
Identity and access have become the primary control points for enterprise security, governance, and operational trust. As organizations expand across cloud platforms, remote work models, third party ecosystems, and automated systems, unmanaged identities now represent one of the highest sources of business risk. This is why every enterprise needs an identity and access management risk assessment as a foundational discipline.
An identity and access management risk assessment evaluates how users, systems, and services are granted, monitored, and revoked access across the enterprise. It helps leadership identify exposure tied to excessive privileges, orphaned accounts, inconsistent policies, and weak governance that traditional perimeter security cannot contain. High profile breaches, stricter regulatory scrutiny, and the rise of machine identities have elevated IAM risk management to a board level concern.
Enterprises today face mounting challenges. Identity sprawl across hybrid environments, rapid onboarding of digital partners, and growing regulatory obligations in healthcare, financial services, manufacturing, and government contracting all increase the cost of IAM failure. At the same time, organizations can reduce identity and access management risks by applying structured assessment frameworks that align security controls with business priorities.
This article explains why an enterprise IAM risk assessment is key, what risks it uncovers, and how leaders can use it to strengthen security, resilience, and operational confidence.
What is an IAM Risk Assessment and Why Do You Need It?
An Identity and Access Management (IAM) risk assessment is a structured evaluation of how users, systems, and third parties access enterprise applications, data, and infrastructure, and where those access pathways expose the business to risk. It answers a simple executive question: Who has access to what, is it justified, and what happens if it is misused or compromised?
For modern enterprises, identity is now the primary security perimeter. Weak IAM controls directly translate into financial loss, operational disruption, regulatory exposure, and brand damage. Most major breaches today do not start with infrastructure failure; they start with compromised credentials, excessive privileges, or unmanaged access. An IAM risk assessment helps leadership quantify these risks, prioritize remediation, and align security investments with measurable business outcomes.
Useful link: Why is Identity Governance and Administration Essential for Enterprise Risk Management?
Why Now? Risk Drivers and Business Impact
| Risk Driver | Business Impact |
| Cloud and SaaS expansion | Uncontrolled access across platforms increases breach likelihood and audit failures |
| Hybrid and remote workforce | Higher risk of credential misuse leading to downtime and data loss |
| Third party and vendor access | Supply chain exposure resulting in regulatory and contractual penalties |
| Ransomware and identity based attacks | Revenue loss, operational disruption, and recovery costs |
| Regulatory pressure (HIPAA, SOX, PCI, NIST, CMMC) | Compliance fines, failed audits, and delayed contracts |
| Mergers and acquisitions | Orphaned accounts and privilege creep increase post merger risk |
| Privileged access sprawl | Elevated blast radius from insider misuse or credential compromise |
| Lack of IAM governance maturity | Inefficient controls, higher security spend with low ROI |
Common IAM Risks and Remediations
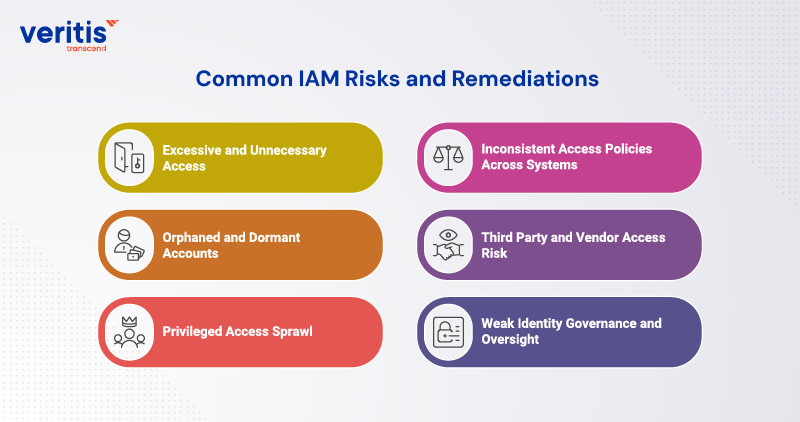
A single control gap rarely causes modern IAM failures. They emerge from accumulated access decisions, weak governance, and rapid digital change. An effective identity and access management risk assessment surfaces these risks early and ties remediation to measurable business outcomes.
1) Excessive and Unnecessary Access
The Risk
Employees, contractors, and service accounts accumulate permissions beyond their roles. This expands the blast radius of breaches and insider misuse.
Business Impact
Higher breach costs, audit findings, and regulatory exposure.
Targeted Remediation
- Enforce least privilege through role based access
- Conduct periodic access reviews as part of IAM risk management
- Automate deprovisioning on role or employment changes
2) Orphaned and Dormant Accounts
The Risk
Accounts remain active after users exit or systems are retired.
Business Impact
Silent attack vectors that bypass perimeter defenses.
Targeted Remediation
- Centralize identity lifecycle management
- Tie HR, IT, and IAM workflows together
- Use continuous IAM risk assessment to flag inactivity
3) Privileged Access Sprawl
The Risk
Admin and elevated accounts are poorly monitored and widely distributed.
Business Impact
A single account compromise can halt operations or expose sensitive data.
Targeted Remediation
- Implement privileged access controls
- Require just in time access approvals
- Monitor privileged activity continuously
4) Inconsistent Access Policies Across Systems
The Risk
Different rules across cloud, local infrastructure, and SaaS environments.
Business Impact
Control gaps, failed audits, and inefficient IAM solutions.
Targeted Remediation
- Standardize access policies enterprise wide
- Align controls through an enterprise IAM risk assessment
- Apply centralized governance models
5) Third Party and Vendor Access Risk
The Risk
Vendors retain broad access beyond contractual need.
Business Impact
Supply chain breaches and contractual liability.
Targeted Remediation
- Limit access scope and duration
- Perform IAM risk assessment for third party identities
- Enforce periodic recertification
6) Weak Identity Governance and Oversight
The Risk
No clear ownership for access decisions or accountability for risk.
Business Impact
High IAM spend with low risk reduction and unclear ROI.
Targeted Remediation
- Assign executive ownership for IAM risk management
- Establish governance metrics tied to business risk
- Engage an IAM risk assessment service provider for independent validation
Most identity and access management risks are preventable when assessed early and managed continuously. A structured enterprise IAM risk assessment enables leadership to reduce identity and access management risks, strengthen compliance posture, and direct IAM investments where they deliver the highest business value.
Useful link: What 12 Proven Best Practices Drive IAM Implementation Success?
Strategies for IAM Risk Management
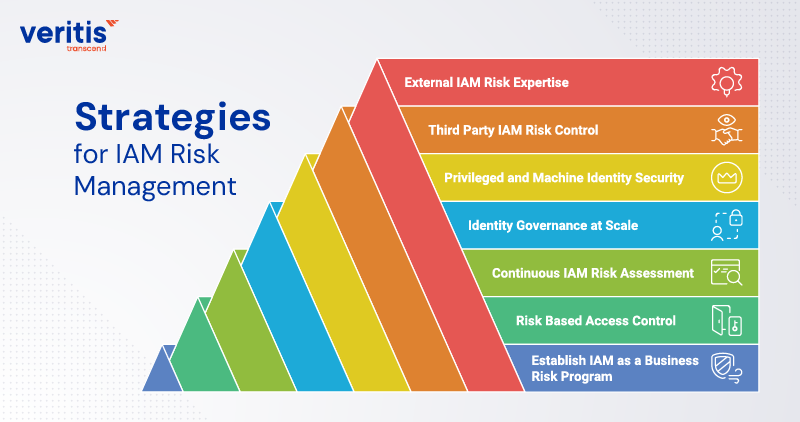
Effective IAM risk management is not a one time control exercise. It is a continuous business discipline that aligns identity decisions with enterprise risk tolerance, regulatory obligations, and growth objectives. The following strategies reflect how leading organizations operationalize identity and access management risk assessment outcomes at scale.
1) Establish IAM as a Business Risk Program
Strategic Intent
Position IAM risk management alongside financial, operational, and regulatory risk.
How Does It Work?
- Treat identity and access management risks as enterprise risks
- Align IAM controls with business critical systems and data
- Report IAM risk posture at the executive and board level
Outcome
Clear ownership, faster decisions, and measurable risk reduction.
2) Risk Based Access Control
Strategic Intent
Move beyond static access rules to adaptive control.
How Does It Work?
- Apply risk scoring to users, roles, and systems
- Adjust access based on role, behavior, and context
- Prioritize remediation based on business impact
Outcome
Reduced exposure without slowing operations.
3) Continuous IAM Risk Assessment
Strategic Intent
Replace periodic reviews with ongoing visibility.
How Does It Work?
- Continuously assess access changes and privilege growth
- Monitor identity behavior across cloud and hybrid environments
- Use IAM risk assessment to surface emerging threats early
Outcome
Early detection of issues before they escalate into incidents.
4) Identity Governance at Scale
Strategic Intent
Eliminate policy fragmentation across systems.
How Does It Work?
- Centralize identity lifecycle and access governance
- Apply consistent policies across SaaS and cloud platforms
- Support enterprise IAM risk assessment with unified reporting
Outcome
Stronger compliance posture and simpler audits.
5) Privileged and Machine Identity Security
Strategic Intent
Control the highest impact access pathways.
How Does It Work?
- Enforce least privilege and just in time access
- Govern service accounts and machine identities
- Monitor privileged activity continuously
Outcome
Smaller blast radius and faster incident containment.
6) Third Party IAM Risk Control
Strategic Intent
Reduce supply chain exposure.
How Does It Work?
- Limit third party access scope and duration
- Perform IAM risk assessment for vendors and partners
- Require periodic access recertification
Outcome
Lower contractual, regulatory, and reputational risk.
7) External IAM Risk Expertise
Strategic Intent
Accelerate maturity and ensure independent validation.
How Does It Work?
- Leverage expert frameworks and benchmarks
- Identify gaps internal teams may overlook
- Align IAM solutions with business and compliance goals
Outcome
Faster time to value and defensible security decisions.
Strong IAM risk management converts identity from a vulnerability into a control point for growth, resilience, and trust. Enterprises that apply continuous identity and access management risk assessment gain clearer visibility, reduce risks, and maximize the ROI of their IAM investments.
Industry Specific IAM Risk Assessment
While IAM principles are universal, identity and access management risk assessment must reflect the regulatory, operational, and threat realities of each industry. Enterprises that apply a one size fits all IAM model often overlook sector specific risks that carry direct financial and compliance consequences.
1) IAM Risk Assessment for Healthcare Organizations
Risk Focus
Clinical systems, patient records, and third party access across hospitals, labs, and insurers.
Primary Challenges
- Overextended access to electronic health records
- Shared credentials in clinical environments
- Vendor and partner access to sensitive systems
Assessment Outcome
An IAM risk assessment for healthcare organizations reduces exposure to data breaches, strengthens audit readiness, and supports HIPAA aligned governance without disrupting care delivery.
2) IAM Risk Assessment for Financial Services
Risk Focus
Customer identities, privileged access, transaction systems, and fraud prevention.
Primary Challenges
- Privilege creep in trading and operations systems
- Weak identity governance across digital channels
- Regulatory scrutiny and audit pressure
Assessment Outcome
IAM risk assessment for financial services improves access control integrity, limits fraud vectors, and aligns IAM risk management with regulatory expectations and business continuity goals.
3) IAM Risk Assessment for Government Contractors
Risk Focus
Controlled data, contractor access, and compliance driven identity controls.
Primary Challenges
- Least privilege enforcement across programs
- Third party and subcontractor identity oversight
- Alignment with NIST, CMMC, and federal mandates
Assessment Outcome
IAM risk assessment for government contractors builds confidence in compliance, protects contract eligibility, and reduces identity driven security findings.
4) IAM Risk Assessment for Manufacturing Enterprises
Risk Focus
IT and OT access, plant systems, and supplier connectivity.
Primary Challenges
- Unmonitored access to operational systems
- Shared and machine identities on factory floors
- Third party access to production environments
Assessment Outcome
IAM risk assessment for manufacturing enterprises reduces downtime risk, protects intellectual property, and strengthens resilience across connected operations.
5) IAM Risk Assessment for Retail and Consumer Enterprises
Risk Focus
Customer identities, digital commerce platforms, and seasonal workforce access.
Primary Challenges
- High volume customer authentication and account takeover risk
- Temporary and contract workforce access during peak seasons
- Fragmented identity controls across online channels, POS, and loyalty systems
Assessment Outcome
An IAM risk assessment for retail and consumer enterprises strengthens customer trust, reduces fraud exposure, protects revenue during peak transaction periods, and supports scalable digital growth.
Industry specific risks require specialized identity and access management services that go beyond tools. Effective services combine assessment, remediation, and continuous IAM risk management to help enterprises reduce risks while supporting growth, compliance, and operational scale.
Useful link: 5 Reasons Why Financial Sector Needs Identity and Access Management (IAM)
IAM Tools Enterprises Should Evaluate
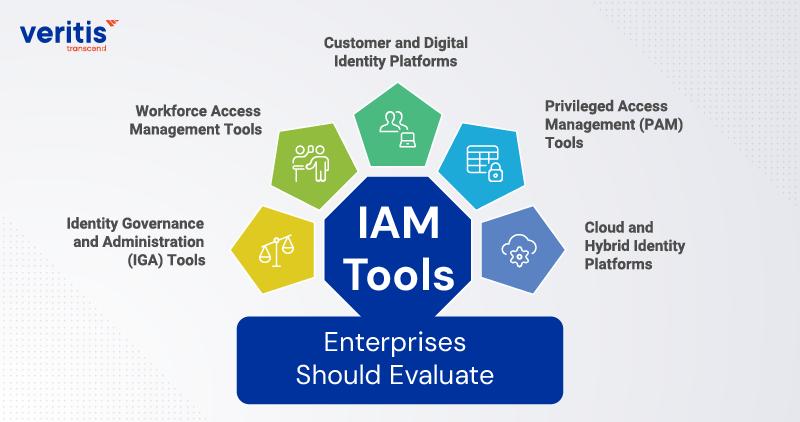
Enterprises typically require multiple IAM tool categories to address governance, access control, and high risk identities. The right mix should be guided by an identity and access management risk assessment, not vendor preference.
1) Identity Governance and Administration (IGA) Tools
Purpose
Define, govern, and audit who should have access.
Common Enterprise Tools
- SailPoint
- Saviynt
- Microsoft Entra ID Governance
- Oracle Identity Governance
Executive Insight
IGA tools surface excessive access and support enterprise IAM risk assessment and audit readiness.
2) Workforce Access Management Tools
Purpose
Control employee and contractor access to enterprise applications.
Common Enterprise Tools
- Microsoft Entra ID
- Okta
- Ping Identity
Executive Insight
These tools reduce identity and access management risks tied to credential misuse and remote work.
3) Customer and Digital Identity Platforms
Purpose
Secure customer facing applications while maintaining user experience.
Common Enterprise Tools
- ForgeRock
- Okta Customer Identity
- Ping Identity
Executive Insight
Customer identity tools protect revenue and brand trust at scale.
4) Privileged Access Management (PAM) Tools
Purpose
Secure administrator, system, and elevated access.
Common Enterprise Tools
- CyberArk
- BeyondTrust
- Delinea
Executive Insight
PAM tools address the highest impact IAM risks across critical systems.
5) Cloud and Hybrid Identity Platforms
Purpose
Manage identities and permissions across cloud and hybrid environments.
Common Enterprise Tools
- AWS IAM
- Azure IAM
- Google Cloud IAM
Executive Insight
Cloud IAM tools are important for reducing misconfiguration risk and supporting enterprise IAM risk management.
Useful link: Best Identity Access Management Tools and Protocols for IAM
Conclusion
Identity has become the control layer that connects security, compliance, and business execution. As enterprises scale across cloud platforms, third party ecosystems, and digital channels, unmanaged access is not a technical gap. It is a measurable business risk. A structured identity and access management risk assessment gives leadership clear visibility into that risk, the confidence to prioritize remediation, and the ability to align IAM investments with tangible business outcomes.
Why Veritis?
- 21+ years delivering enterprise grade security and IAM programs
- Proven identity and access management services across regulated industries
- Risk first approach grounded in enterprise IAM risk assessment, not vendor bias