Table of contents
- How do We Define Passwordless Authentication?
- How Does Passwordless Authentication Work?
- Is Passwordless Authentication Secure?
- Passwordless Connection vs Passwordless Login
- How Can I Use Passwordless Authentication?
- Types of Passwordless Authentication
- Advantages of Passwordless Authentication
- Disadvantages of Passwordless Authentication
- Passwordless Authentication Challenges
- Capping it Off
How do We Define Passwordless Authentication?
Passwordless authentication can be used to confirm a user’s identity without using a password. Instead, users can receive a one-time code or link by entering their email address or mobile number, which they can use to log in.
In recent times, regular passwords have not been secure. Both remembering and resetting lost passwords are complex. Additionally, they are the primary target of cybercriminals. Such that 81% of breaches involve stolen or weak passwords. Although the capabilities of passwordless authentication solutions differ, they all allow individuals to log into the account without creating a static password. Therefore, there is a chance you would improve security and user experience by removing passwords from the login process by going passwordless.
Be a Part of Digital Tranformation
Different sectors and use cases can benefit from passwordless authentication. For instance, businesses can provide physical security keys to authenticate staff members and control access to internal resources. Customers can confirm a transaction on their mobile devices using their fingerprints. Users who have forgotten their passwords may use a link in an email to log in.
However, passwordless authentication solutions aren’t restricted to these techniques or use cases. Instead, it has various implementations with different feature sets and advantages, all of which dwarf the built-in vulnerabilities of passwords.
How Does Passwordless Authentication Work?

Passwords are replaced by alternative authentication variables, which are inherently safer in passwordless authentication. During password-based authentication, a user-provided password is compared to what is kept in the database.
A user’s unique characteristics are compared to passwords in some passwordless systems, such as biometrics, while the comparison process is similar in both cases. For instance, a system can capture a user’s face, extract numerical information from it, and then compare it to verify information, which is stored in the database.
Comparisons may take place in different ways in other passwordless systems. For instance, a system can send an SMS to a user’s mobile device containing a one-time passcode. Following that, the system matches the user-entered passcode to the previous one.
Passwordless authentication follows the same principles as digital certificates, cryptographic key pairs containing private and public keys are the foundations of passwordless authentication. Although both are referred to as “keys,” the private key is the actual key that unlocks the padlock, while the public key serves as the lock.
When it comes to how digital certificates operate, there is only one padlock for each key and vice versa. A tool (a mobile app, a browser extension, etc.) is used by a user to produce a public-private key pair to create a secure account. The private key is kept on the user’s local device and can only be accessed using a security measure like a fingerprint, PIN, or OTP. The user’s system wants a secure account and is given the public key.
Useful link: Security Breaches Rising Exponentially; Weak Authentications Exploited
Is Passwordless Authentication Secure?

Depending on how you define safety, passwordless authentication solutions may or may not be secure. However, passwordless authentication is secure; if by safe, we mean less vulnerable to common cyberattacks and harder to crack.
If you deem ‘safe’ is synonymous with ‘unbreachable’ then the answer is no. There is not a single authentication method in existence that is impenetrable. While there may not be an obvious way to hack it, the most skilled hackers can find a way to get past its safeguards.
Having stated that, passwordless methods are intrinsically more secure than passwords. A dictionary attack, which is frequently regarded as the most basic hacking method, is one example of how a bad actor may compromise a password-based system (keep trying different passwords until you get a match).
A dictionary attack is possible even for amateur hackers. To compromise a passwordless system, on the other hand, requires a substantially higher level of hacking expertise and knowledge. For instance, a hacker can only fake a fingerprint using the most sophisticated AI algorithms.
Passwordless Connection vs Passwordless Login
A passwordless connection is a different kind of link distinct from any company, social, or existing database connection. Although users or social provider may have the same email address, their passwordless connection’s identity is different.
Account linking can use to connect a passwordless login identity with identities from other connections, just like how linking multiple email addresses or mobile phone numbers used for the Passwordless connection.
How Can I Use Passwordless Authentication?
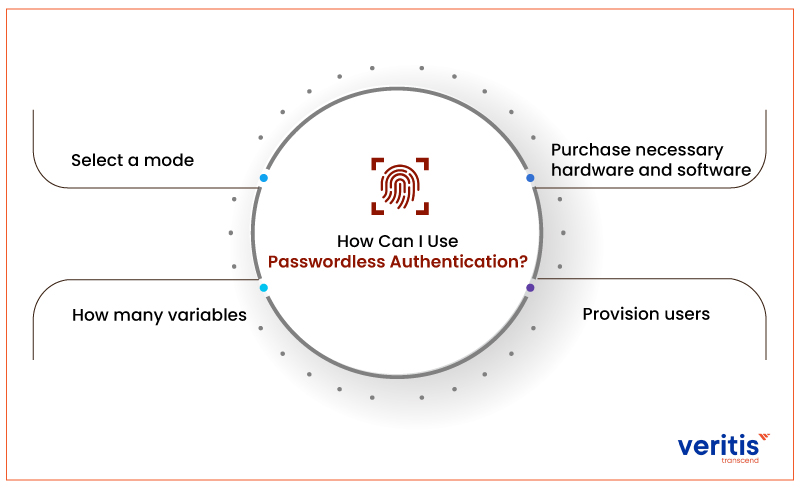
Here’s a strategy for adopting passwordless authentication into practice:
1) Select a Mode: The first step is to decide which type of authentication factor you desire. Options include hardware tokens, fingerprints, retinal scans, and magic linkages.
2) How many Variables? It is recommended to use multiple authentication factors, regardless of passwordless authentication usage. No matter how secure it seems, relying solely on one aspect, it is not advised.
3) Purchase Necessary Hardware and Software: You might need tools to establish biometric-based passwordless authentication. In addition, you might need to purchase software for other options, such as magic links or mobile OTPs.
4) Provision Users: Start adding users to your authentication system.
It can take more time and effort to implement passwordless authentication internally. Therefore, many enterprises prefer to outsource their IAM needs. This expedites the procedure and lowers maintenance expenses and concerns.
Types of Passwordless Authentication
In the case of traditional username and password authentication, users must enter something they are aware of (a password) to prove their identity.
However, password-less authentication approaches call for the user to show that they are something (an inherent factor) or possess something (a possession factor), both of which are more difficult to defeat.
The most popular techniques for confirming both inheritance and possession aspects are listed below:
1) Biometrics
Many physical characteristics are almost unique to each person. Without demanding a password, biometric authentication employs these distinctive physical characteristics to confirm that a person is who they claim to be. For instance, there is a low probability that two faces will be identical—less than one in a trillion—so facial recognition helps identify people.
Examples of Biometric
- Fingerprint Scan
- Voiceprint
- EKG
- Facial Recognition
- Retinal Scan
2) Push Notifications
Users launch the authenticator app using a push notification they receive on their mobile devices from a specific authenticator app (like Google Authenticator) to confirm their identity.
Examples of Push Notifications
- Hardware token
- Authentication app
- Smart card
- Mobile device
3) Magic Links
In this type of password less authentication, the login box prompts the user to input their email address rather than a password. They are then provided a URL in an email that they can use to log in. Every time a user logs in, this procedure is repeated.
Examples of Magic Links
- Accessing a Medium account
- Accessing a new Slack instance
4) One-Time Passwords/Codes:
In contrast, to magic links, one-time passwords (OTPs) or one-time codes (OTCs) require users to enter a code that is sent to them (by email or SMS to their mobile device). Then, when a user logs in, this process is repeated.
5) Email-Based Authentication
This kind of password less authentication encourages users to input their email addresses in the login boxes rather than asking them for passwords. After that, they get an email with a link to a page where they can log in.
6) SMS-Based Authentication
An individual first provides his phone number before a username and password. After entering their mobile number, the customer will receive a one-time-use code through SMS. After entering the one-time-use code in the login box, the user will have access to his application.
7) Link-Based Authentication
One enters his phone number before entering a username and password. Following the entry of their mobile number, the customer will receive a one-time-use code through SMS. The one-time-use code must enter in the login box before the user can access his application.
Useful link: What is Operational Security (OPSEC) and How Does it Protect Critical Data?
Advantages of Passwordless Authentication
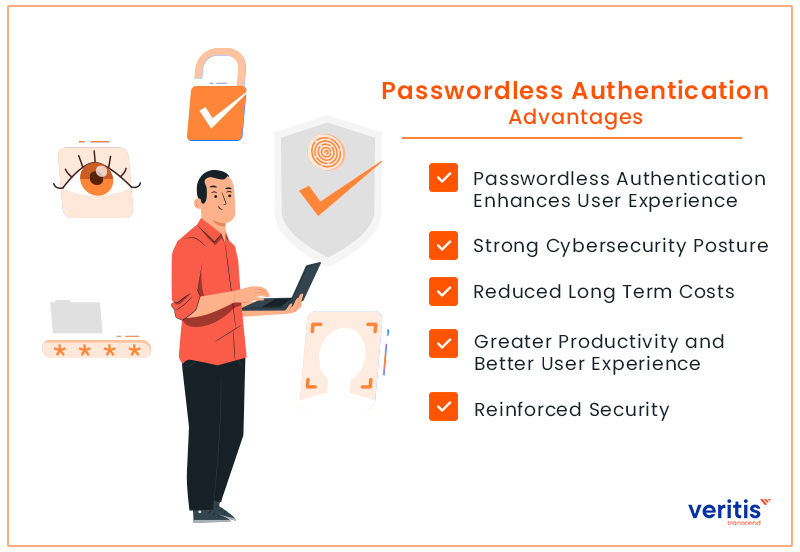
Is it worthwhile to invest the time, effort, and persuasion into establishing password less authentication? Yes, in a nutshell. Let’s look at a few justifications for this.
1) Passwordless Authentication Enhances User Experience
According to NordPass, the average user has between 70 and 80 passwords. You can see how challenging it would be for the typical individual to think of 80 different passwords, let alone remember them all. Users no longer require coming up with robust passwords thanks to password less authentication. No longer is it necessary to memorize passwords.
So, how does this benefit your company? Some users could leave your website or their shopping carts if they need to check in but can’t remember their passwords. People often dislike complexity, which is why they generally dislike resetting the passwords. However, you still need to ensure that their accounts are safe.
2) Strong Cybersecurity Posture
Today’s passwords are no longer a reliable defense against hackers. The same password is frequently used across numerous applications. As a result, there is a reasonable risk that hackers may access numerous accounts if one of the passwords is compromised via phishing, leaked, or stolen. They can collect private client, financial, or intellectual property data.
Passwords are entirely removed in password less authentication solutions, providing defense against the two most common types of cyberattacks: phishing and brute force attacks. Furthermore, there are no credentials for employees to provide using this authentication mechanism, even if they get phishing emails or text messages.
3) Reduced Long Term Costs
Companies invest money and time into managing and storing passwords. The time IT staff spends updating passwords and responding to often altering password storage laws increases the expense. “According to a Forrester analysis, organizations in the US budget over USD 1 million yearly only for support costs associated with passwords. “
Now add that to the time and effort spent finding and preventing password breaches, and you have a sizable annual expense that only rises with time. All these expenses are eliminated by password-less authentication. No more remembering passwords, resetting lost ones or worrying about new compliance regulations.
4) Greater Productivity and Better User Experience
Creating and remembering numerous passwords at once is not advisable. Additionally, the procedure for changing a forgotten password is frequently cumbersome. It is not surprising that employees use the simplest passwords they can remember.
They use the same password for all applications and tools, changing it only when prompted each month by adding a new number or character. In addition, users don’t need to make or remember passwords any longer, thanks to password less authentication. They can authenticate instead using their phone, email, or biometrics.
5) Reinforced Security
Passwords come with dated components, such as password databases. By getting rid of them, theft and security breaches are eliminated. Furthermore, due to redundant password authentication, passwords tend to be repeatable and predictable even when database security is at its highest level.
Disadvantages of Passwordless Authentication
Let’s examine the drawbacks of some forms of passwordless authentication now that we are aware of all the fantastic benefits of passwordless security.
1) Possibly Higher Prices
Although password less authentication offers long-term cost benefits, you could experience short-term increases in expenditures when deploying. For instance, you may have to invest more if you choose a hardware token-based solution. In addition, development costs may be considered when adopting a smartphone-based authentication app or anything similar.
2) Difficult to Troubleshoot
Password resets are annoying, but they are also relatively simple. When employing passwordless authentication, users frequently run into problems due to unfamiliarity. If users misplace their hardware token, troubleshooting becomes considerably more difficult (and expensive). Until the user or client can receive a replacement, your support team will be required to offer a workaround.
Useful link: Zero Trust Strategy, the Modern Security Solution for Cloud
Passwordless Authentication Challenges
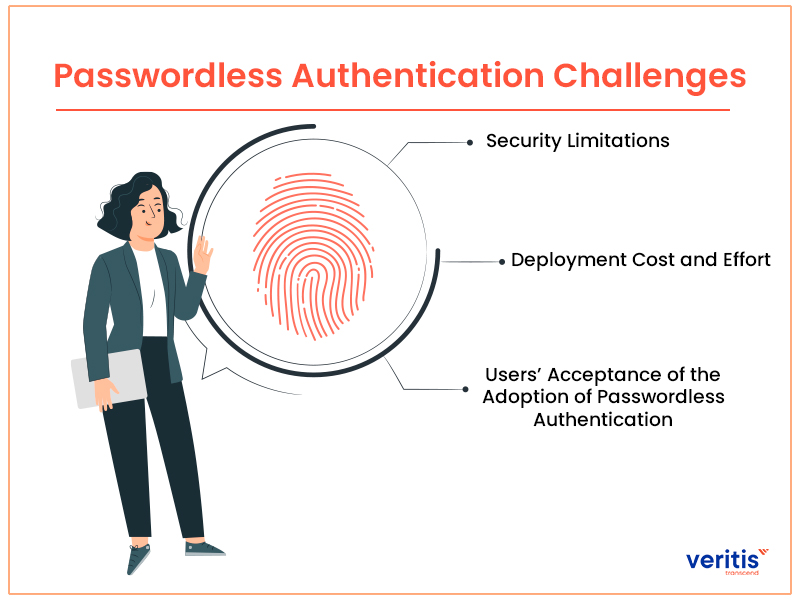
Moreover, there are other security precautions that stakeholders who are reluctant to change and even passwordless authentication cannot overcome. The most frequent difficulties IT teams encounter when attempting to implement passwordless authentication in their organizations are covered in detail below.
1) Security Limitations
Passwordless authentication is a significant advancement over conventional password systems. With passwordless security, threats such as malware, man-in-the-browser attacks, and others are still possible. For instance, One-time passcodes (OTPs) can be intercepted by malware installed by hackers. Additionally, they might install trojans to intercept shared information like magic links or one-time passcodes in web browsers.
Attackers have even reproduced voice recordings and other biometric characteristics. The authentication factor(s) you select will minimize these threats. Additionally, multi-factor authentication (MFA), when combined with other authentication factors, provides even higher levels of protection for passwordless security.
2) Deployment Cost and Effort
Implementing passwordless authentication calls for a comprehensive strategy. It calls for new technology and, in some instances, software. Additionally, employee training is also necessary. Developing a project and change management strategy is necessary to adopt a passwordless feature. The time needed to carry out this plan interferes with other corporate operations or strategic initiatives.
These deployments are expensive. If hardware installation is necessary, you must purchase cards, devices, and tokens for each employee. These will require replacing in the event of further loss or damage. Although using the software may be less expensive, you may need to account for some unanticipated expenses, such as maintenance, software administration, and migration.
3) Users’ Acceptance of the Adoption of Passwordless Authentication
Do many enterprises doubt how to implement passwordless authentication? Implementing passwordless authentication requires a lot of work in the beginning. For each login session, new authentication factors must be applied, necessitating learning new technologies, configuring new hardware, programming biometric authentication factors, and more. Passwordless authentication may not seem convenient to those who are used to password-based authentication.
Overall, it isn’t easy to establish passwordless authentication. But it must solve the challenges in adopting passwordless authentication because it is a successful way to reduce the rising cyber risk associated with password authentication.
Capping it Off
The simplest and least expensive login methods use passwords. An organization’s overall security is increased by switching from traditional passwords to a more secure authentication technique.
Many businesses know that passwords are the main cause of data breaches. Implementing passwordless authentication won’t cost you much compared to the fines and losses brought on by a data breach. As the organization is no longer required to manage password maintenance and resets, passwordless authentication helps businesses save time and resources. We can witness that the use of passwordless authentication is growing. Top tech giants like Microsoft, Google, and Slack have already started using these solutions.
Stevie Award Winner Veritis has provided innovative solutions and advice to Fortune 500 organizations and start-up businesses. Veritis provides multiple technology services as a cost-effective solution for your company. In addition, Veritis can assist your business in transitioning to a password-less environment because we are experts in identity and access management. Contact us to know more about your passwordless feature and secure your solutions.
Consult Our Cybersecurity Expert
Additional Resources:
