
With modern technologies and solutions, security has become a prime concern, especially as identity and access management industry trends continue to evolve. Password and network hacking are becoming increasingly accurate. Hacking an alphanumeric password takes less than a second, reinforcing the urgency behind the latest trends in identity and access management.
Unprotected data or data not stored on a private server can be compromised. Large scale breaches can cause reputation damage, financial losses, and, most importantly, exposure to sensitive clientele information, a growing concern across the identity and access management market.
Hence, IAM has become a priority for organizations that want to add an extra layer of security to the business network, driven by identity and access management trends and rising cyber risk. It is also necessary if your organization has numerous departments with team members holding unique roles.
Organizations can record employee activity through identity and access management trends and IAM trends, and moderate access to programs and applications. This can deny unauthorized access and detect suspicious patterns, transactions, and errors, aligning with emerging trends in identity and access management.
Thanks to the introduction of IAM, organizations are now undergoing a secure and controllable digital transition in identity management and security, in line with broader identity and access management industry trends. IAM aids in creating a user centric and seamless digital workspace where most of the identity access management strategy is automated, reflecting the latest trends in identity and access management.
Organizations must develop optimal strategies to deploy IAM effectively. The friction involved in each IAM implementation determines an initiative’s success or failure. In 2026, IAM researchers and vendors will concentrate more on new directions and security postures to improve IAM implementation, shaping future IAM trends.
According to a recent study, nearly 78% of companies have disclosed an identity related data breach that has negatively affected their operations. Furthermore, 96 percent of respondents believe that the hack and its consequences could have been avoided if they had used better identity based zero trust measures, a key focus area in emerging trends in identity and access management.
Hence, it shouldn’t be surprising that the global cloud identity and access management market is expected to expand at a CAGR of 22.71% to reach USD 13.42 billion by 2027. Although identity and access management frameworks are nothing new, much can be done to keep intruders from breaking into your systems with conventional tactics and technologies as identity and access management trends continue to mature.
Schedule a Call with Our IAM Expert
What is identity and Access Management (IAM)? IAM refers to the procedures, guidelines, and technological tools used to manage digital identities and restrict access to systems and data, forming the foundation of modern identity and access management. IAM systems are designed to prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and other security threats while ensuring that only approved users can access resources.
IAM is the process of controlling user authentication (verifying a user’s identity), authorization (providing access to particular resources depending on a user’s identity and rights), and user management (maintaining a user’s sensitive data such as passwords, roles, and permissions). Effective IAM is crucial for maintaining security and IAM regulatory compliance.
Let’s quickly review some concerns businesses can resolve when implementing an all encompassing IAM solution, especially in line with evolving identity and access management trends.
1) Cost Savings
One of the main issues businesses have been the rapidly rising expenses of resource management and control, a challenge widely discussed in the identity and access management market. IAM might decrease expenses related to managing user accounts and access credentials. In addition, organizations may effectively manage the resources needed to administer user accounts by automating identity and access management best practices operations aligned with IAM trends. This also lowers the possibility of mistakes that could result in security problems, reflecting the latest trends in identity and access management.
2) Scalability
Identity and Access Management services can help manage the complexity of access control and user management as a business expands, while upholding security and compliance, addressing key emerging trends in identity and access management, and anticipating long term industry trends.
3) Security
Identity and Access Management (IAM) provides a multi layered defense system that incorporates access controls, privilege management, and multi factor authentication to ensure that only authorized people can access critical information and resources, a core focus across current identity and access management trends.
4) Productivity
IAM (Identity and Access Management) can boost productivity by automating user access to resources and reducing the time and effort required to manage user accounts and passwords, which is increasingly emphasized in IAM trends and the latest trends in identity and access management.
5) Compliance
Businesses must abide by several legal regulations, including SOX, GDPR, and HIPAA. Identity and access management solutions ensure enterprises have the tools to protect user data and maintain audit logs, helping them comply with these regulations and remain aligned with evolving identity and access management market expectations and emerging trends in identity and access management.
Useful link: IAM Best Practices for Optimal Cloud Security
Key IAM Challenges and Investment Priorities for 2026

The 2026 Identity and Access Management strategy report put a spotlight on primary challenges, gaps, and what works for organizations and security operations teams when it comes to confidential data, information, and workflows:
1) Access Management Challenges
- Lack of automated processes, responsibility to manually create and define access roles and regulations
- A shortage of skilled employees
- High usage and dependency on mobile devices
- Minimal availability of budgets
- Unavailability of proper resources and technologies
2) Impact of Unauthorized Access
Perhaps one of the most significant challenges cybersecurity organizations face is unauthorized access, which leads to
- Hindrance in business activities, workflows, and daily work
- A decline in employee productivity
- High system downtime
- Increased tickets and support for troubleshooting
- Considerable loss in revenues
3) Commonly Used IAM Features
- Role based, limited access control
- Provisioning of automated users
- Single sign on method
- Monitoring of workflows and application access
- Audit reporting
4) Drivers Behind IAM Adoption
- Cybersecurity
- Minimizing data breaches
- Enhancing operational efficiency
5) IAM Investment Focus Areas
Organizations are carving out funds in annual budgets to leverage:
- Privileged access management
- Identity management and governance
- Multi factor authentication program
6) Preferred Authentication Methods
- Username and password
- Software tokens
- Out of band authentication
Useful link: 5 Reasons Why Financial Sector Needs Identity and Access Management (IAM)
How does IAM help your industry?
IAM solutions have been offered to secure and manage identities in industries ranging from finance to healthcare while providing consumers with the convenient, seamless, real time access they demand.
| Finance | Government | Retail |
| Protect sensitive patient information | MFA for mission critical legacy applications | Reduces IT costs with Single Sign On |
| Meet mandatory compliance and regulatory measures | Controlling extensive user access and automating authentication | Manage vendor access via MFA and federated identity |
| Regulate staff access and defy “permission bloat.” | Protecting workflows and systems at entry points | Authenticate users across multiple locations |
| It gives organizations more control to speed up onboarding | To improve information security, identities must be monitored and handled regularly | Improves employee lifecycle management |
Top Identity and Access Management Trends for Enterprises
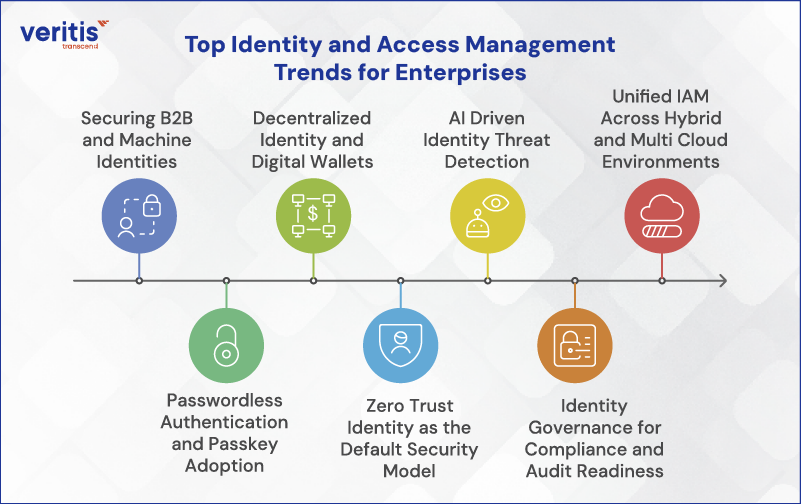
1) Securing B2B and Machine Identities
By 2026, non human identities such as APIs, bots, IoT devices, and third party integrations will outnumber human users by more than 3:1. Enterprises are prioritizing continuous validation, automated lifecycle management, and privileged access controls to reduce supply chain risk and prevent machine based breaches.
2) Passwordless Authentication and Passkey Adoption
Passwordless authentication is moving into the mainstream in enterprises. Passkeys based on FIDO2 and WebAuthn are replacing passwords in high risk sectors like banking and healthcare, reducing phishing exposure while improving user experience and regulatory compliance, including PSD2 and eIDAS 2.0.
3) Decentralized Identity and Digital Wallets
The rise of deepfakes and synthetic identities is accelerating the adoption of decentralized identity models. Blockchain backed identifiers and digital wallets enable verifiable credentials, reduce dependency on centralized identity stores, and give users greater control over personal identity data.
4) Zero Trust Identity as the Default Security Model
Zero Trust has shifted from a framework to a default IAM operating model. Enterprises now enforce continuous authentication, adaptive access policies, and least privilege controls based on identity context rather than network location.
5) AI Driven Identity Threat Detection
IAM platforms increasingly use AI and behavioral analytics to detect anomalous access patterns, insider threats, and account compromise in real time. This enables proactive identity risk scoring rather than reactive incident response.
6) Identity Governance for Compliance and Audit Readiness
Stricter global regulations are driving deeper investment in identity governance and administration (IGA). Automated access reviews, policy enforcement, and audit trails are now essential for regulatory compliance and enterprise risk management.
7) Unified IAM Across Hybrid and Multi Cloud Environments
Enterprises are consolidating IAM across cloud, SaaS, and partner ecosystems. Unified IAM platforms reduce complexity, improve visibility, and ensure consistent access control across increasingly fragmented environments.
Risk Drivers Impacting IAM in 2026
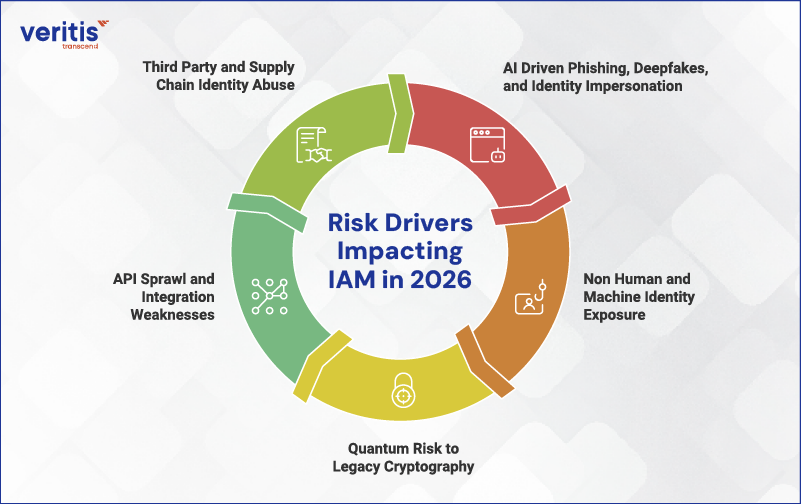
IAM has become the primary control plane for cyber risk. In 2026, identity is the dominant attack surface across enterprises.
1) AI Driven Phishing, Deepfakes, and Identity Impersonation
Attackers are using generative AI to create highly convincing phishing campaigns, voice clones, and deepfake videos that impersonate executives, employees, and trusted partners. In 2026, identity based social engineering has surpassed malware as a leading cause of breaches, bypassing traditional authentication methods.
Risk implication: Static credentials and one time checks are not sufficient.
2) Non Human and Machine Identity Exposure
By 2026, non human identities such as APIs, service accounts, bots, and workloads outnumber human users by more than 3:1 in large enterprises. Poor lifecycle management, over privileged access, and lack of visibility make machine identities a high value target.
Risk implication: Unmanaged machine identities create silent, persistent attack paths.
3) Quantum Risk to Legacy Cryptography
Advances in quantum computing are accelerating concern around the long term viability of traditional cryptographic algorithms. While large scale quantum attacks are not yet mainstream, harvest now, decrypt later strategies are already being used against sensitive identity data.
Risk implication: IAM systems relying on legacy cryptography face future exposure and compliance risk.
4) API Sprawl and Integration Weaknesses
Modern enterprises depend on thousands of APIs connecting SaaS platforms, partners, and internal systems. In 2026, API sprawl combined with inconsistent authentication and authorization controls is a major driver of identity related breaches.
Risk implication: Weak integration governance expands the attack surface beyond human users.
5) Third Party and Supply Chain Identity Abuse
Vendors, contractors, and partners often retain excessive or long lived access. Breaches increasingly originate from compromised third party identities rather than direct attacks on the enterprise itself.
Risk implication: External identities are now among the highest impact risk vectors.
IAM Maturity Model and Key Performance Metrics
To assess and improve your identity and access management strategy, use this simplified maturity framework:
| Stage | Characteristics |
| Basic IAM | Password based login, limited MFA, siloed systems |
| Advanced IAM | SSO, role based access, MFA, some Zero Trust principles |
| Strategic IAM | Passwordless, ITDR enabled, decentralized identity, dynamic access governance |
Identity and Access Management Roadmap for 2026
Transforming your IAM landscape requires a structured rollout. Here’s a tactical roadmap:
- Inventory All Identities: Classify users, machines, B2B partners, and APIs
- Adopt Passkeys: Implement passwordless authentication for high risk roles
- Deploy ITDR Tools: Use platforms like Netwrix or Authomize to monitor abnormal behavior
- Pilot Digital Wallets: Explore decentralized identity options in customer onboarding or workforce use cases
- Shift to Zero Trust: Apply continuous, context aware access evaluation
- Strengthen Governance: Monitor quantum threats, API exposure, and access privilege drift
Emerging IAM Technologies and Standards
1) Passkey and Modern Authentication Standards
These replace passwords and implement phishing resistant login using FIDO2/WebAuthn standards.
- Okta Identity Engine / Okta Adaptive MFA: Supports passkeys and passwordless flows
- Microsoft Entra ID (Azure AD): Native passkey + WebAuthn support
- Google Cloud Identity: Passkey + phishing, resistant authentication
- Duo Beyond (Cisco): Strong MFA + passkey integration
Standards: FIDO2, WebAuthn, CTAP
2) Identity Threat Detection and Response (ITDR)
ITDR tools provide real time detection, analytics, and response for identity abuse across environments.
- CrowdStrike Falcon Identity Threat Protection: Behavioral identity analytics
- Microsoft Defender for Identity (MDI): Detects identity attacks in AD/Azure
- IBM Security Verify with ITDR capabilities: Identity risk insights
- CyberArk Identity Security Posture and Threat Detection
- BeyondTrust Secure Remote Access + Analytics
These tools cover monitoring, anomalous access detection, and automated response, which are essential to evolving IAM trends.
3) Decentralized Identity Frameworks and Verifiable Credentials
Decentralized identity tooling is newer but gaining enterprise pilot adoption.
- Sovrin Foundation / Hyperledger Indy, decentralized ID network
- Evernym Verity, enterprise DID and verifiable credentials platform
- Microsoft ION (Decentralized Identity on Bitcoin), production DID network
- uPort / Transmute DID tools, DID, and VC implementations
Standards: W3C Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs), Verifiable Credentials
4) Biometric and AI Augmented Identity Verification
These tools combine biometrics with AI to deliver robust identity proofing and fraud prevention.
- Ping Identity + PingOne MFA Biometrics
- Okta Verify with Biometrics
- Jumio / Onfido / Socure, AI driven biometric ID proofing, document verification
- BioCatch / BehavioSec, behavioral biometric analytics
- ID.me, multi factor identity verification with biometric checks
These tools strengthen onboarding and high risk access decisions.
5) IAM Platforms with Integrated Advanced Controls
Modern identity platforms consolidate access, governance, MFA, and AI risk detection.
- Okta Identity Cloud: Adaptive access, passwordless, risk analytics
- Microsoft Entra ID + Microsoft Security Suite: Unified identity + security
- IBM Security Verify: Comprehensive IAM + governance + MFA
- ForgeRock Identity Platform: Identity governance and consumer identity
- SailPoint IdentityNow / IdentityIQ: Strong governance + analytics
These are enterprise grade solutions reflecting leading identity and access management market adoption.
6) Identity Governance and Administration (IGA)
These tools help enforce policies, manage the identity lifecycle, and ensure compliance across identities.
- SailPoint IdentityNow / IdentityIQ
- Saviynt Enterprise Identity Cloud
- IBM Security Identity Governance and Intelligence
- Oracle Identity Governance
- Micro Focus NetIQ Identity Manager
These tools are not upgrades; they are essential defenses in the identity and access management market reshaped by hyperconnectivity and AI driven threats.
Case Study: Professional Services Firm Migrates from SailPoint to Azure AD
Veritis guided a major professional services firm through a seamless transition from on premises SailPoint to Azure Active Directory, synchronizing identities, automating provisioning with Azure Automation and PowerShell, and enforcing Conditional Access and MFA. This successful migration not only reduced licensing and infrastructure costs by over 50% and decreased IAM support effort by 30% but also strengthened the security posture and achieved full audit ready compliance with zero downtime, ensuring a smooth and beneficial transition.
Read the complete case study: Successful Migration of a Services Firm from SailPoint to Azure AD
Conclusion
We recognize the demand for a flexible, user friendly IAM platform. Veritis, the Stevie Award winner, offers a one stop shop for all your identity and access management solutions requirements. We provide an automated, centralized, compliant identity governance and administration system with access management and adaptive access management capabilities that address the present identity requirements and potential future difficulties.