By being aware of these top 10 cloud computing security challenges, you and your team may develop a multi-cloud deployment security strategy to safeguard your company.
Securing your cloud-based systems has never been easier. Veritis, a proud recipient of accolades like the Stevie and Globee Business Awards, offers top-notch cloud consulting services. Whether you’re transitioning to the cloud or already there, trust Veritis for advanced security solutions and adaptable cloud computing services. Let your business thrive in dynamic market environments with Veritis.
Therefore, working with a cloud solutions provider like Veritis, the Stevie Award winner, is the most efficient way to secure your cloud-based systems with advanced security, whether you’re moving to the cloud or are already there.
Veritis, a US-based provider of cloud consulting services, offers highly efficient and dependable cloud computing solutions that let businesses adapt quickly to changing market conditions.
Explore Cloud Services Got Questions? Schedule A Call
Additional Resources:
- 6 Ways Why Cloud Based Solutions Benefit Small and Medium Sized Enterprises (SMEs)
- Cloud Adoption Strategy: Which Approach Would be Most Effective for Your Company?
- What is Cloud Migration? Strategy, Process, and Tools
- Global Cloud Market to Reach Nearly USD 800 Billion by 2028: Survey
- Cloud Security Automation: Best Practices, Strategy, and Benefits
- 9 Keys to Selecting a Right Cloud Managed Services Provider (MSP)
- Cloud Infrastructure Automation: The Imperative for Cloud Success!
- Cloud Computing: Trends, Challenges and Benefits