
Table of contents
- What is Cloud Computing?
- What are the Types of Cloud Computing Services?
- What are the Types of Cloud Deployment Models?
- Use Cases of Cloud Computing
- KPIs for Cloud Migration Services
- What are the Benefits of Cloud Computing?
- What are the Services Provided by Cloud Computing?
- Cloud Computing Security
- Why is Cloud Security Important?
- What Types of Cloud Security Solutions are Available?
- How Should You Approach Cloud Security?
- Conclusion
Cloud computing entails immediate access to computing resources as needed, such as various computing resources over the internet. These resources include physical and virtual servers, data storage, networking capabilities, software, and development tools, with flexible pay-per-use pricing models.
This model provides customers with significant advantages in terms of flexibility and scalability compared to traditional on-site infrastructure. Cloud computing is integral to numerous activities in everyday life, such as accessing email through services like Gmail, streaming movies on platforms like Netflix, or playing online video games hosted on remote servers.
In the business world, cloud computing is vital for small startups to large multinational corporations. It facilitates remote work by allowing access to data and applications from anywhere. It supports seamless customer engagement across multiple channels and provides the robust computing power required for advanced technologies like quantum computing.
A cloud services provider (CSP) manages these cloud-based services hosted in remote data centers. Typically, these resources are available for payment based on usage or through a monthly subscription model.
Talk To Our Cloud Computing Consultant
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing enables businesses to rent IT resources instead of purchasing them. Rather than making substantial investments in databases, software, and hardware, companies access computing power through the internet, paying only for what they use. These types of cloud computing services encompass various offerings, including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and business intelligence.
This model delivers the speed, scalability, and flexibility essential for businesses to develop, innovate, and maintain their IT solutions effectively.
How Does Cloud Computing Work?

Cloud computing is one of the most significant paradigm shifts that has helped mankind progress in its digital journey. Providing fully managed services through the Internet is called “cloud computing.” Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS) are the three primary categories or kinds of cloud computing providers under which these services fall.
A cloud can be public, hybrid, or private. With specific access and authorization settings, a private cloud is a proprietary network or data center that offers hosted services to a small group of users. Cloud computing’s private or public objective is to offer simple, scalable access to computer resources and IT services.
The cloud infrastructure includes the hardware and software elements required for a cloud computing model’s correct execution. Utility computing and on-demand computing are other terms for cloud computing. The ‘cloud’ icon, frequently used to symbolize the Internet in flowcharts and diagrams, inspired the name cloud computing.
While the future of cloud computing is up in the air, three main cloud providers are shaping the trends. Amazon Web Services is the global leader with its most significant cloud footprint, followed by Microsoft’s Azure and Google Cloud Provider. These three are the biggest cloud providers in the current market. Let’s understand the concept of cloud computing providers and how this technology works.
In the age of interconnectivity, collaboration is the key. The cloud, with its ability to enable clients to access data and cloud applications from distant physical servers, databases, and computers over the internet, is a testament to this. These distant servers, hosted by cloud providers such as Amazon or Microsoft, are part of a global network that we all contribute to and benefit from.
The front end involves accessing the client device, browser, network, and cloud software applications. The back end, which consists of databases, servers, and computers, is connected via an internet network. The back end serves as a repository, holding the information that the front end may access.
A central server controls communications between the front and back ends. It uses protocols to speed up data sharing and governs cloud migration optimization. The central server also uses software and middleware to control communication between client devices and cloud servers. Usually, each specific application or task has its dedicated server. As the cloud has evolved, different types of cloud offerings have emerged. Let’s have a look at the variants of cloud offerings.
Cloud Computing Data
According to industry forecasts, the global cloud computing market will exceed USD 1 trillion by 2028 and reach USD 1.6 trillion by 2030. In 2024, it was valued at USD 615.68 billion. The market is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 17.43% through 2030.
[Source: Precedence Research]
Cloud computing is experiencing rapid growth in developed economies and regions like Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) and Central and Eastern Europe (CEE), as highlighted by recent Oracle research. Currently, 30% of businesses are utilizing types of cloud computing services. Among larger companies, 50% of those with over 2,500 employees are in the process of planning or assessing their cloud strategies. Similarly, 41% of organizations with 1,000 to 2,500 employees also explore cloud adoption.
A global survey conducted by Wipro FullStride IT Cloud Services with 1,300 C-Suite executives revealed that effective digital transformation significantly boosts revenue and profitability. Companies across various sectors reported positive outcomes, with SaaS companies experiencing the highest profit margins. For instance, finance executives saw revenue growth of up to 15% and a 4% rise in profitability.
Additionally, a Deloitte survey found that small and medium-sized businesses leveraging cloud computing architecture achieved 21% higher profits and 26% faster growth than those that did not adopt cloud computing trends.
According to Oracle, 60% of CxOs identify enhanced security as the primary advantage of cloud computing. This benefit surpasses other vital advantages such as cost savings, scalability, ease of maintenance, and operational speed.
According to PwC, most enterprises find it difficult to realize the return on investment (ROI) from cloud computing. Approximately 53% of businesses have not yet seen significant value from their cloud investments, which can be frustrating for those who migrated to the cloud expecting cost savings.
What are the Types of Cloud Computing Services?
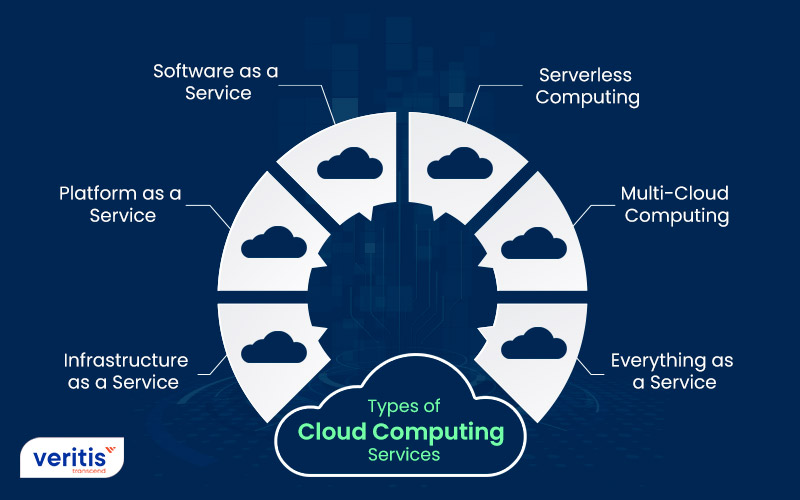
There are different types of cloud computing services. Here, we shall list the most used IT cloud services.
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Application programming interfaces (APIs) are provided by IaaS providers, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), to enable customers to move workloads to virtual machines (VM). Users are given some storage space and can start, stop, access, and modify the virtual machine and storage as needed. For different workload requirements, IaaS providers provide small, medium, big, extra-large, and memory- or compute-optimized instances in addition to providing instance customization. The IaaS cloud model is like a remote data center for commercial customers.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS allows MSPs to provide a development platform to their clients. Here, they host the required tools and environments desired by their clients. Users may access these tools online using APIs, web portals, or gateway software. PaaS is utilized to create all types of software, and several PaaS service providers host the finished product.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Software as a service (SaaS) is a method of distributing programs via the Internet; these programs are sometimes called web services. Users can access SaaS apps and services anywhere via an internet-enabled PC or mobile device. In addition, users get access to databases and application software under the SaaS model. The productivity and email capabilities provided by Microsoft 365 are typical examples of SaaS applications.
- Serverless Computing: Some might find the phrase “serverless” perplexing, but it doesn’t mean your code must run without a server. The goal is to create and operate apps without handling server management. Users are not required to participate in server maintenance. Enterprises don’t have to worry about serverless architecture’s underlying infrastructure. As the cloud vendor handles the back-end services, serverless configuration eliminates several hassles, including maintenance and capacity issues. This allows the business to concentrate its efforts elsewhere.
- Multi-Cloud Computing: Unlike the hybrid cloud, which combines an on-premises private cloud with public cloud services from third parties, multi-cloud is a mix-and-match arrangement of cloud services from various service providers tailored to particular workload requirements. In other words, a multi-cloud is a hybrid cloud that utilizes several different public cloud infrastructures. Multiple strategic advantages are possible with a multi-cloud approach. Businesses relying on one cloud service provider may experience challenges like cloud data center outages or bandwidth problems, which might hurt their operations and even cause them to lose clients. This is especially true when some of their essential apps are involved. Utilizing various cloud services guarantees that downtime and data loss are minimized even if components of one or more software, hardware, network, etc., fail. A multi-cloud approach also allows cloud computing for businesses to meet the varying needs of the many business operations, teams, and departments.
- Everything as a Service: The service, also called XaaS, is one of the upcoming cloud offerings. Organizations worldwide utilize XaaS, or anything-as-a-service, a cloud computing service, to create and introduce products of any size and scope. The infrastructure includes several IT applications, items, and devices connected to remote access and cloud infrastructures. In a word, service is the transformation of any functionality. Organizations are gravitating more and more toward the XaaS model because of its flexibility in terms of price and output.
Organizations that serve millions of clients are increasingly utilizing XaaS. Cloud computing for businesses may have web browsers and app stores that must constantly be accessible online. Users of XaaS-integrated businesses, therefore, frequently experience a fluid workplace because everything is easily accessible on their browser or app.
Explore Cloud Consulting Services
What are the Types of Cloud Deployment Models?
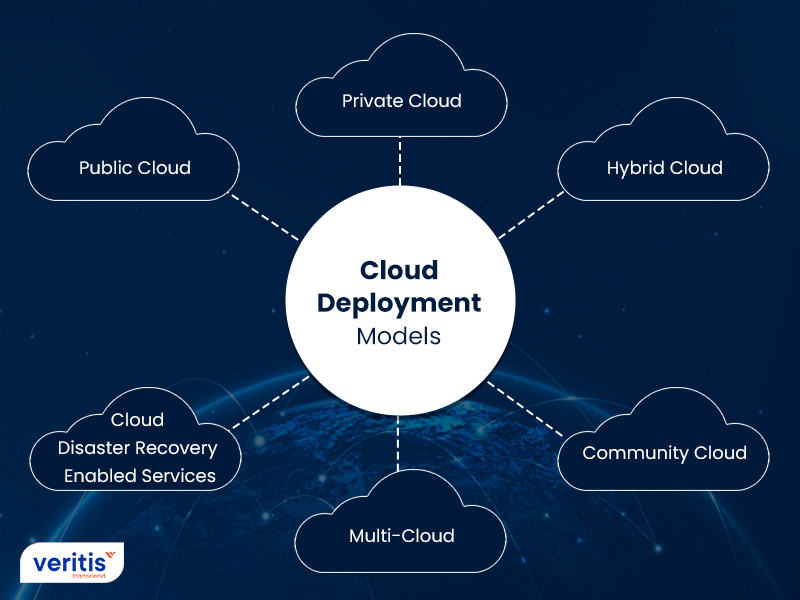
As one can expect, there are different types of cloud deployment models. Let’s dig in:
- Public Cloud: In the public cloud model, a third-party cloud service provider (CSP) delivers the cloud service online. Although many services are accessible with long-term commitments, public cloud services are often supplied on demand and by the minute or hour. Only the central processing unit cycles, storage, or bandwidth that customers use are charged to them. Leading public CSPs include IBM, Oracle, Tencent, AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
- Private Cloud: Internal users receive private cloud services from a company’s data center. An organization creates and manages its underpinning cloud infrastructure using a private cloud. This architecture keeps the administration and security issues in cloud computing control to local data centers while delivering the flexibility and convenience of the cloud computing trends. VMware and OpenStack are standard private cloud technologies and providers.
- Hybrid Cloud: A hybrid cloud combines on-premises private cloud infrastructure with public cloud services, orchestrating and automating operations across the two. Companies can use the public cloud to accommodate workload surges or demand spikes while running mission-critical workloads or sensitive applications on the private cloud. The objective of a hybrid cloud is to provide a unified, automated, scalable environment that makes the most of public cloud infrastructure while keeping mission-critical data under your control.
- Cloud Disaster Recovery Enabled Services: Now and then, unforeseen circumstances bring a company to its knees. Natural disasters are one of those circumstances which can bring forth such results. Clients are roping in MSPs who provide cloud disaster recovery services to ensure such doesn’t happen.
- Multi-Cloud: Companies can respond mainly to the varying needs of their various business activities, teams, and departments thanks to a multi-cloud approach. These include the cloud’s security, privacy, performance, or geographic reach. Multiple strategic advantages are possible with a multi-cloud approach. Businesses that rely only on one cloud service provider may experience challenges like cloud data center outages or bandwidth problems, which might hurt their operations and even cause them to lose clients. This is especially true when some of their essential apps are involved. Utilizing various cloud services guarantees that downtime and data loss are minimized even if components of one or more software, hardware, network, etc., fail. However, multi-cloud installations should become more straightforward as providers’ services and APIs converge and become more standardized through industry initiatives like the Open Cloud Computing Interface.
- Community Cloud: A community cloud, which several enterprises use, serves a specific community with similar goals, policies, security issues in cloud computing needs, and compliance requirements. It may be on or off premises or maintained by these companies or a different provider.
Useful link: Cloud Implementation Services: Strategy, Solutions and Benefits
Use Cases of Cloud Computing
1) Cloud-based Data Storage and Backup
Cloud computing offers a reliable solution for data storage and backup. Organizations can safely store substantial amounts of data in the cloud, minimizing the potential for data loss from hardware failures or other disasters. Cloud storage providers ensure high redundancy and robust data protection, guaranteeing continuous access to critical information.
2) Scalable Application Hosting
Businesses benefit from cloud computing architecture by hosting applications and websites in a scalable environment. Cloud platforms provide the necessary infrastructure for varying traffic loads, ensuring consistent performance for simple web applications and complex enterprise systems.
3) Collaborative Work Environments
Cloud-based collaboration tools have revolutionized teamwork by enabling real-time access to shared documents, spreadsheets, and communication platforms. These tools enhance productivity and efficiency, especially for remote and distributed teams.
4) Software Development and Testing
Developers leverage cloud platforms for software development and testing. By providing access to diverse development tools, virtual machines, and testing environments, the cloud allows for creating, testing, and deploying applications without extensive on-premises infrastructure.
5) Big Data Analytics
The cloud’s processing power and storage capabilities have transformed big data analytics. Organizations can quickly and efficiently analyze large datasets, deriving valuable insights that inform strategic business decisions.
6) Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
Cloud computing is essential for IoT implementations. IoT devices generate extensive data that can be processed, analyzed, and utilized in the cloud computing trends. This enables real-time monitoring, control, and automation across various industries, enhancing operational efficiency.
7) Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
Cloud-based disaster recovery solutions offer businesses a secure and dependable method for backing up critical data and applications. Organizations can swiftly restore operations in a disaster, ensuring business continuity and minimizing downtime.
8) Healthcare and Telemedicine
Cloud computing has driven significant advancements in healthcare and telemedicine. Medical professionals can securely access patient records, collaborate on diagnoses, and conduct remote consultations, broadening healthcare access and improving patient outcomes.
9) Financial Services
The financial sector has embraced cloud computing for online banking, mobile payment applications, and algorithmic trading platforms. Cloud-based solutions provide enhanced security, scalability, and real-time processing capabilities for financial transactions, meeting the industry’s stringent requirements.
10) E-learning and Education
Cloud computing platforms have dramatically impacted the education sector by providing scalable and flexible solutions for e-learning. Educational institutions can deliver online courses, host virtual classrooms, and store vast educational content in the cloud. This facilitates remote learning, provides access to a wide range of resources, and supports collaborative learning environments, enhancing the overall educational experience.
How Different It Is from Traditional Computing
Due to the public cloud’s wide variety of services and capabilities, there has been some confusion about the relationship between cloud computing platforms and essential applications, including web hosting.
Although hosting websites on the public cloud is expected, the two are very different.
Three distinctive qualities set a cloud service apart from conventional web hosting:
- Large quantities of processing power are available to users on demand. It is usually offered for sale by the minute or the hour.
- Thanks to its elastic nature, users can have as much or as little of a service as they want at any time.
- The customer requires a personal computer and internet connectivity because the supplier controls the service entirely. The development of distributed computing, virtualization, and easier access to high-speed internet has significantly increased interest in cloud computing providers.
Importance of Setting KPIs for Cloud Migration Services
For several reasons, establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) for cloud migration is crucial. First, KPIs translate your business objectives into measurable outcomes, ensuring the migration aligns with your strategic goals. Setting these indicators creates a clear measurement framework to evaluate the migration’s success.
KPIs also play a vital role in monitoring and managing the migration process. They offer a structured approach to monitoring progress, detecting potential issues, and making informed decisions during the migration process. Predefined metrics help maintain project alignment and achieve targeted goals.
Moreover, defining KPIs before starting the migration helps in securing stakeholder buy-in. Cloud migration is a significant investment in both time and resources, and it is essential to have the support of key stakeholders. Presenting clear, measurable KPIs demonstrates a well-thought-out plan and helps justify the investment, making it easier for decision-makers to gain approval and commitment.
Setting KPIs for cloud migration services is essential for translating business goals into measurable outcomes, effectively managing the migration process, and securing stakeholder support. These indicators ensure the migration delivers the desired value and aligns with your business strategy.
Types of KPIs
If your team is new to cloud migration, identifying the right metrics to measure can be challenging. Establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) is crucial for tracking progress and success. KPIs for cloud migration projects typically fall into three categories:
1) Customer Experience
These KPIs focus on how your customers interact with your cloud-based services. Consider monitoring:
- Latency: Measure the time data travels between your cloud server and the end user. High latency can negatively impact user experience.
- Error Rates: Track the frequency of errors encountered by users. This can indicate issues with the migration or performance of cloud services.
- Customer Satisfaction: Gauge customer satisfaction post-migration using Net Promoter Scores, surveys, focus groups, and other feedback mechanisms.
2) Performance
This category compares the performance of your systems before and after the migration. Key metrics include:
- Load Average: Assess the average load on your CPU over a specific period to determine system demand trends.
- Memory Utilization: Monitor how efficiently your applications use available memory, a critical resource.
- CPU Utilization: Track CPU usage to ensure it is within optimal ranges. Usage near 100% can indicate performance issues.
- Response Times: Measure the time it takes for user requests to be processed and completed.
- Uptime: Track the availability of your cloud services. While 100% uptime is unrealistic, maintaining high availability is crucial.
3) Security
Security metrics are vital, as breaches can have severe consequences for your business. Key security KPIs include:
- Third-Party Services: Monitor the security of third-party services and contractors accessing your data.
- Indicators of Compromise (IOCs): Track anomalies such as unusual login attempts, spikes in data access, and changes in mobile settings to detect potential security breaches.
- Access Controls: Ensure that access to cloud data is tightly managed. Regularly audit S3 bucket permissions and user access.
- User Audits: Conduct audits to identify how many users need access to your services or applications, focusing on minimizing internal security risks.
- Data Exposure: Analyze your servers and applications for vulnerabilities that could lead to data breaches.
Developing a KPI Strategy
These KPIs are a starting point. Once you’ve identified the metrics most relevant to your business, you can begin to measure and monitor them consistently. Tracking these KPIs over time, not just during the migration process, will provide insights into performance trends and areas for improvement.
Preparing for Cloud Migration
Migrating to the cloud is a sophisticated process that demands thorough preparation. Analyze your current IT environment and processes to identify potential challenges and opportunities. Form a dedicated migration team responsible for planning, executing, and monitoring the migration. This team should also develop and track the selected KPIs to ensure a smooth transition and ongoing cloud environment optimization.
By carefully selecting and monitoring relevant KPIs, you can effectively manage your cloud migration project, ensuring that it meets business objectives and delivers value over the long term.
Useful link: 6 Cloud Trends Which Shall Dominate
What are the Benefits of Cloud Computing?
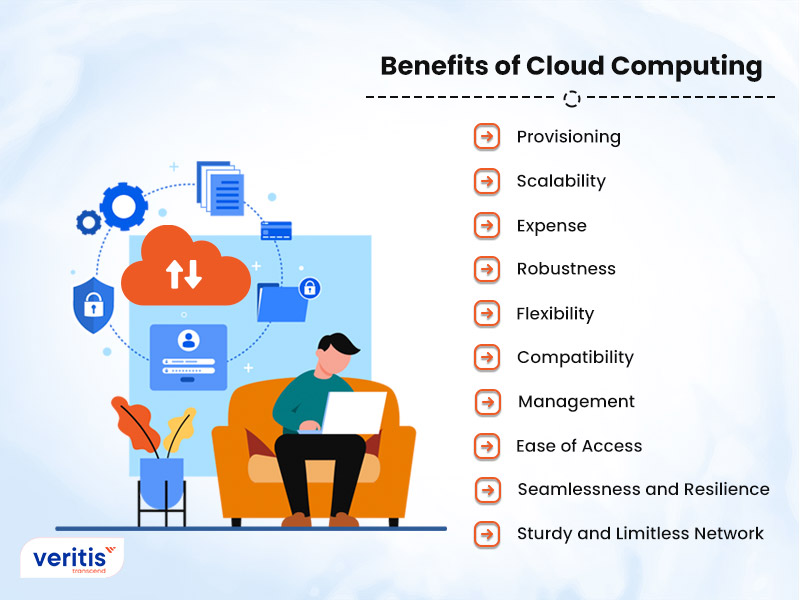
Cloud computing has been around for a while, and today’s cloud computing infrastructure exhibits various traits that have had a significant positive impact on enterprises of all sorts.
The following are some of the properties of cloud computing:
- Provisioning: End users may instantly fire up computing resources for virtually any job. They can now supply computing resources such as server time and network storage, eliminating the requirement for IT administrators to traditionally provision and manage computing resources.
- Scalability: Companies can scale up as computing needs rise and down again as needs fall. As a result, there is no longer a need to make substantial expenditures on local infrastructure that may or may not stay functional.
- Expense: Clouds offer their clients a pay-per-use model. This means that the clients pay for the resources used alone. This is a significant savings mechanism, as clients don’t have to take on resources they don’t need.
- Robustness: MSPs often implement redundant resources to ensure resilient storage and keep users’ critical workloads running across multiple global regions.
- Flexibility: To improve cost savings or take advantage of new services as they become available, organizations can shift specific workloads to or from the cloud—or to other cloud platforms—as requested or automatically.
- Sturdy and Limitless Network: Anywhere with an internet connection, a user may view cloud data or submit the data to the cloud using any device. Any device from any corner of the world can access the same data.
- Compatibility: With multi-tenancy, Multiple clients can share the same physical infrastructures or applications while protecting their data’s privacy and security. Cloud service providers may serve several clients using the same physical resources through resource pooling. The cloud providers’ resource pools have to be sizable and adaptable enough to accommodate the needs of several clients.
- Management: Utilizing cloud infrastructure allows businesses to save on capital expenses by avoiding the high cost of purchasing and maintaining equipment. Because companies don’t need to invest in hardware, buildings, utilities, or the construction of massive data centers to meet their expanding operations, this lowers their capital expenditure expenditures. Additionally, because they can depend on the experience of the teams at their cloud providers, they don’t require sizable IT teams to manage cloud data center operations. Additionally, downtime expenses are reduced via cloud computing platforms. Because downtime is so rare with cloud computing, businesses don’t have to spend time or money resolving potential downtime-related problems.
- Ease of Access: Users who save information in the cloud may access it using any device and internet-connected location. Users no longer need to carry many CDs, USB devices, or external hard drives to access their data. Smartphones and other mobile devices may be used to access company data, allowing distant employees to keep in touch with coworkers and clients. The cloud makes it simple for end users to process, store, retrieve, and restore resources. Additionally, cloud suppliers immediately supply all upgrades and updates, saving time and effort.
- Seamlessness and Resilience: Data loss is a concern for all businesses. Users can always access their data by storing it in the cloud, even if their devices, such as laptops or smartphones, aren’t working. With cloud-based services, cloud computing for businesses may quickly restore their data during calamities like power outages or natural disasters. This is advantageous to BCDR and ensures that workloads and data remain accessible even in the event of damage or disruption to the organization.
Useful link: 10 Awesome Business Benefits of Cloud Computing Services
What are the Services Provided by Cloud Computing?
Amazon, Microsoft, and Google offer the most secure, adaptable, and dependable cloud services dominating the public cloud market. Customers can access various storage, computation, and networking choices through AWS, Azure, and GCP’s cloud platforms. In terms of capability and maturity, AWS is now far more extensive than both Azure and GCP. The other two likewise develop more quickly to demonstrate their superiority in the market. Let’s dig into each of the cloud services.
Amazon Web Services (AWS)

Amazon, a cloud computing leader, entered the cloud services market over ten years ago and continues to dominate in terms of the number of products and users. AWS is the industry standard for cloud service quality.
The infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) products and services that AWS provides fall into the following categories: computing, databases, content delivery and storage, and networking. Using serverless technologies like Amazon Kinesis Streams, Amazon SQS Queues, and AWS Lambda Functions, AWS allows a seamless and adaptable data collection pipeline. In addition, it offers cloud computing businesses a choice to select, among other things, the operating system, database, and programming languages that best suit their needs.
Utilizing AWS management tools like AWS CloudTrail and Amazon CloudWatch for tracking user activity and AWS Config for controlling resource inventory and modifications, it is possible to keep tabs on how much of a cloud infrastructure’s resources are being used.
AWS significantly improves an organization’s efficiency and business expansion. However, the complicated infrastructure and service constraints configured by default to meet the demands of typical users are a couple of its downsides. The largest of the three cloud service providers, Amazon has data centers spread throughout 84 different areas of the globe.
Microsoft’s Azure

Microsoft’s vast network of data centers may be used to create, deploy, and administer various services and applications. Compute, networking, data management, databases, and performance are all included in Azure’s capabilities.
Organizations of all sizes may organize site-to-site replication and data recovery to virtual machines (VMs) hosted on Azure using Azure Site Recovery. Additionally, Azure provides Zone Redundant Storage (ZRS), which is redundant data storage across many data center regions. Through a private link instead of the internet, Azure ExpressRoute allows the data center to connect to Azure, offering more security, excellent dependability, and reduced latency.
Google Cloud

Google Cloud Platform is a compelling alternative to AWS and Azure because of its user-friendly UI, reduced rates, preemptible instances, and configurable computing options. Google fully encrypts all data and communication routes, including traffic between data centers.
Google Cloud and AWS battle fiercely in several areas, including machine learning, cost-effectiveness, privacy, traffic security, and instance and payment configuration. For a commitment of one to three years, all three cloud providers provide up to 75% discounts. Google, however, also provides a sustained use discount of up to 30% on each instance type operating for more than 25% every month.
GCP’s credit of USD 300 for 12 months paired with a free tier that isn’t time-limited matches AWS’ 1-year free trial. The credit approach for GCP is better suited for businesses just starting to use cloud services. Google provides several pre-built APIs for translation, natural language processing, and computer vision. In addition, machine learning developers use the open-source TensorFlow deep learning framework to create models for Google’s Cloud Machine Learning Engine.
Useful link: AWS Vs Azure Vs GCP – The Cloud Platform of Your Choice?
Cloud Computing Security
Contemporary solutions unintentionally planted the seeds for cloud security issues. Unexpected issues have emerged as a result of accessibility. The cloud-hosted solutions were accessible to anybody with the necessary credentials.
Why is Cloud Security Important?

As threat actors infiltrate and attack businesses in numerous industries, security events and accidents are occurring alarmingly, turning the IT industry into a crime scene. Hacks weren’t widespread, but threat actors began focusing on organizations far more vulnerable to coercion after the epidemic. Businesses worldwide are changing their authentication procedures in response to these instances. However, despite their attempts, not all is okay.
According to a study report by Hypr, a multi-factor authentication (MFA) specialist business, the banking industry still faces challenges despite its desire to thwart these attacks. The research found that 3.4% of breaches at financial institutions occurred in the United States and Europe last year. Financial institutions such as banks, credit unions, and investment businesses suffered an average loss of USD 2.19 million due to these breaches. These losses, however, do not consider the “intangible and hidden costs” that these instances entailed.
Useful link: Cloud Security Automation: Best Practices, Strategy, and Benefits
What Types of Cloud Security Solutions are Available?
While there are various solutions, MFA and Zero Trust Strategies are picking pace. In addition, identity and access management solutions (IAM) have been created for companies that want customized security solutions.
Zero trust doesn’t always imply mistrust; instead, it suggests that everyone is scrutinized equally, regardless of their roles and responsibilities. The tactical method uses multi-factor authentication (MFA), requiring at least two keys to open one lock. A corporation may breathe easy knowing that its corporate assets are better protected with MFA when a user selects their primary password and a dynamic password is offered at login.
How Should You Approach Cloud Security?
Organizations should understand that there is no universal plan that works for everyone.
Each zero-trust strategy is distinct since the enterprise’s business needs to determine the implementation and methodology. After the plan has been developed, it must be ensured that it remains relevant in an always-evolving world.
Conclusion
There is a lot more to cloud computing than meets the eye. While most think the cloud only offers storage and pay-as-you-go resources, cloud technology is much more than that, for it ushered in a paradigm shift in our lifestyle and production methodologies. It is commendable how far we have come since the cloud’s inception, but as one may have observed, we are still hurtling through the journey as innovations continue to shape cloud technology.
It is tough to keep up with these innovations, and most solve these worries by roping in Veritis, the Stevie and Globee Business Awards winner. Internationally renowned for excellence, Fortune 500 companies and emerging enterprises rely on our expertise to keep things moving. So, tarry not a moment and approach us to harness the power of the cloud.
Got Questions? Schedule A Call
Additional Resources:
- AWS vs Azure vs GCP: Cloud Cost Comparison
- How to Enhance Security in the Multi-Cloud Era
- Which Cloud has Better Private Connectivity: AWS or Azure or GCP?
- 9 Keys to Selecting a Right Cloud Managed Services Provider (MSP)
- AWS Machine Learning Tools in the Cloud
- Cloud Trends Which Shall Dominate 2024
- Top 5 Reasons for Cloud Migration Failure!
- Hybrid Cloud Vs Multi Cloud: What’s the Difference!