Virtualization and Cloud Computing are the two key buzz words that have really revolutionized the IT industry and the way it operates across the product development lifecycle.
As one forms the basis for the other, these two terms are often confused with one another when it comes to definition and functionality.
The concept of Virtualization forms a base for Cloud Computing by helping the latter in delivery of shared computing resources, data or software, either as a service and on-demand, over the network.
Whereas, Cloud involves Virtualization to deliver computing services and can also act independently with automated management, scalability, self-serving and pay-as you go capabilities.
In a nutshell, Virtualization is a technology that simulates or emulates hardware. Whereas, cloud computing refers to the services that result out of this manipulation.
Virtualization, a Basis to Cloud
Maximum output with a minimum expenditure happens to be the trend in this fast-growing world, and the start-up culture gave a needed boost to that concept.
In addition, technology revolution has given rise to consumer demands, thus creating a need for more number of product releases for the firms to compete in the market.
Here is where the real challenge arose with regard to effective management of resources needed for the development, and hardware plays a vital role.
The basic challenge that many firms report with hardware management is the high capital expenditure.
That’s where they looked at separating physical infrastructures or hardware using software resources for easy execution of process. And, they called it the concept of Virtualization!
Thus, Virtualization is the concept of separating physical infrastructures to create various dedicated resources for multiple operations. It allows implementation of multiple Operating Systems (OS) and applications on the same server at a same time.
With the use of Hypervisor on the top of hardware layer, Virtualization minimizes dependency of workstations, storage and other systems on the physical hardware. This results in cost savings for many firms, helping them achieve efficiency, utilization and flexibility in the management of computer hardware resources.
Refer to Veritis Virtualization Consulting Services for more details on types of Virtualization.
Cloud, A Resultant of Virtualization
While Virtualization is the manipulation of hardware resources, the service that arises out of this manipulation is referred to as Cloud Computing. Cloud computing refers to delivery of shared hardware resources, data or software, as a service or on-demand, over a network.
Refer to Veritis Cloud Computing Consulting Services for more details on Cloud Computing and its types.
Virtualization Vs. Cloud
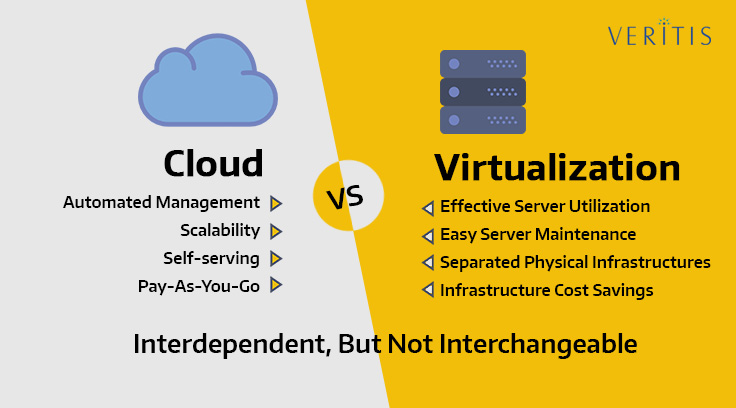
Virtualization and Cloud Computing technologies are interdependent, but not interchangeable.
While Virtualization forms one of the key basis for Cloud operations, a full-fledged Cloud can work independent of Virtualization to offer self-reliability, scalability, automated management and pay-as you go service.
These two technologies also work together to deliver certain services, as in the case of Private Cloud in enterprise networks.
Unlike Cloud, Virtualization allows multiple virtual servers for each single physical server.
Whereas, Cloud cannot offer the similar service despite the presence of large data centers with multiple servers to power cloud offerings. Addressing this, cloud providers partition the data on the server and make them available to the client in the virtual form.
Thus, Virtualization minimizes the need for multiple servers enabling easy server maintenance and ensuring better usage of existing server’s capacity unlike a non-virtualized server, which is called ‘Server Virtualization’.
By creating several virtual environments called Virtual Machines (VM) from a single physical server, Virtualization enables firms to run their operating systems on all these individual VMs minimizing their server maintenance costs.
Similarly, Storage Virtualization enables a full-fledged utilization of the available hardware resources, 20-80 percent more than the non-virtualization hardware. It does so by joining all the computing resources belonging to various storage devices into a single and shared virtual storage repository accessible to multiple users over the network.
This way, Virtualization works better for small firms in minimizing their expenditure and helping them address challenges with regard to servers and storage devices.
Whereas, Cloud Computing might sound little costlier for smaller firms as it involves adoption of services over the Internet rather than having them on the own network. However, Cloud providers have a handful of services for the small businesses in line with their business requirements.
Cloud computing offers a ready-to-go kind of service for small firms who can enjoy advantages such as access to sophisticated software, easier installation of applications and hardware, and the flexibility to try out the software before purchase.
Overall, Virtualization and Cloud operate on a one-to-many model. In a nutshell, Virtualization can make a single system work as different systems, cloud computing brings all at a place as a ready-made service over the network, enabling easier access as a one-stop solution.
It all depends on how we implement it, whether you would wish to have your own environment or depend on something that is ready-made!